| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In general, the word “cloning” means the creation of a perfect replica; however, in biology, the re-creation of a whole organism is referred to as “reproductive cloning.” Long before attempts were made to clone an entire organism, researchers learned how to reproduce desired regions or fragments of the genome, a process that is referred to as molecular cloning .
Unicellular organisms, such as bacteria and yeast, naturally produce clones of themselves when they replicate asexually by binary fission; this is known as cellular cloning . The nuclear DNA duplicates by the process of mitosis, which creates an exact replica of the genetic material.
Reproductive cloning is a method used to make a clone or an identical copy of an entire multicellular organism. Most multicellular organisms undergo reproduction by sexual means, which involves genetic hybridization of two individuals (parents), making it impossible for generation of an identical copy or a clone of either parent. Recent advances in biotechnology have made it possible to artificially induce asexual reproduction of mammals in the laboratory.
Parthenogenesis, or “virgin birth,” occurs when an embryo grows and develops without the fertilization of the egg occurring; this is a form of asexual reproduction. An example of parthenogenesis occurs in species in which the female lays an egg and if the egg is fertilized, it is a diploid egg and the individual develops into a female; if the egg is not fertilized, it remains a haploid egg and develops into a male. The unfertilized egg is called a parthenogenic, or virgin, egg. Some insects and reptiles lay parthenogenic eggs that can develop into adults.
Sexual reproduction requires two cells; when the haploid egg and sperm cells fuse, a diploid zygote results. The zygote nucleus contains the genetic information to produce a new individual. However, early embryonic development requires the cytoplasmic material contained in the egg cell. This idea forms the basis for reproductive cloning. Therefore, if the haploid nucleus of an egg cell is replaced with a diploid nucleus from the cell of any individual of the same species (called a donor), it will become a zygote that is genetically identical to the donor. Somatic cell nuclear transfer is the technique of transferring a diploid nucleus into an enucleated egg. It can be used for either therapeutic cloning or reproductive cloning.
The first cloned animal was Dolly, a sheep who was born in 1996. The success rate of reproductive cloning at the time was very low. Dolly lived for seven years and died of respiratory complications ( [link] ). There is speculation that because the cell DNA belongs to an older individual, the age of the DNA may affect the life expectancy of a cloned individual. Since Dolly, several animals such as horses, bulls, and goats have been successfully cloned, although these individuals often exhibit facial, limb, and cardiac abnormalities. There have been attempts at producing cloned human embryos as sources of embryonic stem cells, sometimes referred to as cloning for therapeutic purposes. Therapeutic cloning produces stem cells to attempt to remedy detrimental diseases or defects (unlike reproductive cloning, which aims to reproduce an organism). Still, therapeutic cloning efforts have met with resistance because of bioethical considerations.
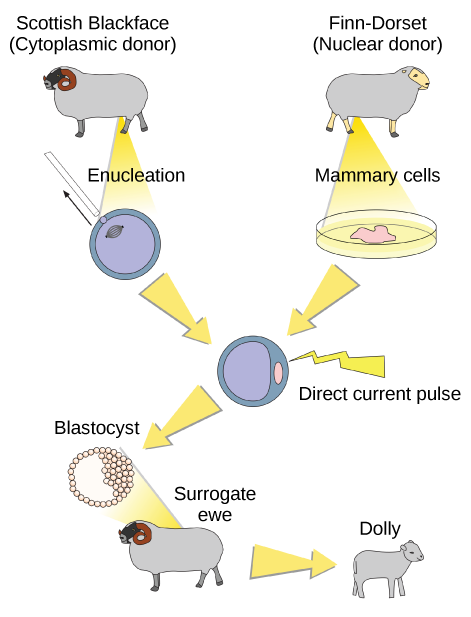
Do you think Dolly was a Finn-Dorset or a Scottish Blackface sheep?
Cloning is a process of making a copy of something's DNA. This copy could be just a section of DNA (molecular cloning), or an entire copy of a cell (cellular cloning), or an entire copy of an organism (molecular cloning).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'General biology part i - mixed majors' conversation and receive update notifications?