| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Given a particular function, we are often interested in determining the largest and smallest values of the function. This information is important in creating accurate graphs. Finding the maximum and minimum values of a function also has practical significance because we can use this method to solve optimization problems, such as maximizing profit, minimizing the amount of material used in manufacturing an aluminum can, or finding the maximum height a rocket can reach. In this section, we look at how to use derivatives to find the largest and smallest values for a function.
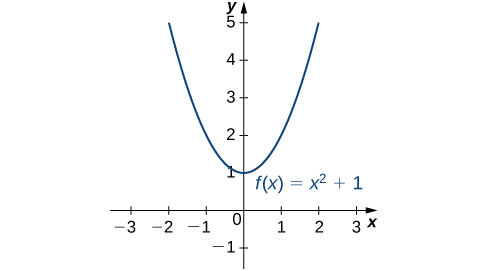
Consider the function over the interval As Therefore, the function does not have a largest value. However, since for all real numbers and when the function has a smallest value, 1, when We say that 1 is the absolute minimum of and it occurs at We say that does not have an absolute maximum (see the following figure).
Let be a function defined over an interval and let We say has an absolute maximum on at if for all We say has an absolute minimum on at if for all If has an absolute maximum on at or an absolute minimum on at we say has an absolute extremum on at
Before proceeding, let’s note two important issues regarding this definition. First, the term absolute here does not refer to absolute value. An absolute extremum may be positive, negative, or zero. Second, if a function has an absolute extremum over an interval at the absolute extremum is The real number is a point in the domain at which the absolute extremum occurs. For example, consider the function over the interval Since
for all real numbers we say has an absolute maximum over at The absolute maximum is It occurs at as shown in [link] (b).
A function may have both an absolute maximum and an absolute minimum, just one extremum, or neither. [link] shows several functions and some of the different possibilities regarding absolute extrema. However, the following theorem, called the Extreme Value Theorem , guarantees that a continuous function over a closed, bounded interval has both an absolute maximum and an absolute minimum.
![This figure has six parts a, b, c, d, e, and f. In figure a, the line f(x) = x3 is shown, and it is noted that it has no absolute minimum and no absolute maximum. In figure b, the line f(x) = 1/(x2 + 1) is shown, which is near 0 for most of its length and rises to a bump at (0, 1); it has no absolute minimum, but does have an absolute maximum of 1 at x = 0. In figure c, the line f(x) = cos x is shown, which has absolute minimums of −1 at ±π, ±3π, … and absolute maximums of 1 at 0, ±2π, ±4π, …. In figure d, the piecewise function f(x) = 2 – x2 for 0 ≤ x < 2 and x – 3 for 2 ≤ x ≤ 4 is shown, with absolute maximum of 2 at x = 0 and no absolute minimum. In figure e, the function f(x) = (x – 2)2 is shown on [1, 4], which has absolute maximum of 4 at x = 4 and absolute minimum of 0 at x = 2. In figure f, the function f(x) = x/(2 − x) is shown on [0, 2), with absolute minimum of 0 at x = 0 and no absolute maximum.](/ocw/mirror/col11964/m53611/CNX_Calc_Figure_04_03_010.jpg)
If is a continuous function over the closed, bounded interval then there is a point in at which has an absolute maximum over and there is a point in at which has an absolute minimum over

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?