| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We can argue that modern chemical science began when scientists started exploring the quantitative as well as the qualitative aspects of chemistry. For example, Dalton’s atomic theory was an attempt to explain the results of measurements that allowed him to calculate the relative masses of elements combined in various compounds. Understanding the relationship between the masses of atoms and the chemical formulas of compounds allows us to quantitatively describe the composition of substances.
In an earlier chapter, we described the development of the atomic mass unit, the concept of average atomic masses, and the use of chemical formulas to represent the elemental makeup of substances. These ideas can be extended to calculate the formula mass of a substance by summing the average atomic masses of all the atoms represented in the substance’s formula.
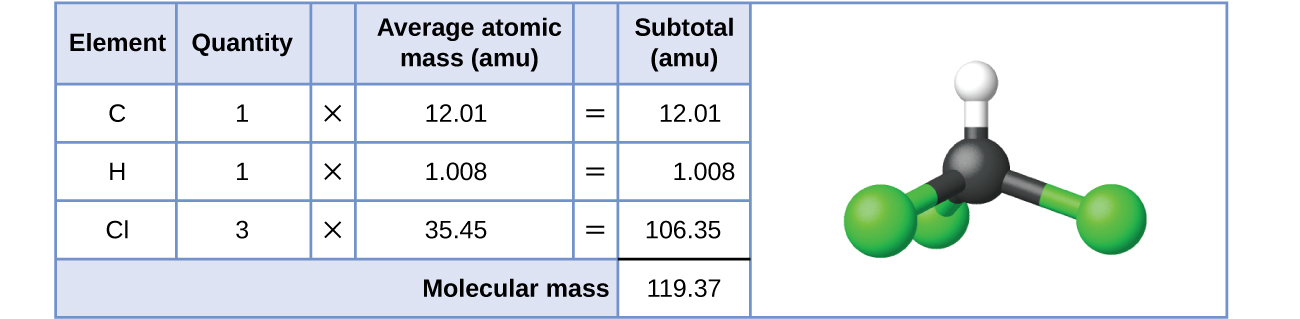
For covalent substances, the formula represents the numbers and types of atoms composing a single molecule of the substance; therefore, the formula mass may be correctly referred to as a molecular mass. Consider chloroform (CHCl 3 ), a covalent compound once used as a surgical anesthetic and now primarily used in the production of the “anti-stick” polymer, Teflon. The molecular formula of chloroform indicates that a single molecule contains one carbon atom, one hydrogen atom, and three chlorine atoms. The average molecular mass of a chloroform molecule is therefore equal to the sum of the average atomic masses of these atoms. [link] outlines the calculations used to derive the molecular mass of chloroform, which is 119.37 amu.
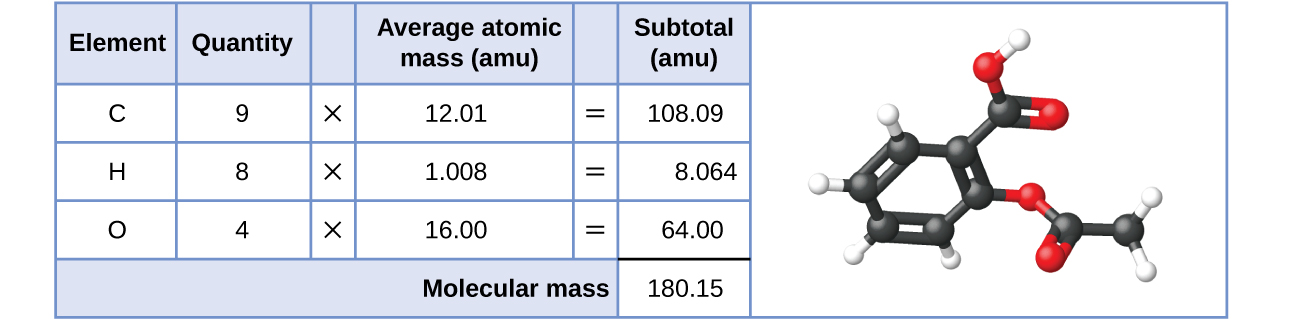
Likewise, the molecular mass of an aspirin molecule, C 9 H 8 O 4 , is the sum of the atomic masses of nine carbon atoms, eight hydrogen atoms, and four oxygen atoms, which amounts to 180.15 amu ( [link] ).
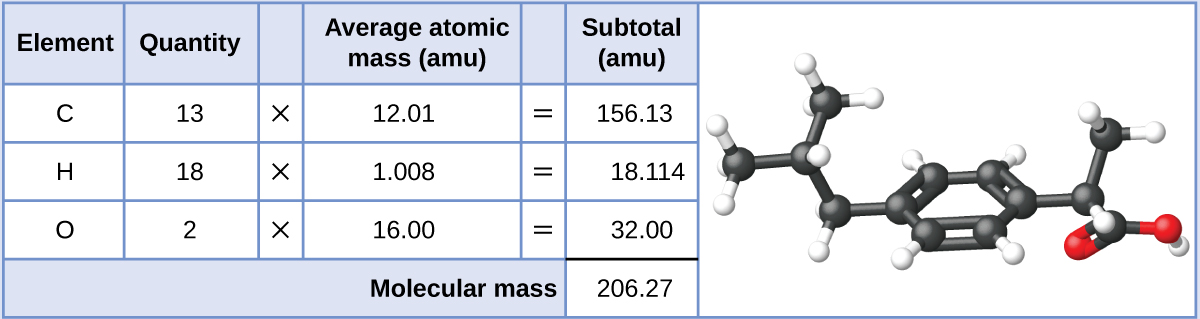
151.16 amu

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?