| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Most pure nitrogen comes from the fractional distillation of liquid air. The atmosphere consists of 78% nitrogen by volume. This means there are more than 20 million tons of nitrogen over every square mile of the earth’s surface. Nitrogen is a component of proteins and of the genetic material (DNA/RNA) of all plants and animals.
Under ordinary conditions, nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas. It boils at 77 K and freezes at 63 K. Liquid nitrogen is a useful coolant because it is inexpensive and has a low boiling point. Nitrogen is very unreactive because of the very strong triple bond between the nitrogen atoms. The only common reactions at room temperature occur with lithium to form Li 3 N, with certain transition metal complexes, and with hydrogen or oxygen in nitrogen-fixing bacteria. The general lack of reactivity of nitrogen makes the remarkable ability of some bacteria to synthesize nitrogen compounds using atmospheric nitrogen gas as the source one of the most exciting chemical events on our planet. This process is one type of nitrogen fixation . In this case, nitrogen fixation is the process where organisms convert atmospheric nitrogen into biologically useful chemicals. Nitrogen fixation also occurs when lightning passes through air, causing molecular nitrogen to react with oxygen to form nitrogen oxides, which are then carried down to the soil.
All living organisms require nitrogen compounds for survival. Unfortunately, most of these organisms cannot absorb nitrogen from its most abundant source—the atmosphere. Atmospheric nitrogen consists of N 2 molecules, which are very unreactive due to the strong nitrogen-nitrogen triple bond. However, a few organisms can overcome this problem through a process known as nitrogen fixation, illustrated in [link] .
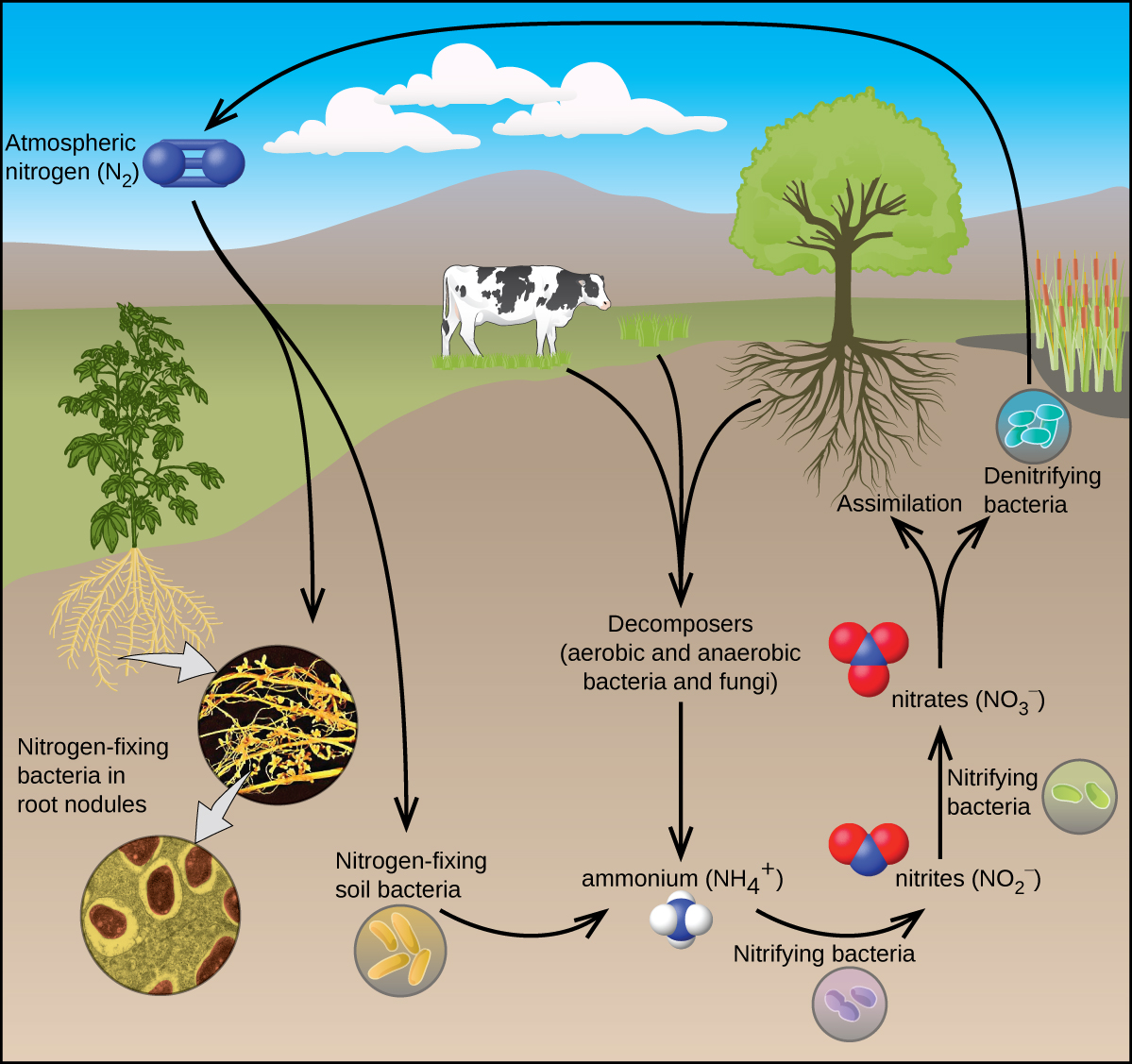
Nitrogen fixation is the process where organisms convert atmospheric nitrogen into biologically useful chemicals. To date, the only known kind of biological organisms capable of nitrogen fixation are microorganisms. These organisms employ enzymes called nitrogenases, which contain iron and molybdenum. Many of these microorganisms live in a symbiotic relationship with plants, with the best-known example being the presence of rhizobia in the root nodules of legumes.
Large volumes of atmospheric nitrogen are necessary for making ammonia—the principal starting material used for preparation of large quantities of other nitrogen-containing compounds. Most other uses for elemental nitrogen depend on its inactivity. It is helpful when a chemical process requires an inert atmosphere. Canned foods and luncheon meats cannot oxidize in a pure nitrogen atmosphere, so they retain a better flavor and color, and spoil less rapidly, when sealed in nitrogen instead of air. This technology allows fresh produce to be available year-round, regardless of growing season.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?