| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
» Extremely fast for large memory sizes
» Cost per bit is 5-10 times that of a “normal” RAM cell
» Example: some cache memory units.
Computer memory system consists a various types of memory. Manufactures produce a number of different types of memory devices having a variety of technologies. The technology affect not only the operating chracteristics but also the manufacturing cost. In the section following we present an overviews of types of memory. You can see the study in detail of memory in the modules 10, 11 and 12.
- RAM (read-write memory): Static RAM, Dynamic RAM
- ROM (Read Only Memories) : ROMs, PROMs, EPROMs, EEPROMs, Flash Memory.
The cache memories are high-speed buffers for holding recently accessed data and neighboring data in main memory. The organization and operations of cache provide an apparently fast memory system.
- Magnetic disks
- RAID technology disks
- Optical disks
- Magnetic tape
No matter how big the main memory, how we can organize effectively the memory system in order to store more information than it can hold. The traditional solution to storing a great deal of data is a memory hierarchy.
– To provide adequate storage capacity at
– An acceptable level of performance
– At a reasonable cost
– Use a hierarchy of storage devices
– Develop automatic space allocation methods for efficient use of the memory
– Through the use of virtual memory techniques, free the user from memory management tasks
– Design the memory and its related interconnection structure so that the proces
Three key characteristics increase for a memory hierarchy. They are the access time, the storage capacity and the cost. The memory hierarchy is illustrated in figure 9.1.
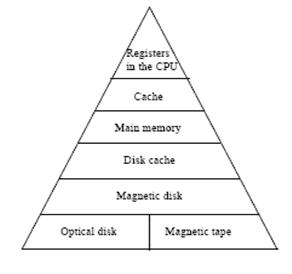
Figure 9.1. The memory hierarchy
We can see the memory hierarchy with six levels. At the top there are CPU registers, which can be accessed at full CPU speed. Next commes the cache memory, which is currently on order of 32 KByte to a few Mbyte. The main memory is next, with size currently ranging from 16 MB for entry-level systems to tens of Gigabytes. After that come magnetic disks, the current work horse for permanent storage. Finally we have magnetic tape and optical disks for archival storage.
– Registers internal to the CPU for temporary data storage (small in number but very fast)
– External storage for data and programs (relatively large and fast)
– External permanent storage (much larger and much slower)

Figure 9.2 Typical Memory Parameters
– Consists of distinct “levels” of memory components
– Each level characterized by its size, access time, and cost per bit
– Each increasing level in the hierarchy consists of modules of larger capacity, slower access time, and lower cost/bit
Goal of the memory hierarchy. Try to match the processor speed with the rate of information transfer from the lowest element in the hierarchy.
The memory hierarchy works because of locality of reference
– Memory references made by the processor, for both instructions and data, tend to cluster together
+ Instruction loops, subroutines
+ Data arrays, tables
– Keep these clusters in high speed memory to reduce the average delay in accessing data
– Over time, the clusters being referenced will change -- memory management must deal with this
Example: Suppsose that the processor has access to two level of memory:
– Two-level memory system
– Level 1 access time of 1 us
– Level 2 access time of 10us
– Ave access time = H(1) + (1-H)(10) ns
where: H is a fraction of all memory access that are found in the faster memory (e.g cache)

Figure 9.3. Performance of a two level memory

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Computer architecture' conversation and receive update notifications?