| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Water also exerts a leveling effect on the strengths of strong bases. For example, the oxide ion, O 2− , and the amide ion, are such strong bases that they react completely with water:
Thus, O 2− and appear to have the same base strength in water; they both give a 100% yield of hydroxide ion.
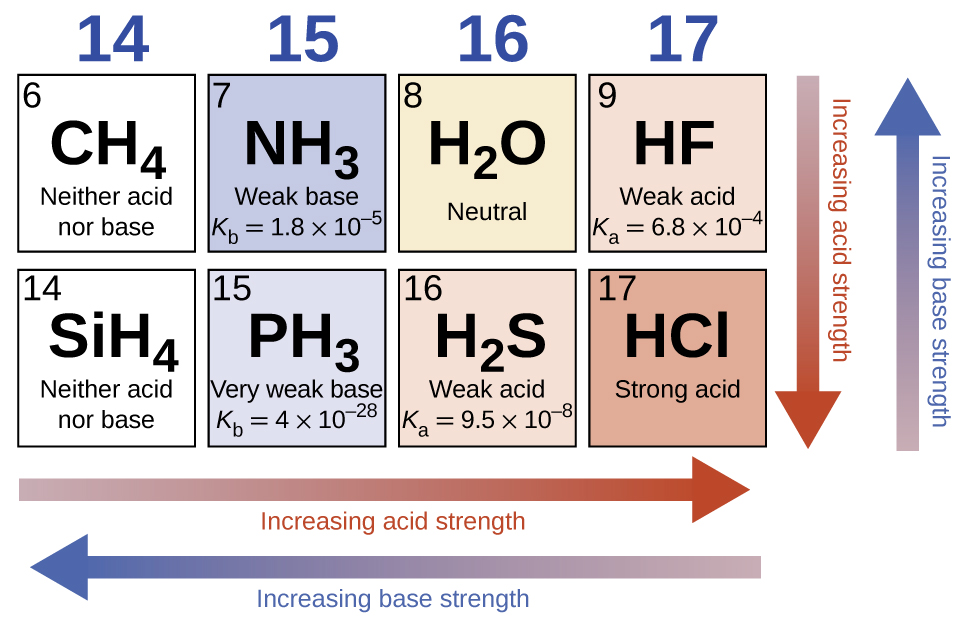
In the absence of any leveling effect, the acid strength of binary compounds of hydrogen with nonmetals (A) increases as the H-A bond strength decreases down a group in the periodic table. For group 7A, the order of increasing acidity is HF<HCl<HBr<HI. Likewise, for group 6A, the order of increasing acid strength is H 2 O<H 2 S<H 2 Se<H 2 Te.
Across a row in the periodic table, the acid strength of binary hydrogen compounds increases with increasing electronegativity of the nonmetal atom because the polarity of the H-A bond increases. Thus, the order of increasing acidity (for removal of one proton) across the second row is CH 4 <NH 3 <H 2 O<HF; across the third row, it is SiH 4 <PH 3 <H 2 S<HCl (see [link] ).
Compounds containing oxygen and one or more hydroxyl (OH) groups can be acidic, basic, or amphoteric, depending on the position in the periodic table of the central atom E, the atom bonded to the hydroxyl group. Such compounds have the general formula O n E(OH) m , and include sulfuric acid, O 2 S(OH) 2 , sulfurous acid, OS(OH) 2 , nitric acid, O 2 NOH, perchloric acid, O 3 ClOH, aluminum hydroxide, Al(OH) 3 , calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH) 2 , and potassium hydroxide, KOH:
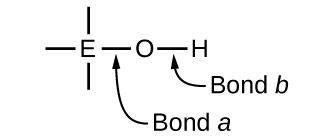
If the central atom, E, has a low electronegativity, its attraction for electrons is low. Little tendency exists for the central atom to form a strong covalent bond with the oxygen atom, and bond a between the element and oxygen is more readily broken than bond b between oxygen and hydrogen. Hence bond a is ionic, hydroxide ions are released to the solution, and the material behaves as a base—this is the case with Ca(OH) 2 and KOH. Lower electronegativity is characteristic of the more metallic elements; hence, the metallic elements form ionic hydroxides that are by definition basic compounds.
If, on the other hand, the atom E has a relatively high electronegativity, it strongly attracts the electrons it shares with the oxygen atom, making bond a relatively strongly covalent. The oxygen-hydrogen bond, bond b , is thereby weakened because electrons are displaced toward E. Bond b is polar and readily releases hydrogen ions to the solution, so the material behaves as an acid. High electronegativities are characteristic of the more nonmetallic elements. Thus, nonmetallic elements form covalent compounds containing acidic −OH groups that are called oxyacids .
Increasing the oxidation number of the central atom E also increases the acidity of an oxyacid because this increases the attraction of E for the electrons it shares with oxygen and thereby weakens the O-H bond. Sulfuric acid, H 2 SO 4 , or O 2 S(OH) 2 (with a sulfur oxidation number of +6), is more acidic than sulfurous acid, H 2 SO 3 , or OS(OH) 2 (with a sulfur oxidation number of +4). Likewise nitric acid, HNO 3 , or O 2 NOH (N oxidation number = +5), is more acidic than nitrous acid, HNO 2 , or ONOH (N oxidation number = +3). In each of these pairs, the oxidation number of the central atom is larger for the stronger acid ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?