| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
An inverse function reverses the operation done by a particular function. In other words, whatever a function does, the inverse function undoes it. In this section, we define an inverse function formally and state the necessary conditions for an inverse function to exist. We examine how to find an inverse function and study the relationship between the graph of a function and the graph of its inverse. Then we apply these ideas to define and discuss properties of the inverse trigonometric functions.
We begin with an example. Given a function and an output we are often interested in finding what value or values were mapped to by For example, consider the function Since any output we can solve this equation for to find that the input is This equation defines as a function of Denoting this function as and writing we see that for any in the domain of Thus, this new function, “undid” what the original function did. A function with this property is called the inverse function of the original function.
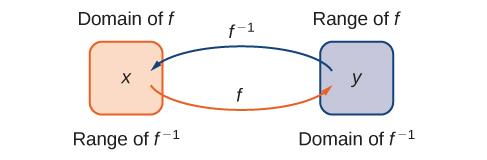
Given a function with domain and range its inverse function (if it exists) is the function with domain and range such that if In other words, for a function and its inverse
Note that is read as “f inverse.” Here, the is not used as an exponent and [link] shows the relationship between the domain and range of f and the domain and range of
Recall that a function has exactly one output for each input. Therefore, to define an inverse function, we need to map each input to exactly one output. For example, let’s try to find the inverse function for Solving the equation for we arrive at the equation This equation does not describe as a function of because there are two solutions to this equation for every The problem with trying to find an inverse function for is that two inputs are sent to the same output for each output The function discussed earlier did not have this problem. For that function, each input was sent to a different output. A function that sends each input to a different output is called a one-to-one function.
We say a is a one-to-one function if when
One way to determine whether a function is one-to-one is by looking at its graph. If a function is one-to-one, then no two inputs can be sent to the same output. Therefore, if we draw a horizontal line anywhere in the -plane, according to the horizontal line test , it cannot intersect the graph more than once. We note that the horizontal line test is different from the vertical line test. The vertical line test determines whether a graph is the graph of a function. The horizontal line test determines whether a function is one-to-one ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?