| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Trigonometric functions are used to model many phenomena, including sound waves, vibrations of strings, alternating electrical current, and the motion of pendulums. In fact, almost any repetitive, or cyclical, motion can be modeled by some combination of trigonometric functions. In this section, we define the six basic trigonometric functions and look at some of the main identities involving these functions.
To use trigonometric functions, we first must understand how to measure the angles. Although we can use both radians and degrees, radians are a more natural measurement because they are related directly to the unit circle, a circle with radius 1. The radian measure of an angle is defined as follows. Given an angle let be the length of the corresponding arc on the unit circle ( [link] ). We say the angle corresponding to the arc of length 1 has radian measure 1.
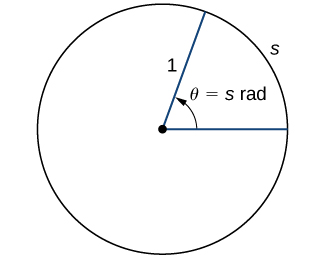
Since an angle of corresponds to the circumference of a circle, or an arc of length we conclude that an angle with a degree measure of has a radian measure of Similarly, we see that is equivalent to radians. [link] shows the relationship between common degree and radian values.
| Degrees | Radians | Degrees | Radians |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 120 | |
| 30 | 135 | ||
| 45 | 150 | ||
| 60 | 180 | ||
| 90 |
Use the fact that is equivalent to radians as a conversion factor:
Trigonometric functions allow us to use angle measures, in radians or degrees, to find the coordinates of a point on any circle—not only on a unit circle—or to find an angle given a point on a circle. They also define the relationship among the sides and angles of a triangle.
To define the trigonometric functions, first consider the unit circle centered at the origin and a point on the unit circle. Let be an angle with an initial side that lies along the positive -axis and with a terminal side that is the line segment An angle in this position is said to be in standard position ( [link] ). We can then define the values of the six trigonometric functions for in terms of the coordinates and
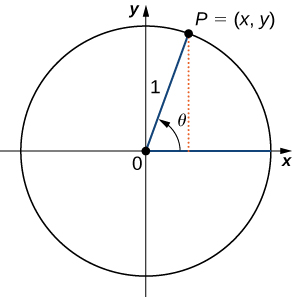
Let be a point on the unit circle centered at the origin Let be an angle with an initial side along the positive -axis and a terminal side given by the line segment The trigonometric functions are then defined as
If and are undefined. If then and are undefined.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?