| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
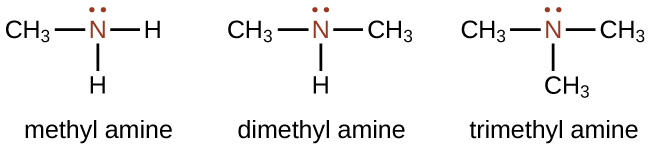
Amines are molecules that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. The nitrogen atom in an amine has a lone pair of electrons and three bonds to other atoms, either carbon or hydrogen. Various nomenclatures are used to derive names for amines, but all involve the class-identifying suffix –ine as illustrated here for a few simple examples:
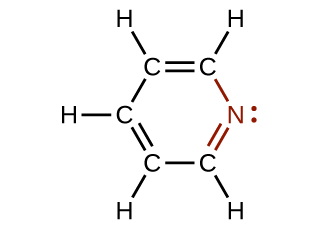
In some amines, the nitrogen atom replaces a carbon atom in an aromatic hydrocarbon. Pyridine ( [link] ) is one such heterocyclic amine. A heterocyclic compound contains atoms of two or more different elements in its ring structure.
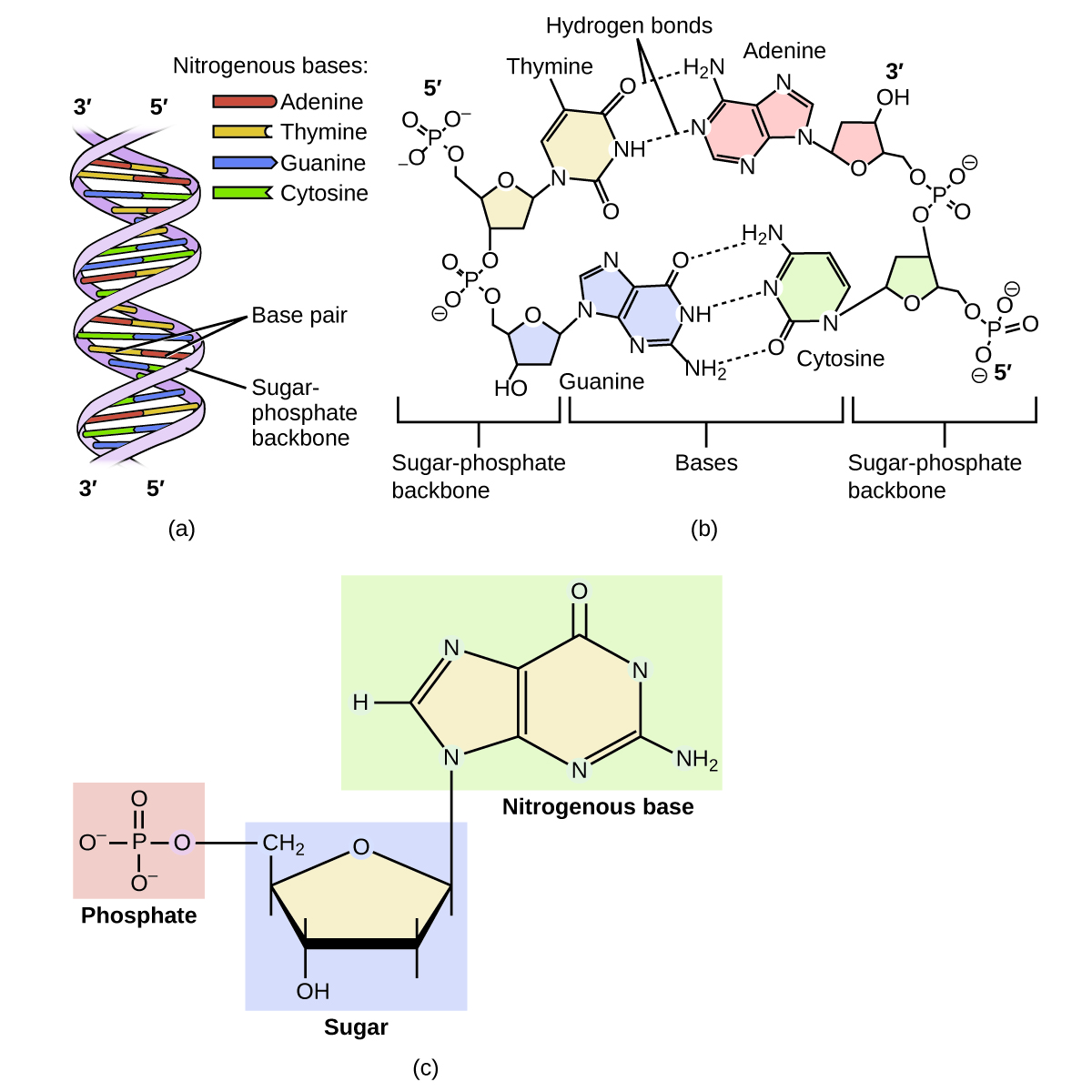
The genetic material for all living things is a polymer of four different molecules, which are themselves a combination of three subunits. The genetic information, the code for developing an organism, is contained in the specific sequence of the four molecules, similar to the way the letters of the alphabet can be sequenced to form words that convey information. The information in a DNA sequence is used to form two other types of polymers, one of which are proteins. The proteins interact to form a specific type of organism with individual characteristics.
A genetic molecule is called DNA, which stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. The four molecules that make up DNA are called nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of a single- or double-ringed molecule containing nitrogen, carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen called a nitrogenous base. Each base is bonded to a five-carbon sugar called deoxyribose. The sugar is in turn bonded to a phosphate group When new DNA is made, a polymerization reaction occurs that binds the phosphate group of one nucleotide to the sugar group of a second nucleotide. The nitrogenous bases of each nucleotide stick out from this sugar-phosphate backbone. DNA is actually formed from two such polymers coiled around each other and held together by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases. Thus, the two backbones are on the outside of the coiled pair of strands, and the bases are on the inside. The shape of the two strands wound around each other is called a double helix (see [link] ).
It probably makes sense that the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA of a cat differs from those of a dog. But it is also true that the sequences of the DNA in the cells of two individual pugs differ. Likewise, the sequences of DNA in you and a sibling differ (unless your sibling is an identical twin), as do those between you and an unrelated individual. However, the DNA sequences of two related individuals are more similar than the sequences of two unrelated individuals, and these similarities in sequence can be observed in various ways. This is the principle behind DNA fingerprinting, which is a method used to determine whether two DNA samples came from related (or the same) individuals or unrelated individuals.
Using similarities in sequences, technicians can determine whether a man is the father of a child (the identity of the mother is rarely in doubt, except in the case of an adopted child and a potential birth mother). Likewise, forensic geneticists can determine whether a crime scene sample of human tissue, such as blood or skin cells, contains DNA that matches exactly the DNA of a suspect.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?