| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Use IS to reinforce your basic strategic positioning.
Source:
(External Link)
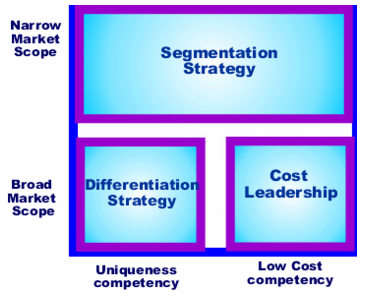
Porter suggests that a business cannot be all things to all people. It must choose between three generic strategies As illustrated in [link] , a business can choose to be a cost leader, it can pursue a differentiated strategy for which consumers are willing to pay more, or it can target a segment of the market with either a low cost or a differentiated strategy. For example, if we consider brands of automobiles, the Tata targets a broad market for low-priced cars, and the Subaru targets a broad differentiated market for low-priced all wheel drive cars. The Mazda Miata targets a segmented market for low-priced sports cars, while Rolls Royce targets a segmented (high priced) market for sedans.
Information systems can assist a business in implementing one of Porter’s three generic strategies by, for example, using IS to create operational efficiencies, thus lowering manufacturing costs. IS can create a differentiated model by, for example, having a website that permits customers to design a personalized version of an automobile and order it online, much the same way that we can buy personal computers online.
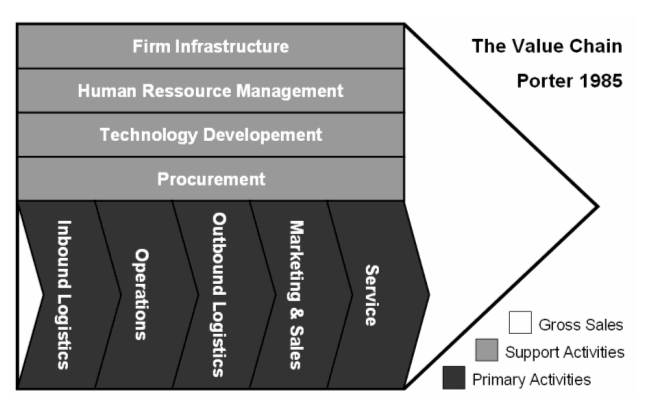
As discussed in Chapter 3 , the Value Chain is a graphical representation of the processes (or activities) involved in most organizations. Analysts use the value chain framework to look for ways to streamline costly activities or add value to certain activities through the use of IS. As just one example, an organization could use IS to outsource a call center service to a lower cost location or, it could use IS to provide a well-designed website to offer a differentiated experience to customers who need to contact the organization, and embody a personalized call center service for issues that cannot be resolved by the customer just by using website features.
It is almost always the case that there are insufficient resources for an organization to take advantage of all of its opportunities to use IS to obtain business benefits. Such resources can be in the form of personnel in an internal IS Department or cash to hire outside consultants or both. Because of this, it is important that organizations be sure they are using their scares resources on IS projects that have the greatest value to the organization. A time-tested way of doing this is to have a process for setting IS development priorities that are consistent with and aligned with organizational priorities. In the literature, this is typically called “Strategic alignment”. There are three general approaches that organizations take to setting priorities for Information Systems projects. (Some practitioners say “there is no such thing as an IS project; there are only business projects. Such a perspective emphasizes the importance of obtaining business benefits from an investment in IS). The three general approaches to setting priorities (also known as developing a strategic plan for the IS function) are:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Business fundamentals' conversation and receive update notifications?