| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
View this simulation to study the process of salts dissolving and forming saturated solutions and precipitates for specific compounds, or compounds for which you select the charges on the ions and the K sp
If the solution contained about equal concentrations of Cl – and I – , then the silver salt with the smallest K sp (AgI) would precipitate first. The concentrations are not equal, however, so we should find the [Ag + ] at which AgCl begins to precipitate and the [Ag + ] at which AgI begins to precipitate. The salt that forms at the lower [Ag + ] precipitates first.
For AgI: AgI precipitates when Q equals K sp for AgI (1.5 10 –16 ). When [I – ] = 0.0010 M :
AgI begins to precipitate when [Ag + ] is 1.5 10 –13 M .
For AgCl: AgCl precipitates when Q equals K sp for AgCl (1.6 10 –10 ). When [Cl – ] = 0.10 M :
AgCl begins to precipitate when [Ag + ] is 1.6 10 –9 M .
AgI begins to precipitate at a lower [Ag + ] than AgCl, so AgI begins to precipitate first.
[Ag + ] = 1.0 10 –11 M ; AgBr precipitates first
As we saw when we discussed buffer solutions, the hydronium ion concentration of an aqueous solution of acetic acid decreases when the strong electrolyte sodium acetate, NaCH 3 CO 2 , is added. We can explain this effect using Le Châtelier’s principle. The addition of acetate ions causes the equilibrium to shift to the left, decreasing the concentration of to compensate for the increased acetate ion concentration. This increases the concentration of CH 3 CO 2 H:
Because sodium acetate and acetic acid have the acetate ion in common, the influence on the equilibrium is called the common ion effect .
The common ion effect can also have a direct effect on solubility equilibria. Suppose we are looking at the reaction where silver iodide is dissolved:
If we were to add potassium iodide (KI) to this solution, we would be adding a substance that shares a common ion with silver iodide. Le Châtelier’s principle tells us that when a change is made to a system at equilibrium, the reaction will shift to counteract that change. In this example, there would be an excess of iodide ions, so the reaction would shift toward the left, causing more silver iodide to precipitate out of solution.
View this simulation to see how the common ion effect work with different concentrations of salts.
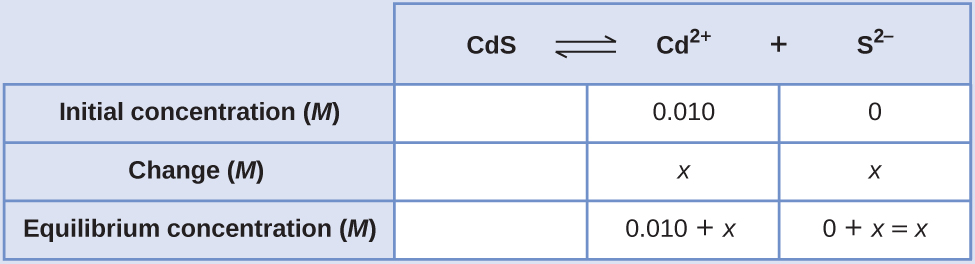
We can solve this equation using the quadratic formula, but we can also make an assumption to make this calculation much simpler. Since the K sp value is so small compared with the cadmium concentration, we can assume that the change between the initial concentration and the equilibrium concentration is negligible, so that 0.010 + x ~ 0.010. Going back to our K sp expression, we would now get:
Therefore, the molar solubility of CdS in this solution is 1.0 10 –26 M .
1 10 –10 M

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?