| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Again, note that when calculating standard reduction potentials always remain the same even when a half-reaction is multiplied by a factor. Standard reduction potentials for selected reduction reactions are shown in [link] . A more complete list is provided in Appendix L .
| Selected Standard Reduction Potentials at 25 °C | |
|---|---|
| Half-Reaction | E ° (V) |
| +2.866 | |
| +1.69 | |
| +1.507 | |
| +1.498 | |
| +1.35827 | |
| +1.229 | |
| +1.20 | |
| +1.0873 | |
| +0.7996 | |
| +0.7973 | |
| +0.771 | |
| +0.558 | |
| +0.5355 | |
| +0.49 | |
| +0.337 | |
| +0.26808 | |
| +0.22233 | |
| +0.151 | |
| 0.00 | |
| −0.126 | |
| −0.1262 | |
| −0.257 | |
| −0.28 | |
| −0.3505 | |
| −0.4030 | |
| −0.447 | |
| −0.744 | |
| −1.185 | |
| −1.245 | |
| −0.7618 | |
| −1.662 | |
| −2.372 | |
| −2.71 | |
| −2.868 | |
| −2.912 | |
| −2.931 | |
| −3.04 |
Tables like this make it possible to determine the standard cell potential for many oxidation-reduction reactions.
Galvanic cells have positive cell potentials, and all the reduction reactions are reversible. The reaction at the anode will be the half-reaction with the smaller or more negative standard reduction potential. Reversing the reaction at the anode (to show the oxidation) but not its standard reduction potential gives:
The least common factor is six, so the overall reaction is
The reduction potentials are not scaled by the stoichiometric coefficients when calculating the cell potential, and the unmodified standard reduction potentials must be used.
From the half-reactions, Ni is oxidized, so it is the reducing agent, and Au 3+ is reduced, so it is the oxidizing agent.
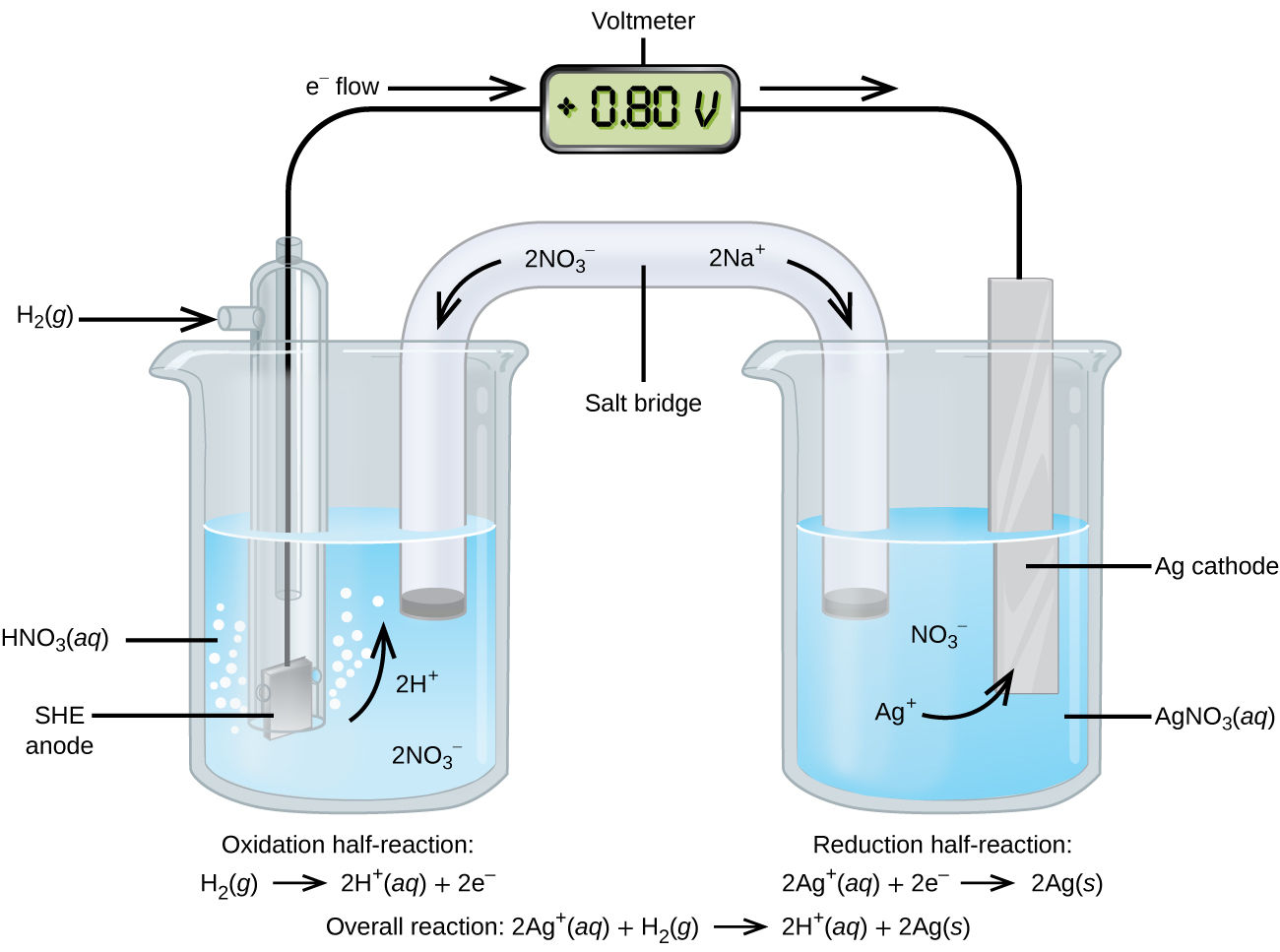
Assigning the potential of the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) as zero volts allows the determination of standard reduction potentials, E° , for half-reactions in electrochemical cells. As the name implies, standard reduction potentials use standard states (1 bar or 1 atm for gases; 1 M for solutes, often at 298.15 K) and are written as reductions (where electrons appear on the left side of the equation). The reduction reactions are reversible, so standard cell potentials can be calculated by subtracting the standard reduction potential for the reaction at the anode from the standard reduction for the reaction at the cathode. When calculating the standard cell potential, the standard reduction potentials are not scaled by the stoichiometric coefficients in the balanced overall equation.
For each reaction listed, determine its standard cell potential at 25 °C and whether the reaction is spontaneous at standard conditions.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(a) +2.115 V (spontaneous); (b) +0.4626 V (spontaneous); (c) +1.0589 V (spontaneous); (d) +0.727 V (spontaneous)
For each reaction listed, determine its standard cell potential at 25 °C and whether the reaction is spontaneous at standard conditions.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Determine the overall reaction and its standard cell potential at 25 °C for this reaction. Is the reaction spontaneous at standard conditions?
+1.16 V; spontaneous
Determine the overall reaction and its standard cell potential at 25 °C for the reaction involving the galvanic cell made from a half-cell consisting of a silver electrode in 1 M silver nitrate solution and a half-cell consisting of a zinc electrode in 1 M zinc nitrate. Is the reaction spontaneous at standard conditions?
Determine the overall reaction and its standard cell potential at 25 °C for the reaction involving the galvanic cell in which cadmium metal is oxidized to 1 M cadmium(II) ion and a half-cell consisting of an aluminum electrode in 1 M aluminum nitrate solution. Is the reaction spontaneous at standard conditions?
−1.259 V; nonspontaneous
Determine the overall reaction and its standard cell potential at 25 °C for these reactions. Is the reaction spontaneous at standard conditions? Assume the standard reduction for Br
2 (
l ) is the same as for Br
2 (
aq ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?