| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

For example: we have a program as the following
public class foo {
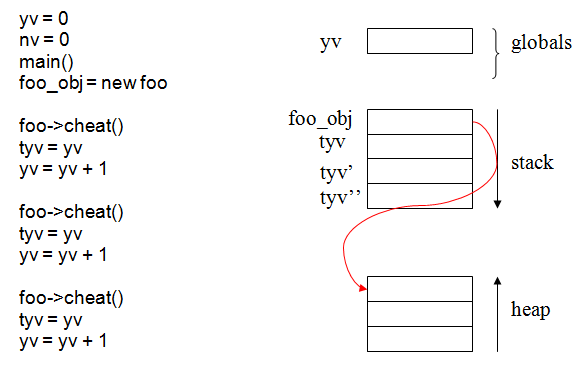
static private int yv = 0;static private int nv = 0;
public static void main() {foo foo_obj = new foo;
foo_obj->cheat();
}public cheat() {
int tyv = yv;yv = yv + 1;
if (tyv<10) {
cheat();}
}}
The questions are:
How to map a program like this to a Von Neuman machine?
Where to keep yv, nv?
What about foo_obj and tyv?
How to do foo->cheat()?
For the variable like yv, nv, we can easily give them some space on the memory. However, why can’t we do the same for the local variable as tyv? Because while program is executing, we don’t know it will invoke the procedure cheat() how many times, it means we don’t know how much space we need to allocate for this variable. In this case, we will use stack, every time a new cheat() is called, the current tyv will be put in the stack, then we can pop it later when the program returns to this procedure. To find data allocated dynamically on stack, a stack pointer which always point at current activation record is used. We will discuss about activation record on section 2.2.

What about new objects? Of course, a memory location will be allocated for foo_obj. Is the stack an appropriate place to keep this object? Since this kind of object has many reusable code (all methods of class), we will waste a lot of our limited memory when we still use the stack for the new object. Heap is used in this case. Suppose we execute as the following:
Whenever you call a procedure there is certain information the program associates with that procedure call. The return address is a good example of some information the program maintains for a specific procedure call. Parameters and automatic local variables (i.e., those you declare in the VAR section) are additional examples of information the program maintains for each procedure call. Activation record is the term we'll use to describe the information the program associates with a specific call to a procedure.
Activation record is an appropriate name for this data structure. The program creates an activation record when calling (activating) a procedure and the data in the structure is organized in a manner identical to records. Perhaps the only thing unusual about an activation record (when comparing it to a standard record) is that the base address of the record is in the middle of the data structure, so you must access fields of the record at positive and negative offsets.
Construction of an activation record begins in the code that calls a procedure. The caller pushes the parameter data (if any) onto the stack. Then the execution of the CALL instruction pushes the return address onto the stack. At this point, construction of the activation record continues within in the procedure itself. The procedure pushes registers and other important state information and then makes room in the activation record for local variables. The procedure must also update the EBP register so that it points at the base address of the activation record.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Operating systems' conversation and receive update notifications?