| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The undigested food is sent to the colon from the ileum via peristaltic movements. The ileum ends and the large intestine begins at the ileocecal valve. The vermiform, “worm-like,” appendix is located at the ileocecal valve. The appendix of humans has a minor role in immunity.
The large intestine reabsorbs the water from indigestible food material and processes the waste material ( [link] ). The human large intestine is much smaller in length compared to the small intestine but larger in diameter. It has three parts: the cecum, the colon, and the rectum. The cecum joins the ileum to the colon and is the receiving pouch for the waste matter. The colon is home to many bacteria or “intestinal flora” that aid in the digestive processes. The colon has four regions, the ascending colon, the transverse colon, the descending colon and the sigmoid colon. The main functions of the colon are to extract the water and mineral salts from undigested food, and to store waste material.
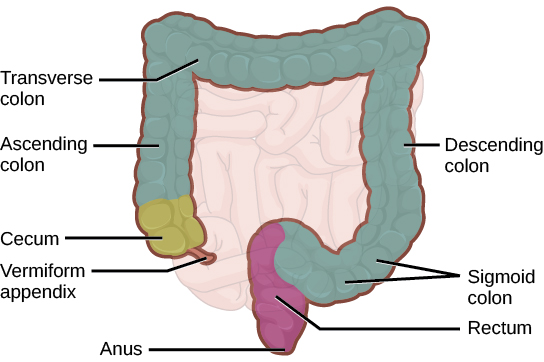
The rectum ( [link] ) stores feces until defecation. The feces are propelled using peristaltic movements during elimination. The anus is an opening at the far-end of the digestive tract and is the exit point for the waste material. Two sphincters regulate the exit of feces, the inner sphincter is involuntary and the outer sphincter is voluntary.
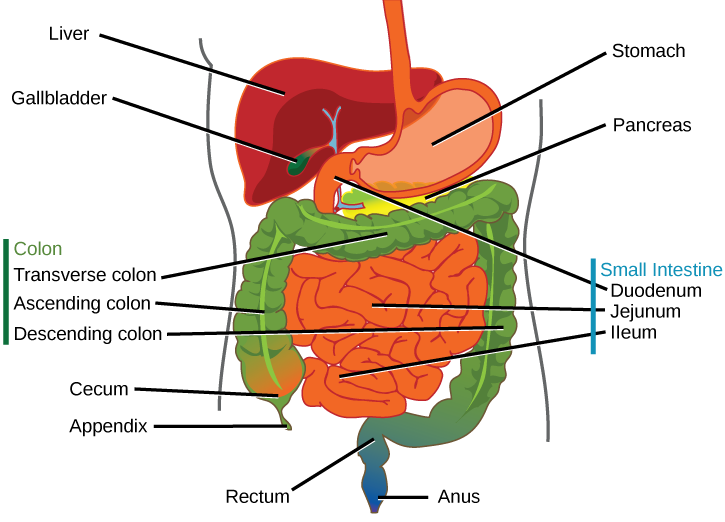
The organs discussed above are the organs of the digestive tract through which food passes. Accessory organs add secretions and enzymes that break down food into nutrients. Accessory organs include the salivary glands, the liver, the pancreas, and the gall bladder. The secretions of the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder are regulated by hormones in response to food consumption.
The liver is the largest internal organ in humans and it plays an important role in digestion of fats and detoxifying blood. The liver produces bile, a digestive juice that is required for the breakdown of fats in the duodenum. The liver also processes the absorbed vitamins and fatty acids and synthesizes many plasma proteins. The gallbladder is a small organ that aids the liver by storing bile and concentrating bile salts.
The pancreas secretes bicarbonate that neutralizes the acidic chyme and a variety of enzymes (trypsin, amylase, and lipase) for the digestion of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats, respectively.
The human diet should be well balanced to provide nutrients required for bodily function and the minerals and vitamins required for maintaining structure and regulation necessary for good health and reproductive capability ( [link] ).

Explore this interactive United States Department of Agriculture website to learn more about each food group and the recommended daily amounts.
The organic molecules required for building cellular material and tissues must come from food. During digestion, digestible carbohydrates are ultimately broken down into glucose and used to provide energy within the cells of the body. Complex carbohydrates, including polysaccharides, can be broken down into glucose through biochemical modification; however, humans do not produce the enzyme necessary to digest cellulose (fiber). The intestinal flora in the human gut are able to extract some nutrition from these plant fibers. These plant fibers are known as dietary fiber and are an important component of the diet. The excess sugars in the body are converted into glycogen and stored for later use in the liver and muscle tissue. Glycogen stores are used to fuel prolonged exertions, such as long-distance running, and to provide energy during food shortage. Fats are stored under the skin of mammals for insulation and energy reserves.
Proteins in food are broken down during digestion and the resulting amino acids are absorbed. All of the proteins in the body must be formed from these amino-acid constituents; no proteins are obtained directly from food.
Fats add flavor to food and promote a sense of satiety or fullness. Fatty foods are also significant sources of energy, and fatty acids are required for the construction of lipid membranes. Fats are also required in the diet to aid the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and the production of fat-soluble hormones.
While the animal body can synthesize many of the molecules required for function from precursors, there are some nutrients that must be obtained from food. These nutrients are termed essential nutrients , meaning they must be eaten, because the body cannot produce them. Essential nutrients include some fatty acids, some amino acids, vitamins, and minerals.
There are many organs that work together to digest food and absorb nutrients. The mouth is the point of ingestion and the location where both mechanical and chemical breakdown of food begins. Saliva contains an enzyme called amylase that breaks down carbohydrates and an enxyme lipase that breaks down triglycerides. The food bolus travels through the esophagus by peristaltic movements to the stomach. The stomach has an extremely acidic environment. The enzyme pepsin digests protein in the stomach. Further digestion and absorption take place in the small intestine. The large intestine reabsorbs water from the undigested food and stores waste until elimination.
Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are the primary components of food. Some essential nutrients are required for cellular function but cannot be produced by the animal body. These include vitamins (both fat and water soluble) , minerals, some fatty acids, and some amino acids. Food intake in more than necessary amounts is stored as glycogen in the liver and muscle cells, and in adipose tissue. Excess adipose storage can lead to obesity and serious health problems.
[link] Which of the following statements about the digestive system is false?
[link] B

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Human biology' conversation and receive update notifications?