| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
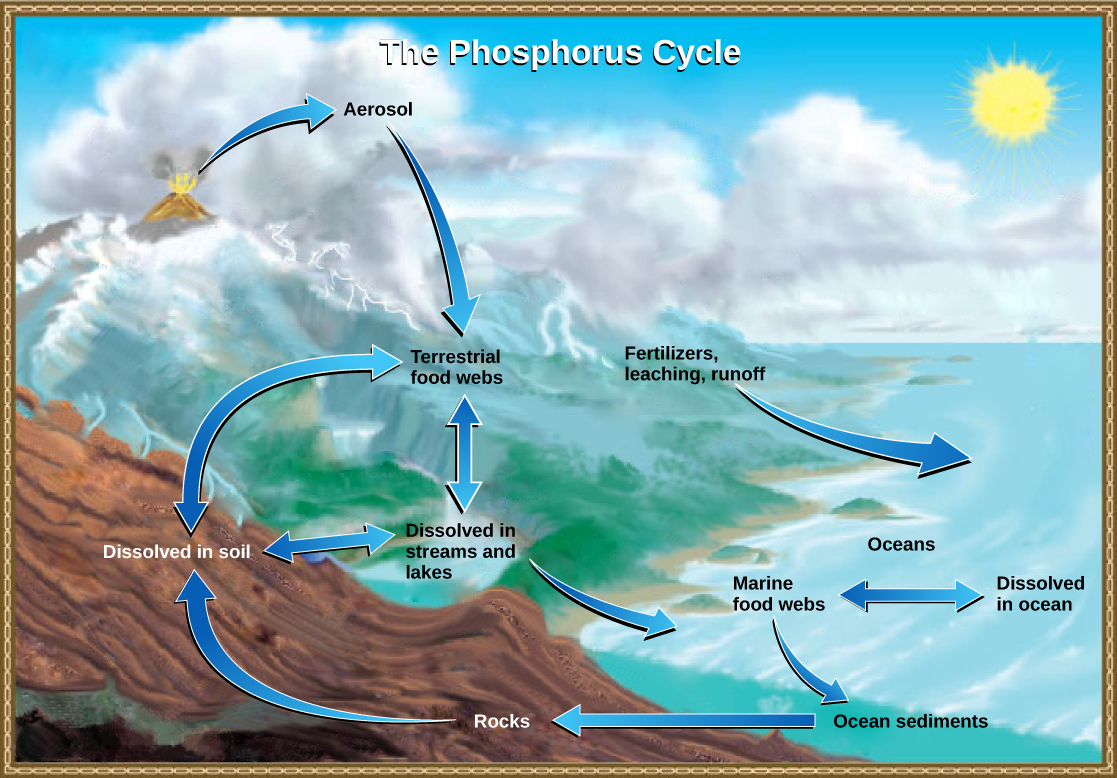
Phosphorus is an essential nutrient for living processes; it is a major component of nucleic acids and phospholipids, and, as calcium phosphate, makes up the supportive components of our bones. Phosphorus is often the limiting nutrient (necessary for growth) in aquatic, particularly freshwater, ecosystems.
Phosphorus occurs in nature as the phosphate ion (PO 4 3- ). In addition to phosphate runoff as a result of human activity, natural surface runoff occurs when it is leached from phosphate-containing rock by weathering, thus sending phosphates into rivers, lakes, and the ocean. This rock has its origins in the ocean. Phosphate-containing ocean sediments form primarily from the bodies of ocean organisms and from their excretions. However, volcanic ash, aerosols, and mineral dust may also be significant phosphate sources. This sediment then is moved to land over geologic time by the uplifting of Earth’s surface. ( [link] )
Phosphorus is also reciprocally exchanged between phosphate dissolved in the ocean and marine organisms. The movement of phosphate from the ocean to the land and through the soil is extremely slow, with the average phosphate ion having an oceanic residence time between 20,000 and 100,000 years.
Excess phosphorus and nitrogen that enter these ecosystems from fertilizer runoff and from sewage cause excessive growth of algae. The subsequent death and decay of these organisms depletes dissolved oxygen, which leads to the death of aquatic organisms, such as shellfish and finfish. This process is responsible for dead zones in lakes and at the mouths of many major rivers and for massive fish kills, which often occur during the summer months (see [link] ).
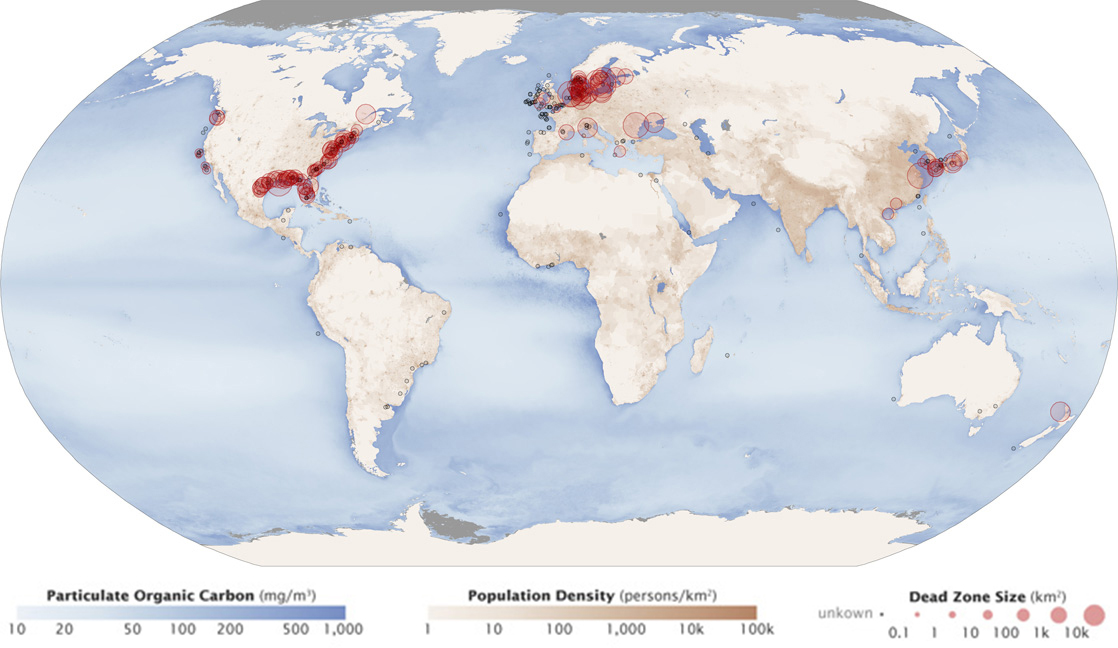
A dead zone is an area in lakes and oceans near the mouths of rivers where large areas are periodically depleted of their normal flora and fauna; these zones can be caused by eutrophication, oil spills, dumping toxic chemicals, and other human activities. The number of dead zones has increased for several years, and more than 400 of these zones were present as of 2008. One of the worst dead zones is off the coast of the United States in the Gulf of Mexico: fertilizer runoff from the Mississippi River basin created a dead zone of over 8,463 square miles. Phosphate and nitrate runoff from fertilizers also negatively affect several lake and bay ecosystems including the Chesapeake Bay in the eastern United States.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?