| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The numerator for this solution’s mole fraction is, therefore, 3.0 mol NaCl. The denominator may be computed by deriving the molar amount of water corresponding to 1.0 kg
and then substituting these molar amounts into the definition for mole fraction.
1.50 m
As described in the chapter on liquids and solids, the equilibrium vapor pressure of a liquid is the pressure exerted by its gaseous phase when vaporization and condensation are occurring at equal rates:
Dissolving a nonvolatile substance in a volatile liquid results in a lowering of the liquid’s vapor pressure. This phenomenon can be rationalized by considering the effect of added solute molecules on the liquid's vaporization and condensation processes. To vaporize, solvent molecules must be present at the surface of the solution. The presence of solute decreases the surface area available to solvent molecules and thereby reduces the rate of solvent vaporization. Since the rate of condensation is unaffected by the presence of solute, the net result is that the vaporization-condensation equilibrium is achieved with fewer solvent molecules in the vapor phase (i.e., at a lower vapor pressure) ( [link] ). While this kinetic interpretation is useful, it does not account for several important aspects of the colligative nature of vapor pressure lowering. A more rigorous explanation involves the property of entropy , a topic of discussion in a later text chapter on thermodynamics. For purposes of understanding the lowering of a liquid's vapor pressure, it is adequate to note that the greater entropy of a solution in comparison to its separate solvent and solute serves to effectively stabilize the solvent molecules and hinder their vaporization. A lower vapor pressure results, and a correspondingly higher boiling point as described in the next section of this module.
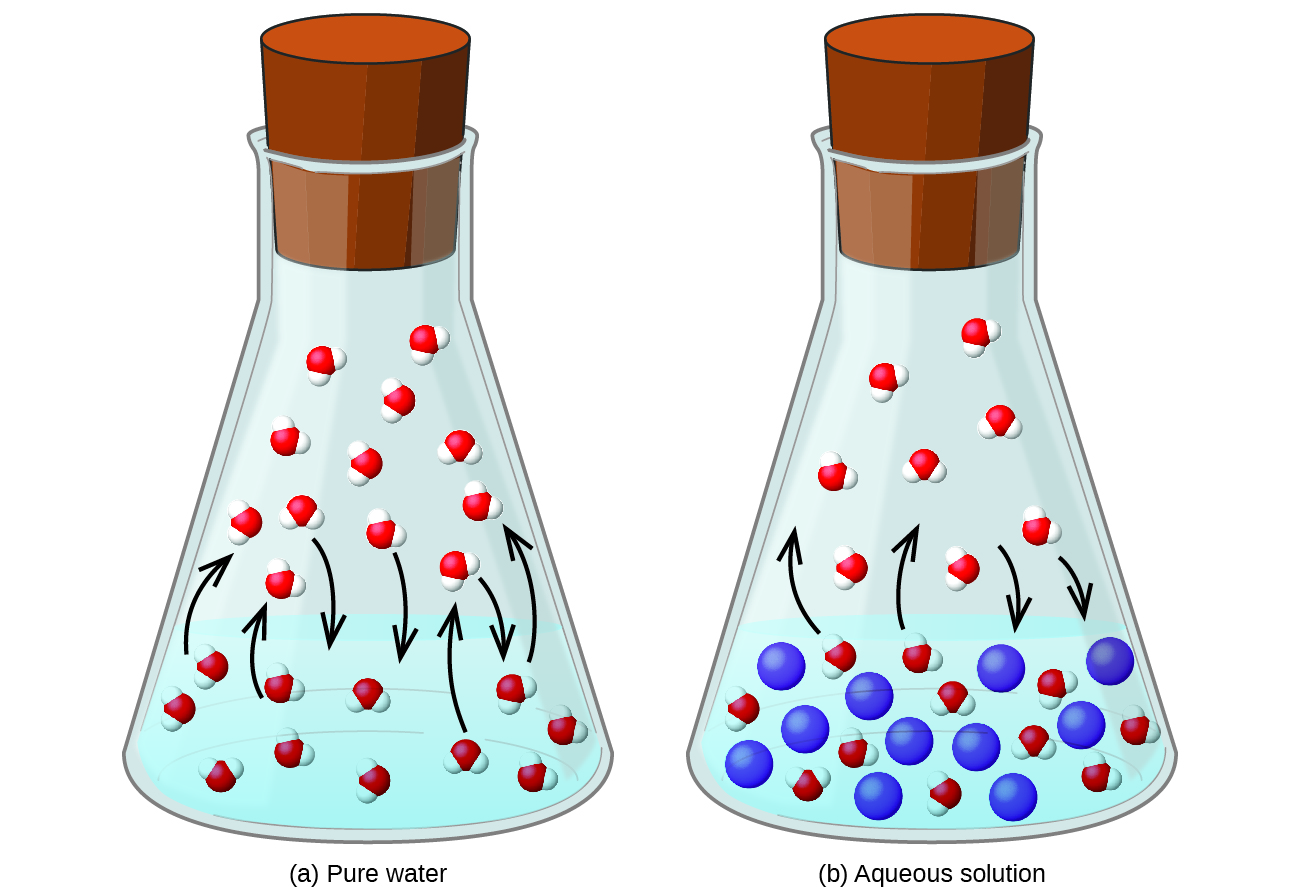
The relationship between the vapor pressures of solution components and the concentrations of those components is described by Raoult’s law : The partial pressure exerted by any component of an ideal solution is equal to the vapor pressure of the pure component multiplied by its mole fraction in the solution.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?