| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
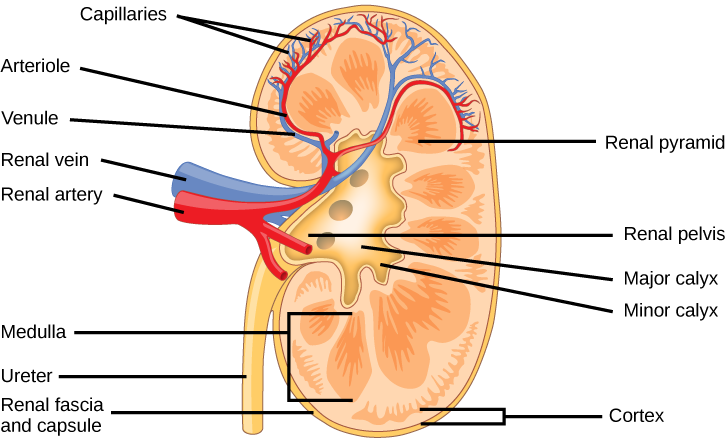
Because the kidney filters blood, its network of blood vessels is an important component of its structure and function. The arteries, veins, and nerves that supply the kidney enter and exit at the renal hilum. Renal blood supply starts with the branching of the aorta into the renal arteries and ends with the exiting of the renal veins to join the inferior vena cava , which transports blood back to the right atrium of the heart. The renal arteries split multiple times to form other blood vessels before branching into numerous afferent arterioles, and then enter the capillaries supplying the nephrons.
As mentioned previously, the functional unit of the kidney is the nephron, illustrated in [link] . Each kidney is made up of over one million nephrons that dot the renal cortex. A nephron consists of three parts—a renal corpuscle , a renal tubule , and the associated capillary network.
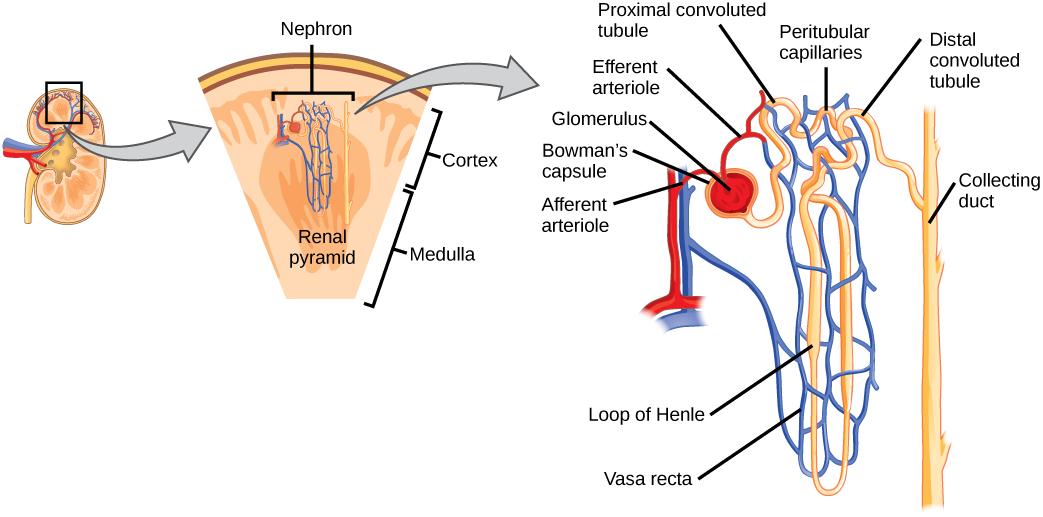
The renal corpuscle, located in the renal cortex, is made up of a network of capillaries known as the glomerulus and the capsule, a cup-shaped chamber that surrounds it, called the glomerular or Bowman's capsule .
The renal tubule is a long and convoluted structure that emerges from the glomerulus and can be divided into three parts based on function. The first part is called the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) due to its proximity to the glomerulus. The second part is called the loop of Henle , because it forms a loop (with descending and ascending limbs ). The third part of the renal tubule is called the distal convoluted tubule (DCT) . The DCT, which is the last part of the nephron, connects and empties its contents into collecting ducts. The urine will ultimately move into the renal pelvis and then into the ureters.
The capillary network that originates from the renal arteries supplies the nephron with blood that needs to be filtered. The branch that enters the glomerulus is called the afferent arteriole . The branch that exits the glomerulus is called the efferent arteriole . Within the glomerulus, the network of capillaries is called the glomerular capillary bed. Once the efferent arteriole exits the glomerulus, it forms the peritubular capillary network , which surrounds and interacts with parts of the renal tubule.
Go to this website to see another section of the kidney and to explore an animation of the workings of nephrons.
Kidneys filter blood in a three-step process. First, the nephrons filter blood that runs through the capillary network in the glomerulus. Almost all solutes, except for proteins, are filtered out into the glomerulus by a process called glomerular filtration . Second, the filtrate is collected in the renal tubules. Most of the solutes get reabsorbed in the PCT by a process called tubular reabsorption . In the loop of Henle, the filtrate continues to exchange solutes and water with the peritubular capillary network. Water is also reabsorbed during this step. Then, additional solutes and wastes are secreted into the kidney tubules during tubular secretion , which is, in essence, the opposite process to tubular reabsorption. The collecting ducts collect filtrate coming from the nephrons and this filtrate, called urine, will be transported into the renal pelvis and then to the ureters. This entire process is illustrated in [link] .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Human biology' conversation and receive update notifications?