| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The extent to which the vapor pressure of a solvent is lowered and the boiling point is elevated depends on the total number of solute particles present in a given amount of solvent, not on the mass or size or chemical identities of the particles. A 1 m aqueous solution of sucrose (342 g/mol) and a 1 m aqueous solution of ethylene glycol (62 g/mol) will exhibit the same boiling point because each solution has one mole of solute particles (molecules) per kilogram of solvent.

109.2 °C
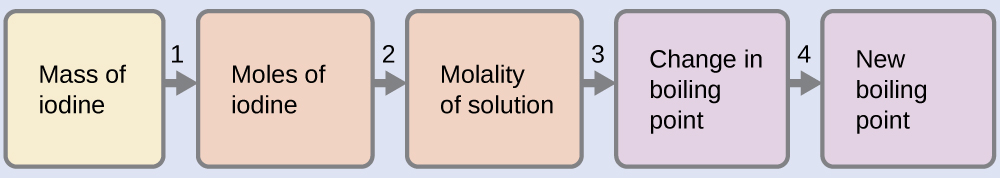
100.12 °C
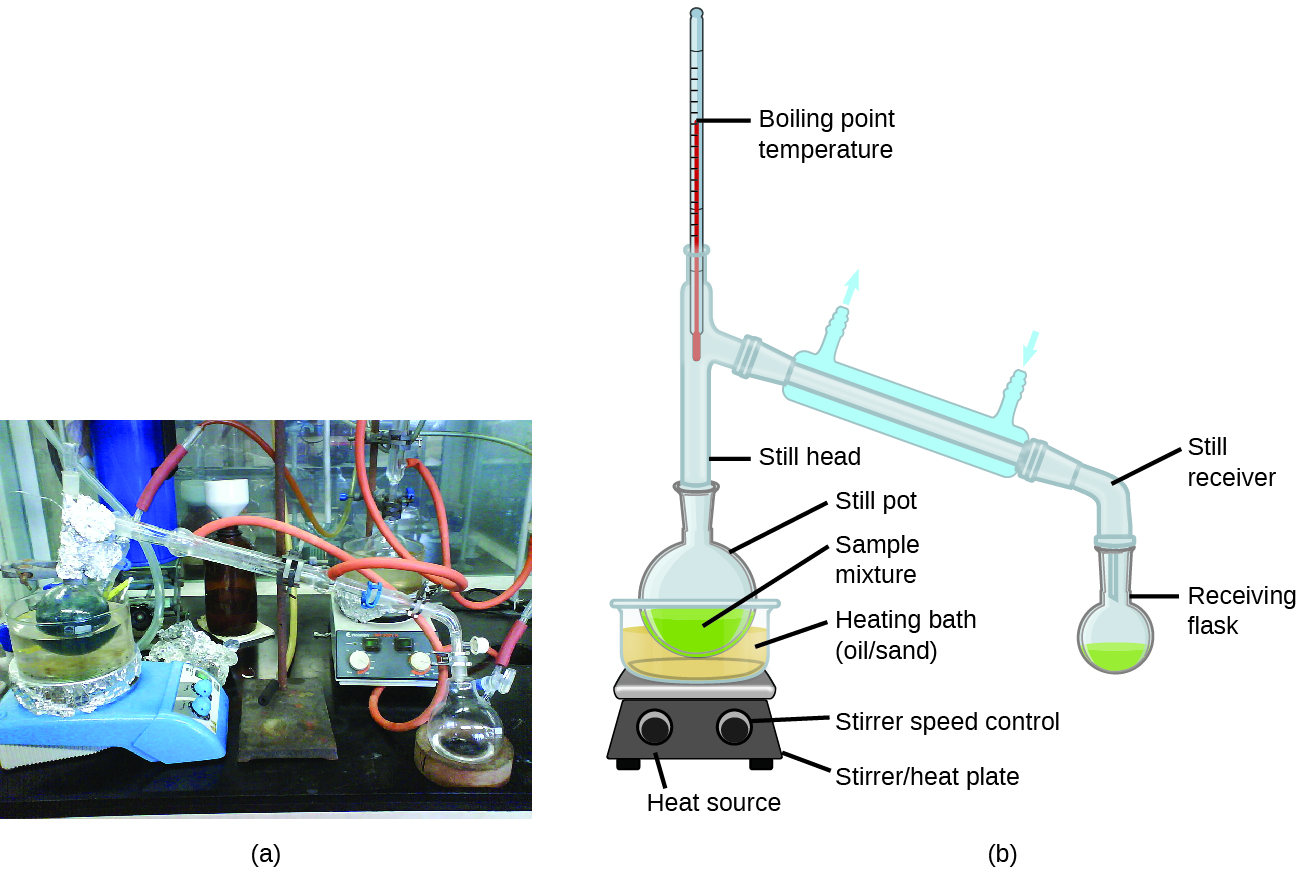
Distillation is a technique for separating the components of mixtures that is widely applied in both in the laboratory and in industrial settings. It is used to refine petroleum, to isolate fermentation products, and to purify water. This separation technique involves the controlled heating of a sample mixture to selectively vaporize, condense, and collect one or more components of interest. A typical apparatus for laboratory-scale distillations is shown in [link] .
Oil refineries use large-scale fractional distillation to separate the components of crude oil. The crude oil is heated to high temperatures at the base of a tall fractionating column , vaporizing many of the components that rise within the column. As vaporized components reach adequately cool zones during their ascent, they condense and are collected. The collected liquids are simpler mixtures of hydrocarbons and other petroleum compounds that are of appropriate composition for various applications (e.g., diesel fuel, kerosene, gasoline), as depicted in [link] .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?