| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

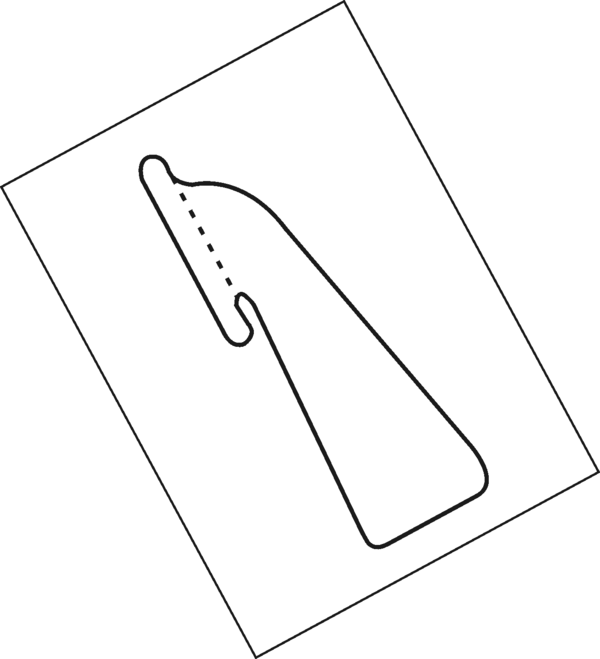
Use the sketch in Appendix 1. It is important to give the rocket tail-fins so that it will be able to stand upright for the launch (See Appendix 1). Stick the page onto cardboard. Cut out the fin. Use the template of the fin and trace four fins on thicker, more rigid cardboard. Cut them out carefully. Fold on the dotted line and stick the fins around the bottle at equal distances. (Look at the sketch to see exactly where.)
NB:
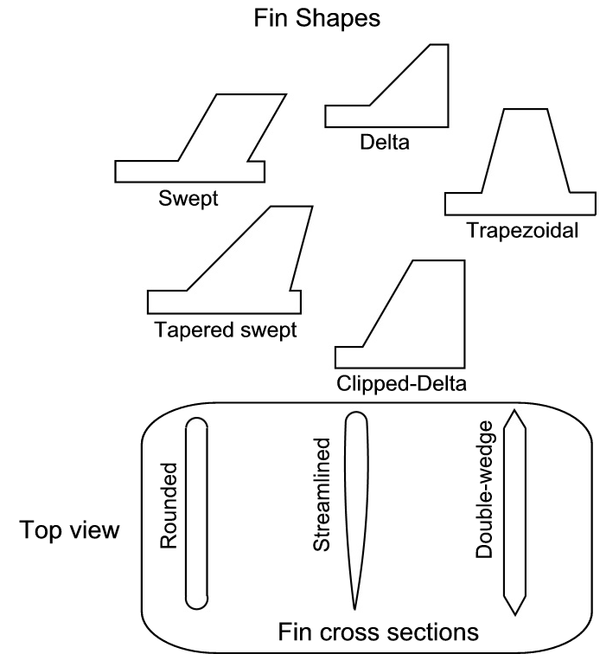
Do you know how to enlarge this sketch of a fin according to scale/proportional to a fin of ± 20 cm?
Instructions
Make the body of the rocket by following the instructions below. Cut one 2ℓ bottle right through along the second line just below the sticker (Sketch 1). The part that has the cork in it will be the top section of your rocket. The intact bottle with the opening pointing down forms the lower section of your rocket. You need a weight in the top section of your rocket.
Why?



Now affix the fins as planned. Once the rocket has been tentatively completed, it is now necessary to find your rocket’s centre of gravity and its centre of pressure.
| Learning outcomes(LOs) |
| LO 1 |
| Technological processes and skillsThe learner will be able to apply technological processes and skills ethically and responsibly using appropriate information and communication technology. |
| Assessment standards(ASs) |
| We know this when the learner: |
| Investigates:1.3 investigates the background context, the nature of the need, the environmental situation, and the people concerned when given a problem, need or opportunity set in a local context; |
| Designs:1.7 generates at least two alternative solutions and annotates the ideas; |
| 1.8 chooses possible solutions, gives sensible reasons for choice, and develops a chosen idea using graphics or modelling techniques; |
| Makes:1.10 chooses and uses appropriate tools and materials to make products by measuring, marking, cutting or separating, shaping or forming, joining or combining, and finishing different materials with some accuracy; |
| 1.11 use safe working practices and shows awareness of efficient ways of using materials and tools; |
| Evaluates:1.12 evaluates the product or system based on criteria linked directly to the design brief and some of the specifications and constraints, and suggests improvements or modifications; |
| 1.13 evaluates the efficiency of the plan of action followed and suggests improving future plans; |
| Communicates:1.14 presents ideas (in a project portfolio) using two-dimensional or three-dimensional sketches, circuit diagrams or system diagrams. |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Technology grade 7' conversation and receive update notifications?