| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In the previous section, we discussed how to write Lewis structures for molecules and polyatomic ions. As we have seen, however, in some cases, there is seemingly more than one valid structure for a molecule. We can use the concept of formal charges to help us predict the most appropriate Lewis structure when more than one is reasonable.
The formal charge of an atom in a molecule is the hypothetical charge the atom would have if we could redistribute the electrons in the bonds evenly between the atoms. Another way of saying this is that formal charge results when we take the number of valence electrons of a neutral atom, subtract the nonbonding electrons, and then subtract the number of bonds connected to that atom in the Lewis structure.
Thus, we calculate formal charge as follows:
We can double-check formal charge calculations by determining the sum of the formal charges for the whole structure. The sum of the formal charges of all atoms in a molecule must be zero; the sum of the formal charges in an ion should equal the charge of the ion.
We must remember that the formal charge calculated for an atom is not the actual charge of the atom in the molecule. Formal charge is only a useful bookkeeping procedure; it does not indicate the presence of actual charges.
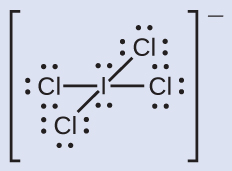
C −1, O +1
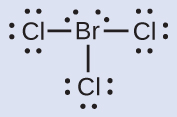
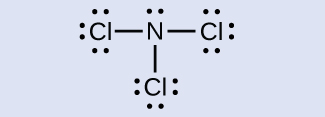
N: 0; all three Cl atoms: 0

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?