| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Definisie : Hulpbronne is dinge wat ons nodig het om dinge mee te doen/maak.
Is die volgende almal hulpbronne? Kyk weer na die definisie hierbo en bespreek eers die moontlike antwoorde met ‘n maat.
|
| ||
|
| ||
|
| ||
|
| ||
|
| ||
|
| ||
|
| ||
|
|
Nog ’n hulpbron: Die Mens
Wat kan sonder die bestuurder en die werker gebeur? Niks!
Onthou: omdat die mens ’n belangrike hulpbron is, moet daar goed na hom omgesien word, maar die natuur voorsien die ander hulpbronne – dit moet ook baie goed opgepas word. Meer hieroor later!
Uitslag van die toets:
Dalk het jy en jou maat lekker gestry oor wat hulpbronne is. Die een wat die beste gevaar het, is die een wat gesê het dat al sestien name hulpbronne is.
Dink so ‘n bietjie en voeg nog voorbeelde by die voorbeelde wat reeds verskaf is.
grond, fosfate (vir die maak van kunsmis), water, kraalmis
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
steenkool, hout, olie, gas
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
hout, metale, steenkool, olie
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
steenkool, hout, metale
hout, metale, steenkool, olie
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
Dink mooi na oor al die hulpbronne wat genoem is, ook dit wat deur julle bygevoeg is. Watter van hierdie hulpbronne kan nooit opraak nie? Skryf dit in die lyntjies neer. Daarvan sal julle meer in Graad 5 leer.
Daar is so baie arm mense in Suid-Afrika en Afrika wat beesmis in koeke droogmaak om vuur mee te maak, dat dit eintlik ook ‘n energiebron genoem kan word
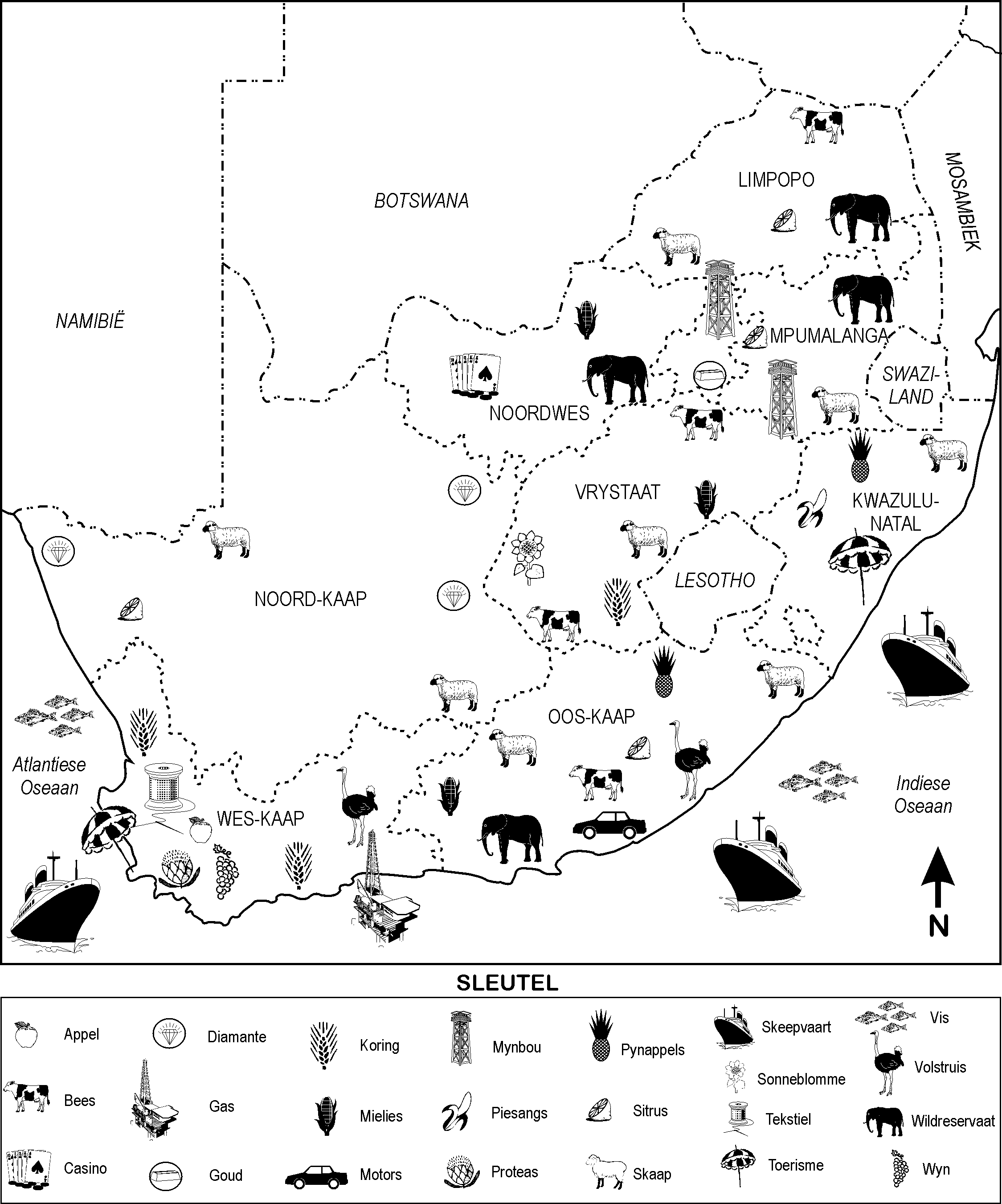
Watter myne vind ons in Gauteng? ......................................................................
Watter myne vind ons in die Noord-Kaap? .............................................................
Watter tipe boerdery sal jy in die Vrystaat vind? ....................................................
Watter dierbronne kom in jou provinsie voor?.........................................................
In watter provinsie vind ons weinig boerdery? (Gee ‘n rede vir jou antwoord.)
................................................................................................................................
Die leerder is in staat om ondersoekvaardighede te gebruik om aardrykskundige en omgewingsbegrippe en -prosesse te ondersoek.
Dis duidelik wanneer die leerder
1.1 inligting uit verskillende bronne identifiseer (kaarte, atlasse, boeke).
Die leerder is in staat om aardrykskundige en omgewingskennis en -begrip te toon.
Dis duidelik wanneer die leerder
2.1 die eienskappe van die plaaslike nedersetting, insluitend landgebruik, beskryf en dit vergelyk met voorbeelde van ander plekke (mense en plekke).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Aardrykskunde graad 4' conversation and receive update notifications?