| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In this section, we will learn about alcohols and ethers.
Incorporation of an oxygen atom into carbon- and hydrogen-containing molecules leads to new functional groups and new families of compounds. When the oxygen atom is attached by single bonds, the molecule is either an alcohol or ether.
Alcohols are derivatives of hydrocarbons in which an –OH group has replaced a hydrogen atom. Although all alcohols have one or more hydroxyl (–OH) functional groups, they do not behave like bases such as NaOH and KOH. NaOH and KOH are ionic compounds that contain OH – ions. Alcohols are covalent molecules; the –OH group in an alcohol molecule is attached to a carbon atom by a covalent bond.
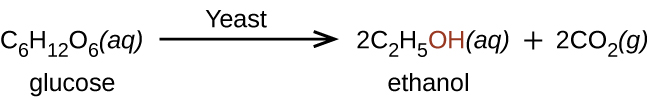
Ethanol, CH 3 CH 2 OH, also called ethyl alcohol, is a particularly important alcohol for human use. Ethanol is the alcohol produced by some species of yeast that is found in wine, beer, and distilled drinks. It has long been prepared by humans harnessing the metabolic efforts of yeasts in fermenting various sugars:
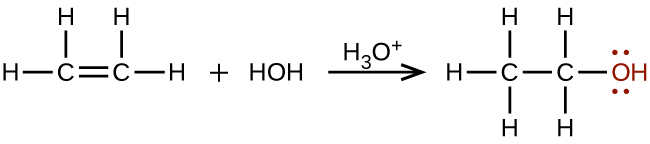
Large quantities of ethanol are synthesized from the addition reaction of water with ethylene using an acid as a catalyst:
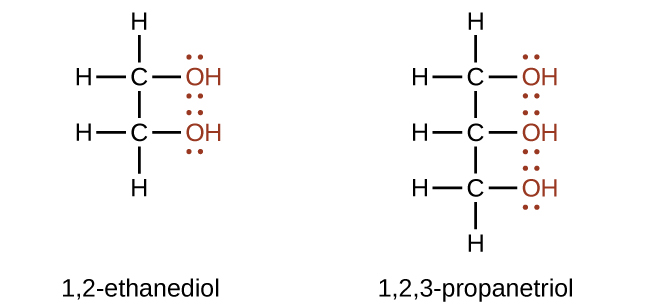
Alcohols containing two or more hydroxyl groups can be made. Examples include 1,2-ethanediol (ethylene glycol, used in antifreeze) and 1,2,3-propanetriol (glycerine, used as a solvent for cosmetics and medicines):
The name of an alcohol comes from the hydrocarbon from which it was derived. The final -e in the name of the hydrocarbon is replaced by -ol , and the carbon atom to which the –OH group is bonded is indicated by a number placed before the name. The IUPAC adopted new nomenclature guidelines in 2013 that require this number to be placed as an “infix” rather than a prefix. For example, the new name for 2-propanol would be propan-2-ol. Widespread adoption of this new nomenclature will take some time, and students are encouraged to be familiar with both the old and new naming protocols.
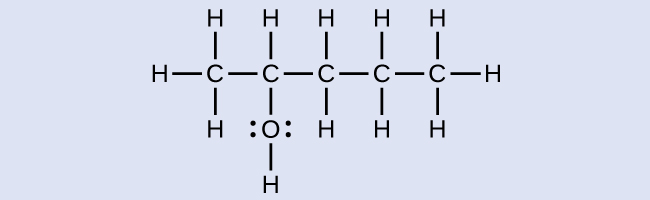
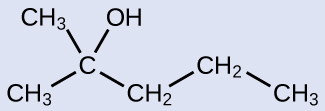
2-methyl-2-pentanol
Ethers are compounds that contain the functional group –O–. Ethers do not have a designated suffix like the other types of molecules we have named so far. In the IUPAC system, the oxygen atom and the smaller carbon branch are named as an alkoxy substituent and the remainder of the molecule as the base chain, as in alkanes. As shown in the following compound, the red symbols represent the smaller alkyl group and the oxygen atom, which would be named “methoxy.” The larger carbon branch would be ethane, making the molecule methoxyethane. Many ethers are referred to with common names instead of the IUPAC system names. For common names, the two branches connected to the oxygen atom are named separately and followed by “ether.” The common name for the compound shown in [link] is ethylmethyl ether:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?