| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Business Fundamentals was developed by the Global Text Project, which is working to create open-content electronictextbooks that are freely available on the website http://globaltext.terry.uga.edu. Distribution is also possible viapaper, CD, DVD, and via this collaboration, through Connexions. The goal is to make textbooks available to the manywho cannot afford them. For more information on getting involved with the Global Text Project or Connexions email us atdrexel@uga.edu and dcwill@cnx.org.
Authors: Vlad Malamud, Yevgeniy Rotenberg
Editor: Douglas Allen
Reviewers: Dean Murray Young (Thompson Rivers University, Canada) Timothy B Folta (Purdue University)
Contributing authors: Wesley Scott Cables, Ricardo Cubillos, Mike Davis, Vesselin Dotkov, Loiuse Doyle, Barbara Gabhauer, Glenna Gagliardi, Melissa Harrison Hiatt, Katie Holtmeier, Alisa Jeffrey, Alexia Jennings, TimPitner, Ashley Randall, Dag Johan Sundby, Nathalie Tryon, Jeffrey Wiant, Sarah Wilson
The topics surrounding Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) have become more complex due to the globalization of the economy and the issues that arise from companies competing in international markets. Companies are manufacturing goods, hiring local labor, utilizing raw materials and resources extracted from the environment in international locations.
This heightened awareness of CSR and sustainable development has been endorsed by an increased responsiveness to ethical, social, environmental and other global issues. In recent years, companies have been the center of scandals regarding accounting practices, damages to the environment, inadequate treatment of employees and workers and the effect of its products on the society.
For example, in January 2009, the Chairman of one of India’s largest technology companies, Satyam Computer Services Ltd., said he fabricated key financial results, including a fictitious cash balance of more than USD 1 billion (Sheth, 2009). Cases like this, and others such as Enron Corporation and Worldcom in the United States, prompt concerns about corporate governance and accounting standards globally. Further, corporate fraud puts into question one of the fundamental reasons of why shareholders invest in public companies, the need for transparency.
As a result, companies are responding to increased public expectations of responsibility and incorporating the concept of CSR into their operating plans and strategy.
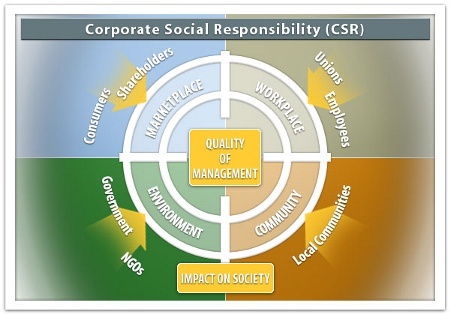
Traditionally, CSR has been defined as the corporation’s responsibility to comply with the laws and responsibilities to its shareholders. This concept of CSR has evolved to include the organization’s responsibility for its impact on different stakeholders such as employees, customers, investors, local communities, and government.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Business fundamentals' conversation and receive update notifications?