| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Business Fundamentals was developed by the Global Text Project, which is working to create open-content electronictextbooks that are freely available on the website http://globaltext.terry.uga.edu. Distribution is also possible viapaper, CD, DVD, and via this collaboration, through Connexions. The goal is to make textbooks available to the manywho cannot afford them. For more information on getting involved with the Global Text Project or Connexions email us atdrexel@uga.edu and dcwill@cnx.org.
Editors: Salvador Treviño and Carlos Ruy Martinez (ITESM, Monterrey Campus, Mexico)
Contributors: Carlos Alberto Alanis, Gaspar Rivera, Jorge Echeagaray, Jose de Jesus Montes, Juana Monica Garcia, Ramiro Robles, and Roberto Sanchez
As mentioned previously, the essence of applying the marketing model lies in the finding of needs and filling them wisely. We will assess this issue of “Identifying market needs” by introducing a conceptual framework known as Abraham Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs .
This model focuses in the psychological features that explain the basic dimensions of human needs.
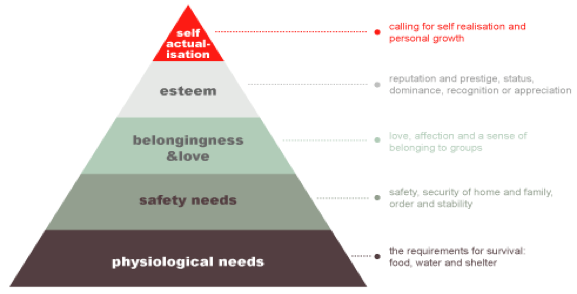
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, a staple of sociology and psychology courses, provides a useful framework for understanding how and why local products and brands are being selected and additionally how they can be extended beyond home country borders. Maslow hypothesized that people’s desires can be arranged into a hierarchy of five needs. As an individual fulfils needs at each level, he or she progresses to higher levels (see Exhibit 3 Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs). At the most basic level of human existence, physiological and safety needs must be met. People need food, clothing, and shelter, and a product that meets these basic needs has potential for introduction into a specific market. However, the basic human need to consume food and liquids is not the same thing as wanting or preferring a hamburger and a soft drink.
An additional consideration is that preferences are deeply embedded in local cultures. Responding to such differences has required the creation of products and brands for specific regional or country markets.
Mid-level needs in the hierarchy include self-respect, self-esteem, and the esteem of others. These social needs, which can create a powerful internal motivation, driving demand for status-oriented products, cut across the various stages of country development.
Luxury goods marketers are especially skilled at catering to esteem needs on a global basis. Some consumers flaunt their wealth by buying expensive products and brands that others will notice. Such behaviour is referred to as “ conspicuous consumption ” or “ luxury badging ”. Any company with a premium product or brand that has proven itself in a local market by fulfilling esteem needs should consider devising a strategy for taking the product global.
Source:
(External Link)
A process to determine the actual needs of consumers requires the identification of the market factors that produce them. In this process companies should find real consumption motivators that eventually evolve into product offerings. Furthermore, a correct business definition leads to a natural market orientation; for instance, Charles Revson famous quote “in the factory we make cosmetics; in the drug store we sell hope” (www.thinkexist.com) made possible for the company to develop cosmetic products based on women’s hopes rather than product features. Several potential pitfalls should be avoided. First, the natural tendency to impose a personal point of view when launching a new product or entering a new market. Second, simple imitation about competitors’ moves. Third, lack of sufficient research and market knowledge to produce market proved ideas. A framework has been proposed to align customer’s needs and wants with companies capabilities. This framework was introduced by Sherri Dorfman in her 2005 marketing article entitled “What do Customers Really, Really Want”.
In the article aforementioned, Dorfman proposes a three-step process to develop a natural market orientation:
To learn about customer needs and priorities, to identify opportunities in the company to fulfill these needs, and to create new or enhanced product offerings. These ideas must be incorporated in a market research process involving customers and other clients and suppliers in the Value Chain.
In this step, Dorfman proposes prioritizing features and benefits identified by clients, suppliers, and customers. Different qualitative research techniques such as in-depth interviews, ethnographies, and focus group sessions permit the identification of the core market needs.
Further communication with consumers validate the final definition of a market based product or service. This validation takes place as prototypes are assessed by consumers to identify potential problems and to smooth out design issues.
All these models take into account the so-called end consumer perspective, which implies that consumers buying, using, or recommending the products are the driving force behind successful marketing efforts.
However, there are other marketing perspectives that assume that organizations of many sorts, given their importance in the overall size of the global economy are the real forces behind markets’ success. This implies that marketing efforts should be aimed at understanding their behaviour as consumption entities, and use this knowledge to develop marketing strategies.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Business fundamentals' conversation and receive update notifications?