| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In this section, we use definite integrals to find the arc length of a curve. We can think of arc length as the distance you would travel if you were walking along the path of the curve. Many real-world applications involve arc length. If a rocket is launched along a parabolic path, we might want to know how far the rocket travels. Or, if a curve on a map represents a road, we might want to know how far we have to drive to reach our destination.
We begin by calculating the arc length of curves defined as functions of then we examine the same process for curves defined as functions of (The process is identical, with the roles of and reversed.) The techniques we use to find arc length can be extended to find the surface area of a surface of revolution, and we close the section with an examination of this concept.
In previous applications of integration, we required the function to be integrable, or at most continuous. However, for calculating arc length we have a more stringent requirement for Here, we require to be differentiable, and furthermore we require its derivative, to be continuous. Functions like this, which have continuous derivatives, are called smooth . (This property comes up again in later chapters.)
Let be a smooth function defined over We want to calculate the length of the curve from the point to the point We start by using line segments to approximate the length of the curve. For let be a regular partition of Then, for construct a line segment from the point to the point Although it might seem logical to use either horizontal or vertical line segments, we want our line segments to approximate the curve as closely as possible. [link] depicts this construct for
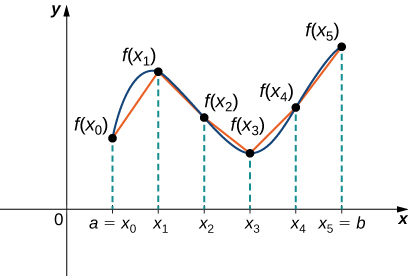
To help us find the length of each line segment, we look at the change in vertical distance as well as the change in horizontal distance over each interval. Because we have used a regular partition, the change in horizontal distance over each interval is given by The change in vertical distance varies from interval to interval, though, so we use to represent the change in vertical distance over the interval as shown in [link] . Note that some (or all) may be negative.

By the Pythagorean theorem, the length of the line segment is We can also write this as Now, by the Mean Value Theorem, there is a point such that Then the length of the line segment is given by Adding up the lengths of all the line segments, we get
This is a Riemann sum. Taking the limit as we have

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?