| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Changes of nuclei that result in changes in their atomic numbers, mass numbers, or energy states are nuclear reactions . To describe a nuclear reaction, we use an equation that identifies the nuclides involved in the reaction, their mass numbers and atomic numbers, and the other particles involved in the reaction.
Many entities can be involved in nuclear reactions. The most common are protons, neutrons, alpha particles, beta particles, positrons, and gamma rays, as shown in [link] . Protons also represented by the symbol and neutrons are the constituents of atomic nuclei, and have been described previously. Alpha particles also represented by the symbol are high-energy helium nuclei. Beta particles also represented by the symbol are high-energy electrons, and gamma rays are photons of very high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Positrons also represented by the symbol are positively charged electrons (“anti-electrons”). The subscripts and superscripts are necessary for balancing nuclear equations, but are usually optional in other circumstances. For example, an alpha particle is a helium nucleus (He) with a charge of +2 and a mass number of 4, so it is symbolized This works because, in general, the ion charge is not important in the balancing of nuclear equations.
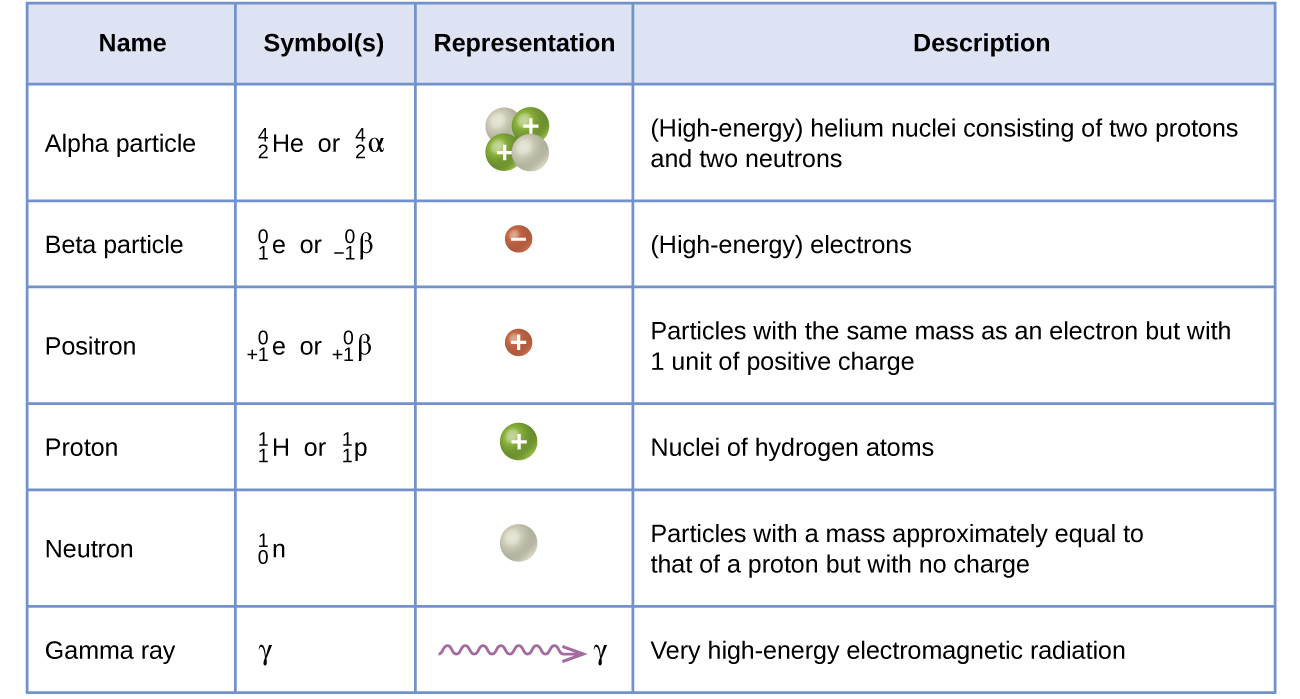
Note that positrons are exactly like electrons, except they have the opposite charge. They are the most common example of antimatter , particles with the same mass but the opposite state of another property (for example, charge) than ordinary matter. When antimatter encounters ordinary matter, both are annihilated and their mass is converted into energy in the form of gamma rays (γ) —and other much smaller subnuclear particles, which are beyond the scope of this chapter—according to the mass-energy equivalence equation E = mc 2 , seen in the preceding section. For example, when a positron and an electron collide, both are annihilated and two gamma ray photons are created:
As seen in the chapter discussing light and electromagnetic radiation, gamma rays compose short wavelength, high-energy electromagnetic radiation and are (much) more energetic than better-known X-rays that can behave as particles in the wave-particle duality sense. Gamma rays are produced when a nucleus undergoes a transition from a higher to a lower energy state, similar to how a photon is produced by an electronic transition from a higher to a lower energy level. Due to the much larger energy differences between nuclear energy shells, gamma rays emanating from a nucleus have energies that are typically millions of times larger than electromagnetic radiation emanating from electronic transitions.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?