| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
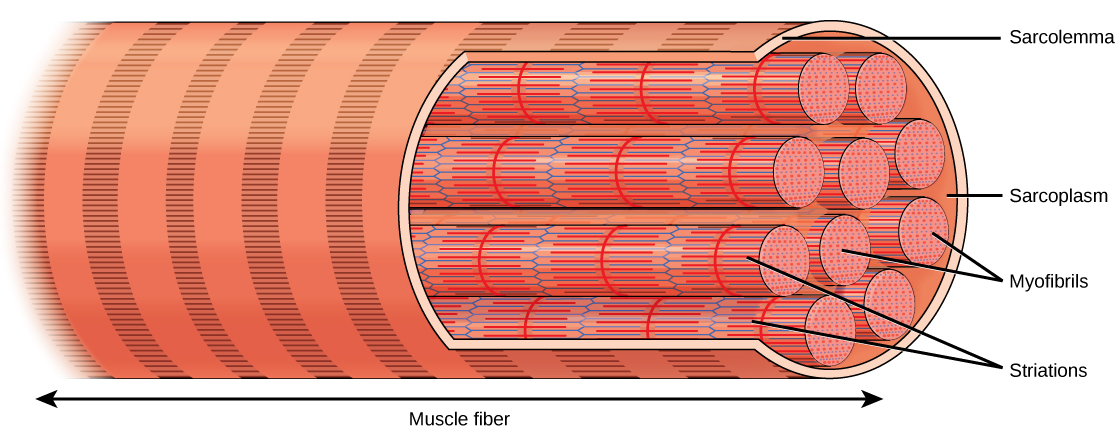
The striated appearance of skeletal muscle tissue is a result of repeating bands of the proteins actin and myosin that are present along the length of myofibrils. The alignment of myofibrils in the cell causes the entire cell to appear striated or banded.
The Z lines mark the border of units called sarcomeres , which are the functional units of skeletal muscle. A myofibril is composed of many sarcomeres running along its length, and as the sarcomeres individually contract, the myofibrils and muscle cells shorten ( [link] ).
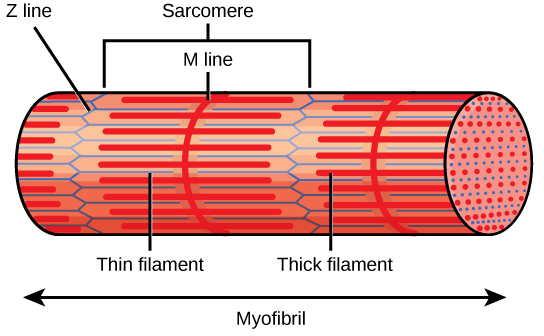
Myofibrils are composed of smaller structures called myofilaments . There are two main types of filaments: thick filaments and thin filaments; each has different compositions and locations. Thick filaments (composed of the protein myosin) and Thin filaments (composed of the protein actin).
The myosin thick filaments contain two regions designated as the head and the tail. These regions are important in the process of muscle contraction and will be discussed in more detail. Two components of the thin filaments are tropomyosin and troponin. Actin has binding sites for myosin attachment. Strands of tropomyosin block the binding sites and prevent actin–myosin interactions when the muscles are at rest. Troponin consists of three globular subunits. One subunit binds to tropomyosin, one subunit binds to actin, and one subunit binds Ca 2+ ions.
For a muscle cell to contract, the sarcomere must shorten. However, thick and thin filaments—the components of sarcomeres—do not shorten. Instead, they slide by one another, causing the sarcomere to shorten while the filaments remain the same length. The sliding filament theory of muscle contraction was developed to fit the differences observed in the named bands on the sarcomere at different degrees of muscle contraction and relaxation. The mechanism of contraction is the binding of myosin to actin, forming cross-bridges that generate filament movement ( [link] ).
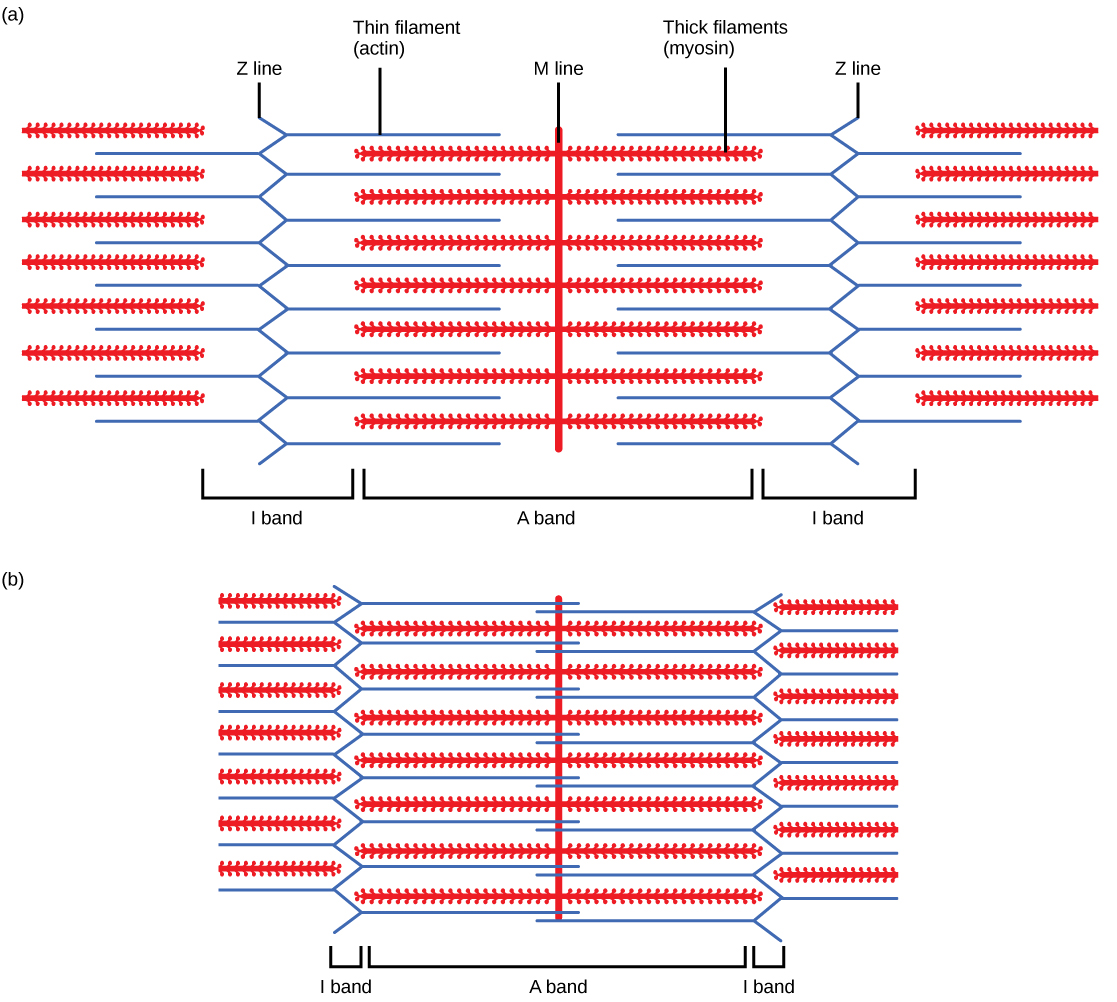
When a sarcomere shortens, some regions shorten whereas others stay the same length. A sarcomere is defined as the distance between two consecutive Z lines; when a muscle contracts, the distance between the Z lines is reduced. Thin filaments are pulled by the thick filaments toward the center of the sarcomere until the Z lines approach the thick filaments. The zone of overlap, in which thin filaments and thick filaments occupy the same area, increases as the thin filaments move inward.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Human biology' conversation and receive update notifications?