| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In Introduction to Integration , we developed the concept of the definite integral to calculate the area below a curve on a given interval. In this section, we expand that idea to calculate the area of more complex regions. We start by finding the area between two curves that are functions of beginning with the simple case in which one function value is always greater than the other. We then look at cases when the graphs of the functions cross. Last, we consider how to calculate the area between two curves that are functions of
Let and be continuous functions over an interval such that on We want to find the area between the graphs of the functions, as shown in the following figure.
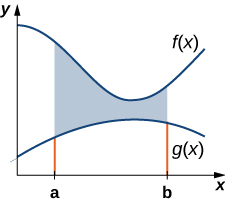
As we did before, we are going to partition the interval on the and approximate the area between the graphs of the functions with rectangles. So, for let be a regular partition of Then, for choose a point and on each interval construct a rectangle that extends vertically from to [link] (a) shows the rectangles when is selected to be the left endpoint of the interval and [link] (b) shows a representative rectangle in detail.
Use this calculator to learn more about the areas between two curves.
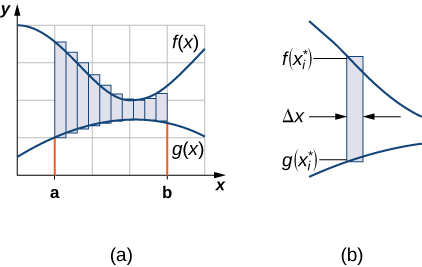
The height of each individual rectangle is and the width of each rectangle is Adding the areas of all the rectangles, we see that the area between the curves is approximated by
This is a Riemann sum, so we take the limit as and we get
These findings are summarized in the following theorem.
Let and be continuous functions such that over an interval Let denote the region bounded above by the graph of below by the graph of and on the left and right by the lines and respectively. Then, the area of is given by
We apply this theorem in the following example.
If R is the region bounded above by the graph of the function and below by the graph of the function over the interval find the area of region
The region is depicted in the following figure.
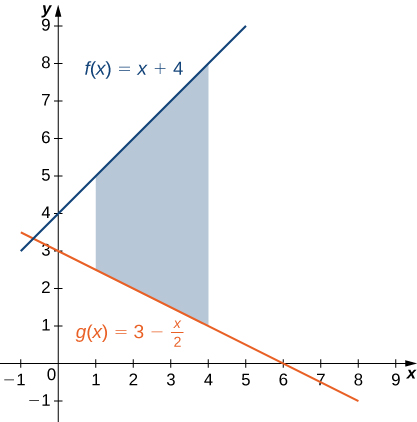
We have
The area of the region is

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?