| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Principe:
- The Control Unit is viewed and designed as a combinatorial and sequential logic circuit.
- The Control Unit is implemented by using any of a variety of “standard” digital logic techniques. The logic circuit generate the fixed sequences of control signals
- This approach is used to generate fixed sequences of control signals with the higher speed.
Remarks:
The ideal of microprogrammed Control Unit is that the Control Unit design must include the logics for sequencing through micro-operations, for executing micro-operation, for executing micro-instructions, for interpreting opcodes and for making decision based on ALU flags. So the design is relatively inflexible. It is difficul to change the design if one wishes to add a new machine instruction.
The principal disadvantage of a microprogrammed control unit is that it will be slower than hardwired unit of comparable technology. Despite this, microprogramming is the dominant technique for implementing control unit in the contemporary CISC processor, due to its ease of implementation.
The control unit operates by performing consecutive control storage reads to generate the next set of control function outputs. Performing the series of control memory accesses is, in effect, executing a program for each instruction in the machine’s instruction set -- hence the term microprogramming.
The two basic tasks performed by a microprogrammed control unit are as follows:
- Micro-instruction sequencing: the microprogrammed control unit get the next mico-instruction from the control memory
- Micro-instruction execution: the microprogrammed control unit generate the control signals needed to execute the micro-instruction.
The control unit design must consider both affect the format of the micro-instruction and the timing of the control unit.
Two problems are involved in the design of a micro-instruction sequencing technique is the size of micro-instruction and the address-generation time. The first concern is obvious minimizing the size of the control memory. The second concern is simply a desire to execute microinstruction as fast as possible.
In executing a microprogram, the address of the next microinstruction to be executed is one of these categories:
- Determined by instruction register
- Next sequential address
- Branch.
It is important to design compact time-efficient techniques for micro-instruction branching.
Three general categories for a control memory address are as follows:
- Two address fields
- Single address field
- Variable format
In Figure 7.3, the branch control logic with a single address field is illustrated.
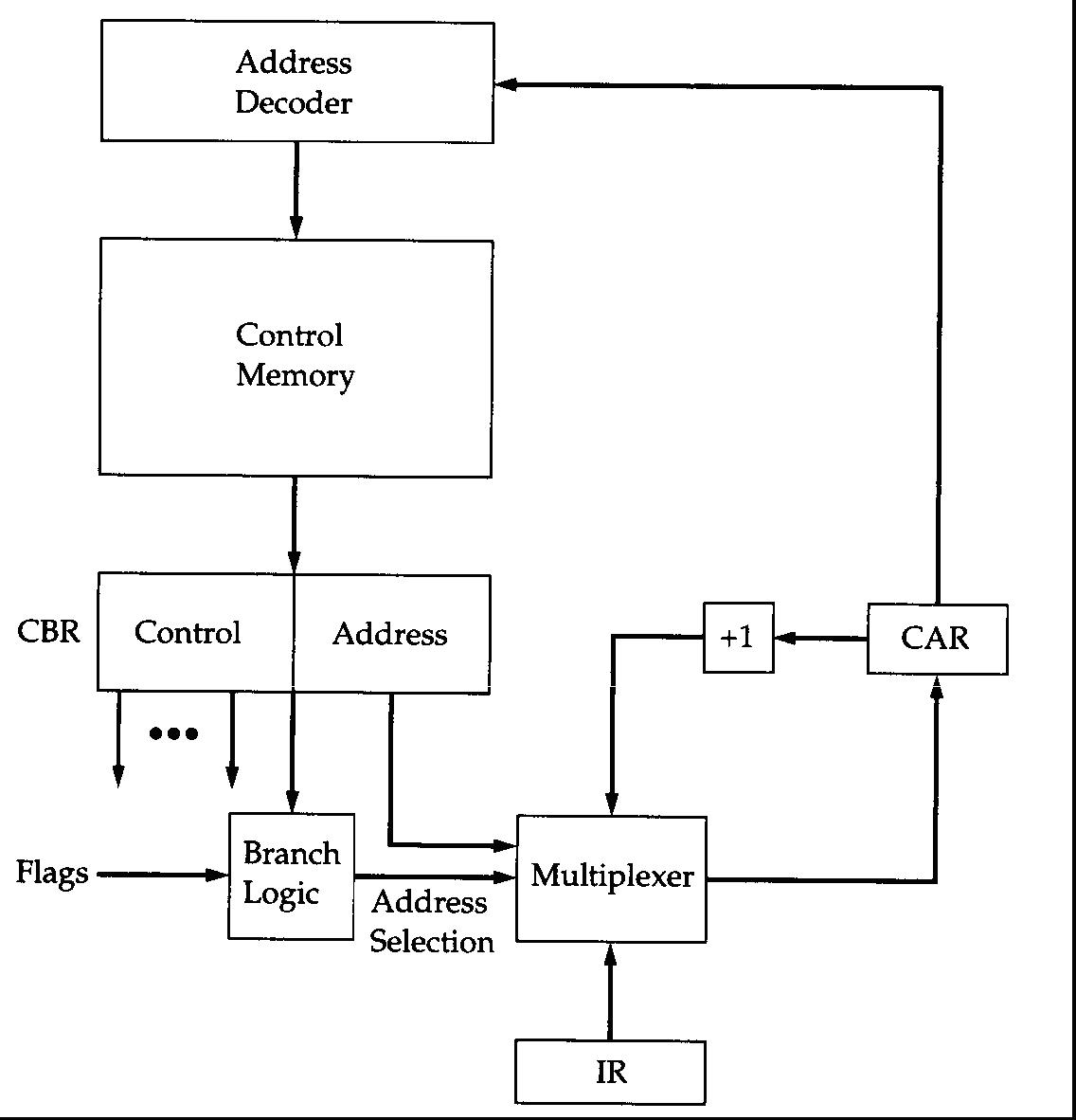
Figure 7.3. Branch Control unit of Microprogrammed Control Unit with with a single address field
The problem is to consider the various ways in which the next address can be derived or computed. The various techniques of the address generation is geven in the following.

Table 1: Microinstruction Address Generation techiques
The microinstruction cycle is the basic event on a microprogrammed processor. Each cycle is made up the two parts: fetch and execute. This section deals with the execution of microinstruction. The effect of the execution of a microinstruction is to generate control signals for both the internal control to processor and the external control to processor.
A organization of a control unit is shown in Figure 7.4
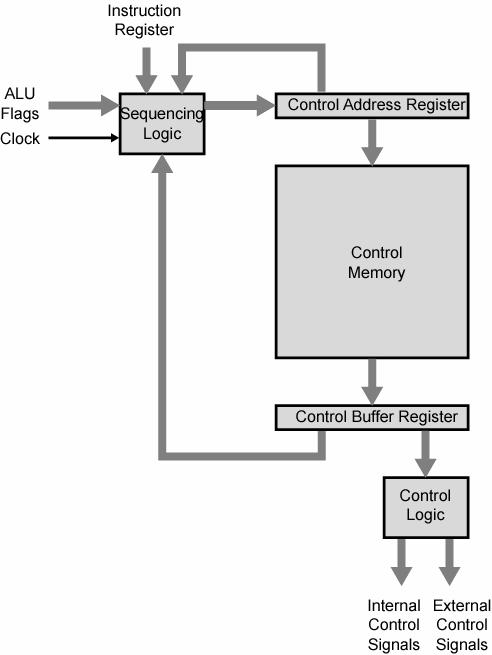
Figure 7.4. Microprogrammed Control Unit Organization
Microinstruction can be classified in variety of ways in which the designer must choose the parallel “power” of each instruction. There are the following.
– Vertical microprogramming: Each microinstruction specifies a single (or few) microoperations to be performed
– Horizontal microprogramming: Each microinstruction specifies many different
microoperations to be performed in parallel.
– Width is narrow: n control signals can be encoded into log2n control bits
– Limited ability to express parallelism
– Considerable encoding of control information requires external memory word decoder to identify the exact control line being manipulated
– Wide memory word
– High degree of parallel operations are possible
– Little to no encoding of control information
– Divide control signals into disjoint groups
– Implement each group as a separate field in the memory word
– Supports reasonable levels of parallelism without too much complexity
– Use a 2-level control storage organization
– Top level is a vertical format memory
Output of the top level memory drives the address register of the bottom (nano-level) memory
– Nanomemory uses the horizontal formal. The produces the actual control signal outputs
– The advantage to this approach is significant saving in control memory size (bits)
– Disadvantage is more complexity and slower operation (doing 2 memory accesses fro each microinstruction).
- For the typically large microprocessor systems today:
+ There are many instructions and associated register level hardware
+ There are many control point to be manipulated.
- Emulation
– The use of a microprogram on one machine to execute programs originally written to run on another machine.
– By changing the microcode of a machine, you can make it execute software from another machine.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Computer architecture' conversation and receive update notifications?