| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
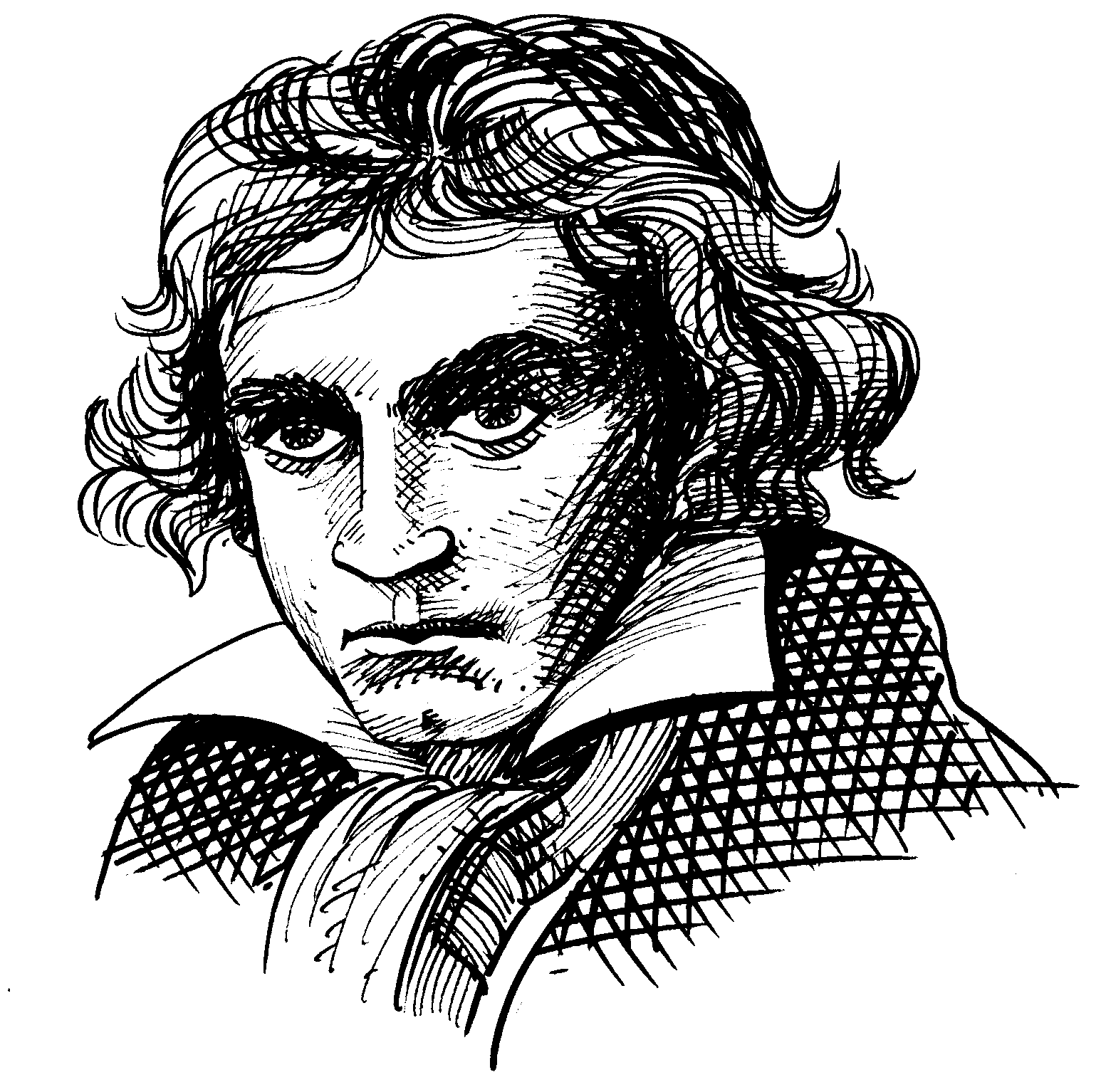
Beethoven
Listen to a true story about Ludwig van Beethoven and complete the activities below.
1. Read the statements and decide if they are true or false.
| STATEMENTS | TRUE | FALSE |
| Ludwig composed classical music. | ||
| Ludwig was French. | ||
| When he was still a child, he was forced to play music in the middle of the night. | ||
| Ludwig loved music. | ||
| His father was his only teacher. | ||
| His father was very kind to him. | ||
| Ludwig was nine years old when his first piece was published. | ||
| Ludwig looked very sweet and friendly. | ||
| He lost all interest in music when he became deaf. | ||
| Ludwig was the best pianist in Europe at that time. | ||
| Ludwig became deaf when he was sixty-one year’s old. | ||
| The rules about classical music were set in stone. |
2. Discuss the following questions in your groups and then write your own ideas down in the space provided.
i) What type of person do you think Ludwig van Beethoven was?
…………………………………………………………………………..
ii) How would you feel if you became deaf today?
………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………….
iii) What do you think of Ludwig’s father?
…………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………
iv) How should mothers and fathers treat their children?
………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………..
Revise the story as a group. Now retell it to the class in your own words.
FOLK MUSIC
Actually, classical music is music that was composed between 1750 and 1830, but today any serious, more permanent music than popular or light music is called “classical” music. At concerts this kind of music is usually played by a symphony orchestra, that is, a team of musicians playing together.
Classical music is only one kind of music. There are many different styles of music today. Long ago, people did not have television or radio, so they had fun by getting together and singing and dancing. The music they made was called ‘folk music’. It was music that belonged to a specific country or group of people in a country - their traditional music. The old people taught their songs and dances to their children who in turn passed it on to their children. Folk instruments were usually cheap and easy to carry. Here are some sketches of folk instruments:

1. Here is a list of some of the instruments shown above. Next to it is a list of the countries in which they are played. Match up the instrument with its country. You may have to use a dictionary.
Didgeridoo South Africa
Balalaika North India
Guitar West Africa
Sitar Australia
Marimba Spain
Concertina Russia
Instrument Country
……………………………… ……………………………….
……………………………… ……………………………….
……………………………… ……………………………….
……………………………… ……………………………….
……………………………… ……………………………….
……………………………… ……………………………….
2. Prepare a talk at home on one of the above instruments. Tell the class about the nation who plays the instrument as well as something about the country where the instrument is played.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'English first additional language grade 4' conversation and receive update notifications?