| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals in their behavior.
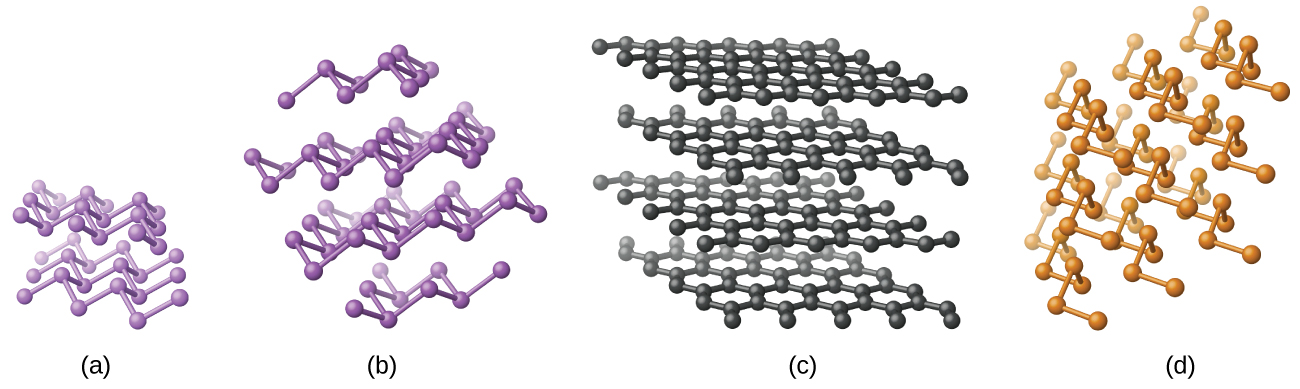
Elemental silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, and tellurium are lustrous, metallic-looking solids. Silicon and germanium crystallize with a diamond structure. Each atom within the crystal has covalent bonds to four neighboring atoms at the corners of a regular tetrahedron. Single crystals of silicon and germanium are giant, three-dimensional molecules. There are several allotropes of arsenic with the most stable being layer like and containing puckered sheets of arsenic atoms. Each arsenic atom forms covalent bonds to three other atoms within the sheet. The crystal structure of antimony is similar to that of arsenic, both shown in [link] . The structures of arsenic and antimony are similar to the structure of graphite, covered later in this chapter. Tellurium forms crystals that contain infinite spiral chains of tellurium atoms. Each atom in the chain bonds to two other atoms.
Explore a cubic diamond crystal structure.
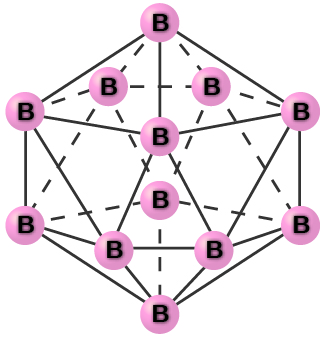
Pure crystalline boron is transparent. The crystals consist of icosahedra, as shown in [link] , with a boron atom at each corner. In the most common form of boron, the icosahedra pack together in a manner similar to the cubic closest packing of spheres. All boron-boron bonds within each icosahedron are identical and are approximately 176 pm in length. In the different forms of boron, there are different arrangements and connections between the icosahedra.
The name silicon is derived from the Latin word for flint, silex . The metalloid silicon readily forms compounds containing Si-O-Si bonds, which are of prime importance in the mineral world. This bonding capability is in contrast to the nonmetal carbon, whose ability to form carbon-carbon bonds gives it prime importance in the plant and animal worlds.
Boron constitutes less than 0.001% by weight of the earth’s crust. In nature, it only occurs in compounds with oxygen. Boron is widely distributed in volcanic regions as boric acid, B(OH) 3 , and in dry lake regions, including the desert areas of California, as borates and salts of boron oxyacids, such as borax, Na 2 B 4 O 7 ⋅10H 2 O.
Elemental boron is chemically inert at room temperature, reacting with only fluorine and oxygen to form boron trifluoride, BF 3 , and boric oxide, B 2 O 3 , respectively. At higher temperatures, boron reacts with all nonmetals, except tellurium and the noble gases, and with nearly all metals; it oxidizes to B 2 O 3 when heated with concentrated nitric or sulfuric acid. Boron does not react with nonoxidizing acids. Many boron compounds react readily with water to give boric acid, B(OH) 3 (sometimes written as H 3 BO 3 ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?