| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Radioactive decay follows first-order kinetics. Since first-order reactions have already been covered in detail in the kinetics chapter, we will now apply those concepts to nuclear decay reactions. Each radioactive nuclide has a characteristic, constant half-life ( t 1/2 ), the time required for half of the atoms in a sample to decay. An isotope’s half-life allows us to determine how long a sample of a useful isotope will be available, and how long a sample of an undesirable or dangerous isotope must be stored before it decays to a low-enough radiation level that is no longer a problem.
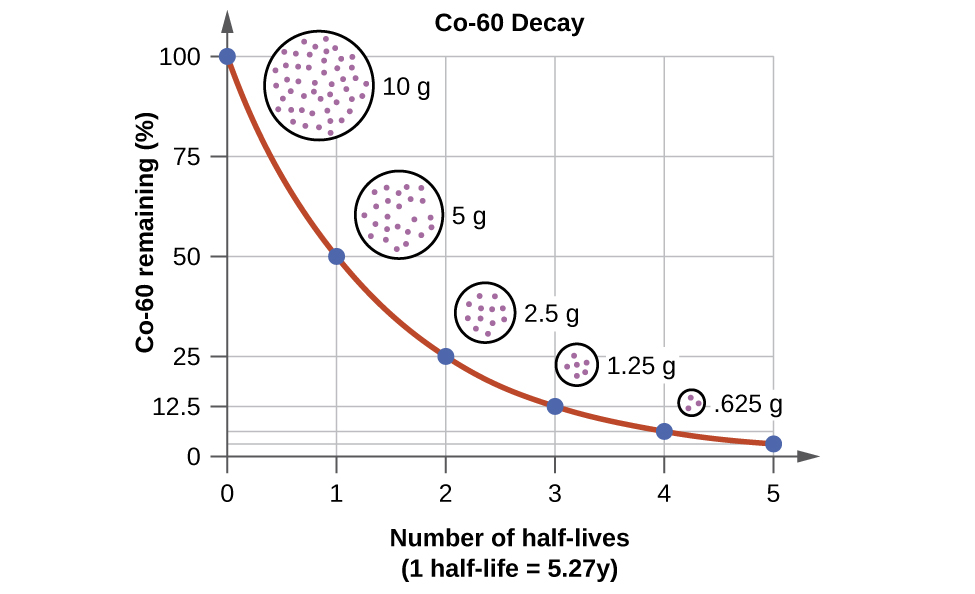
For example, cobalt-60, an isotope that emits gamma rays used to treat cancer, has a half-life of 5.27 years ( [link] ). In a given cobalt-60 source, since half of the nuclei decay every 5.27 years, both the amount of material and the intensity of the radiation emitted is cut in half every 5.27 years. (Note that for a given substance, the intensity of radiation that it produces is directly proportional to the rate of decay of the substance and the amount of the substance.) This is as expected for a process following first-order kinetics. Thus, a cobalt-60 source that is used for cancer treatment must be replaced regularly to continue to be effective.
Since nuclear decay follows first-order kinetics, we can adapt the mathematical relationships used for first-order chemical reactions. We generally substitute the number of nuclei, N , for the concentration. If the rate is stated in nuclear decays per second, we refer to it as the activity of the radioactive sample. The rate for radioactive decay is:
decay rate = λN with λ = the decay constant for the particular radioisotope
The decay constant, λ , which is the same as a rate constant discussed in the kinetics chapter. It is possible to express the decay constant in terms of the half-life, t 1/2 :
The first-order equations relating amount, N , and time are:
where N 0 is the initial number of nuclei or moles of the isotope, and N t is the number of nuclei/moles remaining at time t . [link] applies these calculations to find the rates of radioactive decay for specific nuclides.
(a) What is the decay constant for the radioactive disintegration of cobalt-60?
(b) Calculate the fraction of a sample of the isotope that will remain after 15 years.
(c) How long does it take for a sample of to disintegrate to the extent that only 2.0% of the original amount remains?
(b) The fraction of that is left after time t is given by Rearranging the first-order relationship N t = N 0 e – λt to solve for this ratio yields:
The fraction of that will remain after 15.0 years is 0.138. Or put another way, 13.8% of the originally present will remain after 15 years.
(c) 2.00% of the original amount of is equal to 0.0200 N 0 . Substituting this into the equation for time for first-order kinetics, we have:
11.1 days

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?