| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
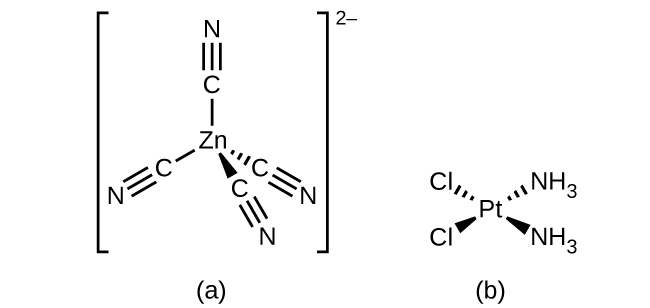
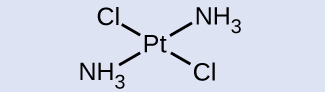
Isomers are different chemical species that have the same chemical formula. Transition metals often form geometric isomers , in which the same atoms are connected through the same types of bonds but with differences in their orientation in space. Coordination complexes with two different ligands in the cis and trans positions from a ligand of interest form isomers. For example, the octahedral [Co(NH 3 ) 4 Cl 2 ] + ion has two isomers. In the cis configuration , the two chloride ligands are adjacent to each other ( [link] ). The other isomer, the trans configuration , has the two chloride ligands directly across from one another.
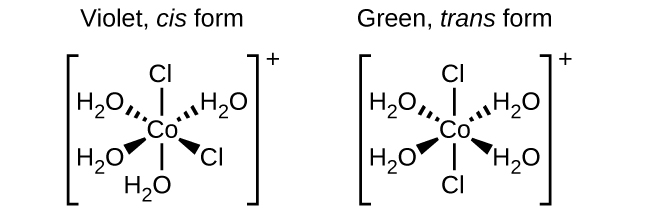
Different geometric isomers of a substance are different chemical compounds. They exhibit different properties, even though they have the same formula. For example, the two isomers of [Co(NH 3 ) 4 Cl 2 ]NO 3 differ in color; the cis form is violet, and the trans form is green. Furthermore, these isomers have different dipole moments, solubilities, and reactivities. As an example of how the arrangement in space can influence the molecular properties, consider the polarity of the two [Co(NH 3 ) 4 Cl 2 ]NO 3 isomers. Remember that the polarity of a molecule or ion is determined by the bond dipoles (which are due to the difference in electronegativity of the bonding atoms) and their arrangement in space. In one isomer, cis chloride ligands cause more electron density on one side of the molecule than on the other, making it polar. For the trans isomer, each ligand is directly across from an identical ligand, so the bond dipoles cancel out, and the molecule is nonpolar.
Another important type of isomers are optical isomers , or enantiomers , in which two objects are exact mirror images of each other but cannot be lined up so that all parts match. This means that optical isomers are nonsuperimposable mirror images. A classic example of this is a pair of hands, in which the right and left hand are mirror images of one another but cannot be superimposed. Optical isomers are very important in organic and biochemistry because living systems often incorporate one specific optical isomer and not the other. Unlike geometric isomers, pairs of optical isomers have identical properties (boiling point, polarity, solubility, etc.). Optical isomers differ only in the way they affect polarized light and how they react with other optical isomers. For coordination complexes, many coordination compounds such as [M(en) 3 ] n+ [in which M n+ is a central metal ion such as iron(III) or cobalt(II)] form enantiomers, as shown in [link] . These two isomers will react differently with other optical isomers. For example, DNA helices are optical isomers, and the form that occurs in nature (right-handed DNA) will bind to only one isomer of [M(en) 3 ] n+ and not the other.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?