| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
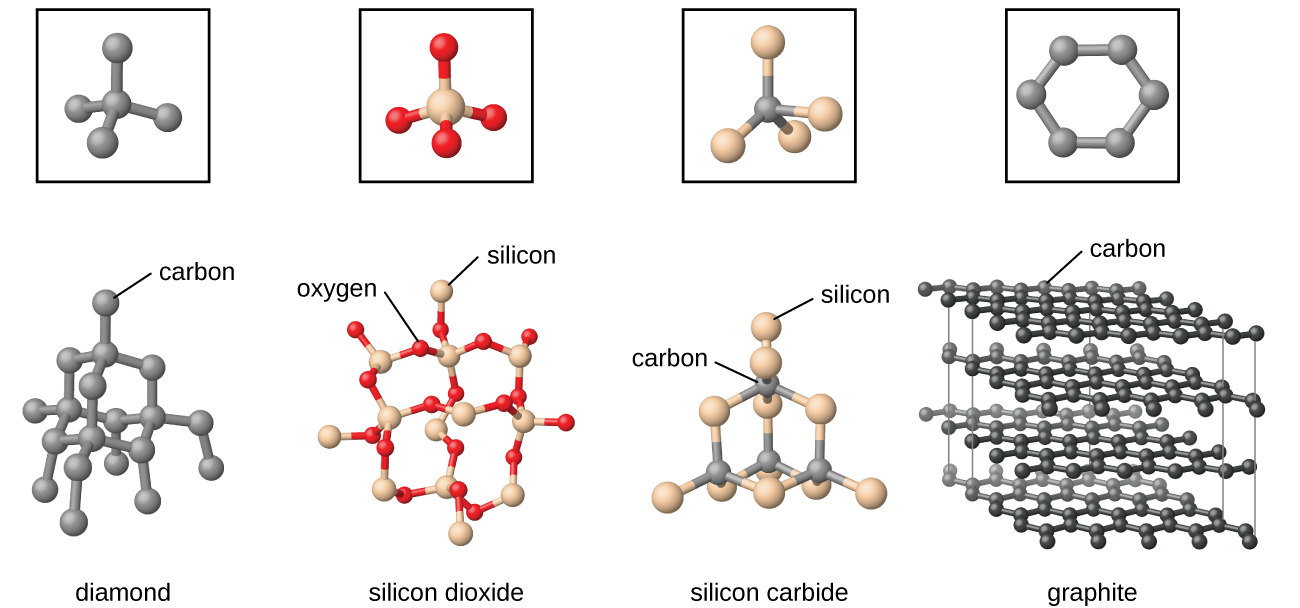
Covalent network solids include crystals of diamond, silicon, some other nonmetals, and some covalent compounds such as silicon dioxide (sand) and silicon carbide (carborundum, the abrasive on sandpaper). Many minerals have networks of covalent bonds. The atoms in these solids are held together by a network of covalent bonds, as shown in [link] . To break or to melt a covalent network solid, covalent bonds must be broken. Because covalent bonds are relatively strong, covalent network solids are typically characterized by hardness, strength, and high melting points. For example, diamond is one of the hardest substances known and melts above 3500 °C.
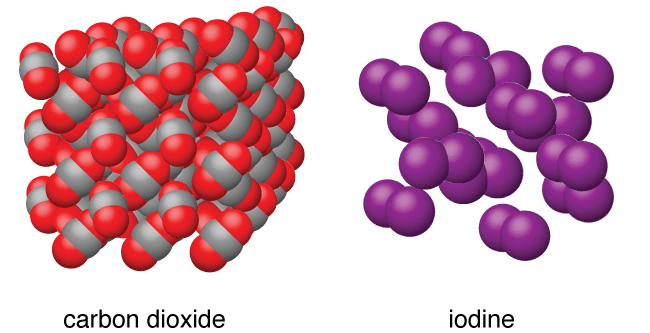
Molecular solids , such as ice, sucrose (table sugar), and iodine, as shown in [link] , are composed of neutral molecules. The strengths of the attractive forces between the units present in different crystals vary widely, as indicated by the melting points of the crystals. Small symmetrical molecules (nonpolar molecules), such as H 2 , N 2 , O 2 , and F 2 , have weak attractive forces and form molecular solids with very low melting points (below −200 °C). Substances consisting of larger, nonpolar molecules have larger attractive forces and melt at higher temperatures. Molecular solids composed of molecules with permanent dipole moments (polar molecules) melt at still higher temperatures. Examples include ice (melting point, 0 °C) and table sugar (melting point, 185 °C).
A crystalline solid, like those listed in [link] , has a precise melting temperature because each atom or molecule of the same type is held in place with the same forces or energy. Thus, the attractions between the units that make up the crystal all have the same strength and all require the same amount of energy to be broken. The gradual softening of an amorphous material differs dramatically from the distinct melting of a crystalline solid. This results from the structural nonequivalence of the molecules in the amorphous solid. Some forces are weaker than others, and when an amorphous material is heated, the weakest intermolecular attractions break first. As the temperature is increased further, the stronger attractions are broken. Thus amorphous materials soften over a range of temperatures.
| Types of Crystalline Solids and Their Properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of Solid | Type of Particles | Type of Attractions | Properties | Examples |
| ionic | ions | ionic bonds | hard, brittle, conducts electricity as a liquid but not as a solid, high to very high melting points | NaCl, Al 2 O 3 |
| metallic | atoms of electropositive elements | metallic bonds | shiny, malleable, ductile, conducts heat and electricity well, variable hardness and melting temperature | Cu, Fe, Ti, Pb, U |
| covalent network | atoms of electronegative elements | covalent bonds | very hard, not conductive, very high melting points | C (diamond), SiO 2 , SiC |
| molecular | molecules (or atoms) | IMFs | variable hardness, variable brittleness, not conductive, low melting points | H 2 O, CO 2 , I 2 , C 12 H 22 O 11 |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?