| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of an atom is called the electron configuration of the atom. We describe an electron configuration with a symbol that contains three pieces of information ( [link] ):
For example, the notation 2 p 4 (read "two–p–four") indicates four electrons in a p subshell ( l = 1) with a principal quantum number ( n ) of 2. The notation 3 d 8 (read "three–d–eight") indicates eight electrons in the d subshell (i.e., l = 2) of the principal shell for which n = 3.
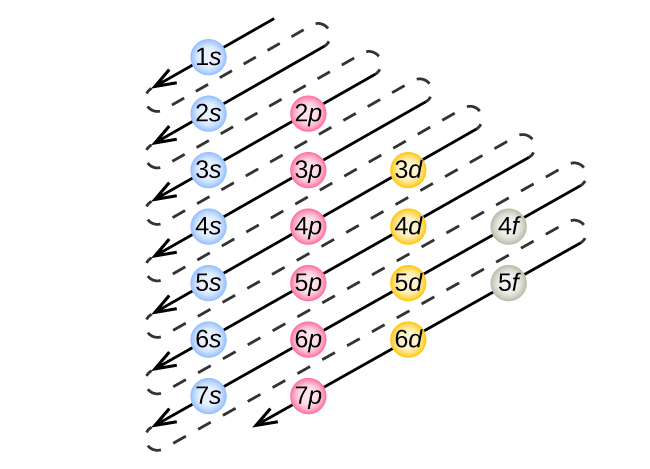
To determine the electron configuration for any particular atom, we can “build” the structures in the order of atomic numbers. Beginning with hydrogen, and continuing across the periods of the periodic table, we add one proton at a time to the nucleus and one electron to the proper subshell until we have described the electron configurations of all the elements. This procedure is called the Aufbau principle , from the German word Aufbau (“to build up”). Each added electron occupies the subshell of lowest energy available (in the order shown in [link] ), subject to the limitations imposed by the allowed quantum numbers according to the Pauli exclusion principle. Electrons enter higher-energy subshells only after lower-energy subshells have been filled to capacity. [link] illustrates the traditional way to remember the filling order for atomic orbitals. Since the arrangement of the periodic table is based on the electron configurations, [link] provides an alternative method for determining the electron configuration. The filling order simply begins at hydrogen and includes each subshell as you proceed in increasing Z order. For example, after filling the 3 p block up to Ar, we see the orbital will be 4s (K, Ca), followed by the 3 d orbitals.
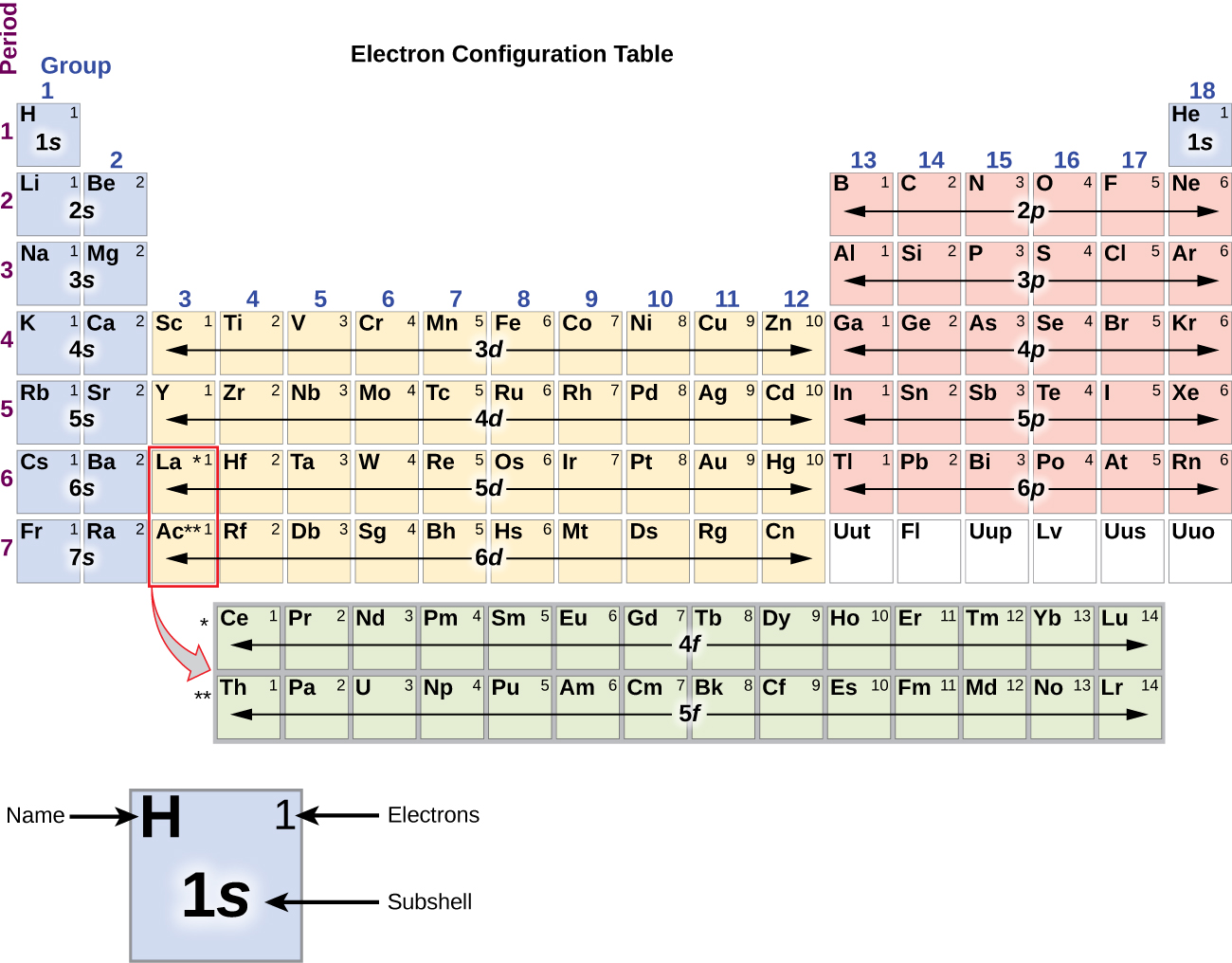
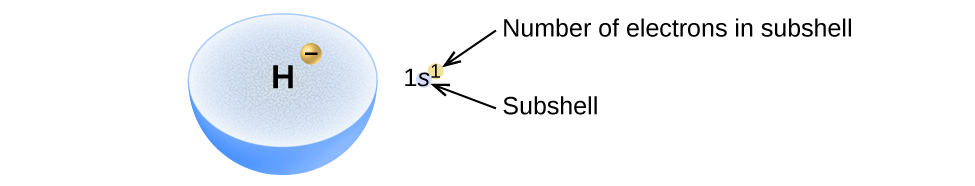
We will now construct the ground-state electron configuration and orbital diagram for a selection of atoms in the first and second periods of the periodic table. Orbital diagrams are pictorial representations of the electron configuration, showing the individual orbitals and the pairing arrangement of electrons. We start with a single hydrogen atom (atomic number 1), which consists of one proton and one electron. Referring to [link] or [link] , we would expect to find the electron in the 1 s orbital. By convention, the value is usually filled first. The electron configuration and the orbital diagram are:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?