| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Thermochemistry is a branch of chemical thermodynamics , the science that deals with the relationships between heat, work, and other forms of energy in the context of chemical and physical processes. As we concentrate on thermochemistry in this chapter, we need to consider some widely used concepts of thermodynamics.
Substances act as reservoirs of energy, meaning that energy can be added to them or removed from them. Energy is stored in a substance when the kinetic energy of its atoms or molecules is raised. The greater kinetic energy may be in the form of increased translations (travel or straight-line motions), vibrations, or rotations of the atoms or molecules. When thermal energy is lost, the intensities of these motions decrease and the kinetic energy falls. The total of all possible kinds of energy present in a substance is called the internal energy ( U ) , sometimes symbolized as E .
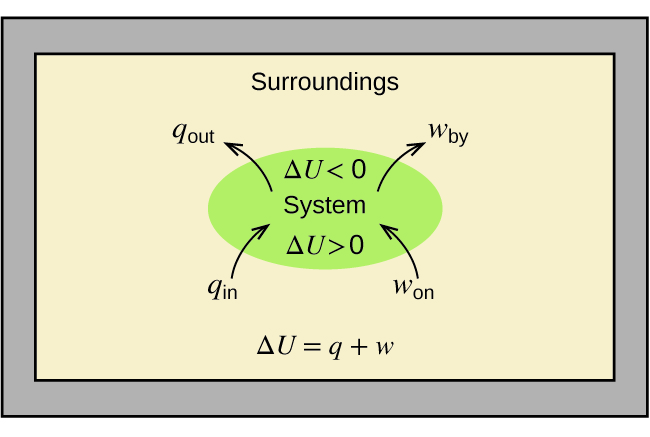
As a system undergoes a change, its internal energy can change, and energy can be transferred from the system to the surroundings, or from the surroundings to the system. Energy is transferred into a system when it absorbs heat ( q ) from the surroundings or when the surroundings do work ( w ) on the system. For example, energy is transferred into room-temperature metal wire if it is immersed in hot water (the wire absorbs heat from the water), or if you rapidly bend the wire back and forth (the wire becomes warmer because of the work done on it). Both processes increase the internal energy of the wire, which is reflected in an increase in the wire’s temperature. Conversely, energy is transferred out of a system when heat is lost from the system, or when the system does work on the surroundings.
The relationship between internal energy, heat, and work can be represented by the equation:
as shown in [link] . This is one version of the first law of thermodynamics , and it shows that the internal energy of a system changes through heat flow into or out of the system (positive q is heat flow in; negative q is heat flow out) or work done on or by the system. The work, w , is positive if it is done on the system and negative if it is done by the system.
A type of work called expansion work (or pressure-volume work) occurs when a system pushes back the surroundings against a restraining pressure, or when the surroundings compress the system. An example of this occurs during the operation of an internal combustion engine. The reaction of gasoline and oxygen is exothermic. Some of this energy is given off as heat, and some does work pushing the piston in the cylinder. The substances involved in the reaction are the system, and the engine and the rest of the universe are the surroundings. The system loses energy by both heating and doing work on the surroundings, and its internal energy decreases. (The engine is able to keep the car moving because this process is repeated many times per second while the engine is running.) We will consider how to determine the amount of work involved in a chemical or physical change in the chapter on thermodynamics.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?