| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We should not be surprised that atoms, molecules, or ions must collide before they can react with each other. Atoms must be close together to form chemical bonds. This simple premise is the basis for a very powerful theory that explains many observations regarding chemical kinetics, including factors affecting reaction rates.
Collision theory is based on the following postulates:
The rate of a reaction is proportional to the rate of reactant collisions:
The reacting species must collide in an orientation that allows contact between the atoms that will become bonded together in the product.
The collision must occur with adequate energy to permit mutual penetration of the reacting species’ valence shells so that the electrons can rearrange and form new bonds (and new chemical species).
We can see the importance of the two physical factors noted in postulates 2 and 3, the orientation and energy of collisions, when we consider the reaction of carbon monoxide with oxygen:
Carbon monoxide is a pollutant produced by the combustion of hydrocarbon fuels. To reduce this pollutant, automobiles have catalytic converters that use a catalyst to carry out this reaction. It is also a side reaction of the combustion of gunpowder that results in muzzle flash for many firearms. If carbon monoxide and oxygen are present in sufficient quantity, the reaction is spontaneous at high temperature and pressure.
The first step in the gas-phase reaction between carbon monoxide and oxygen is a collision between the two molecules:
Although there are many different possible orientations the two molecules can have relative to each other, consider the two presented in [link] . In the first case, the oxygen side of the carbon monoxide molecule collides with the oxygen molecule. In the second case, the carbon side of the carbon monoxide molecule collides with the oxygen molecule. The second case is clearly more likely to result in the formation of carbon dioxide, which has a central carbon atom bonded to two oxygen atoms This is a rather simple example of how important the orientation of the collision is in terms of creating the desired product of the reaction.
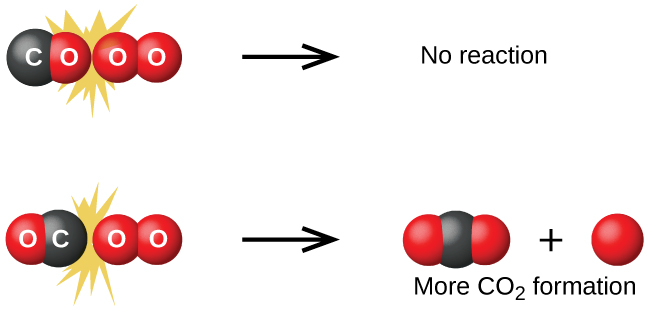
If the collision does take place with the correct orientation, there is still no guarantee that the reaction will proceed to form carbon dioxide. Every reaction requires a certain amount of activation energy for it to proceed in the forward direction, yielding an appropriate activated complex along the way. As [link] demonstrates, even a collision with the correct orientation can fail to form the reaction product. In the study of reaction mechanisms, each of these three arrangements of atoms is called a proposed activated complex or transition state .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?