| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
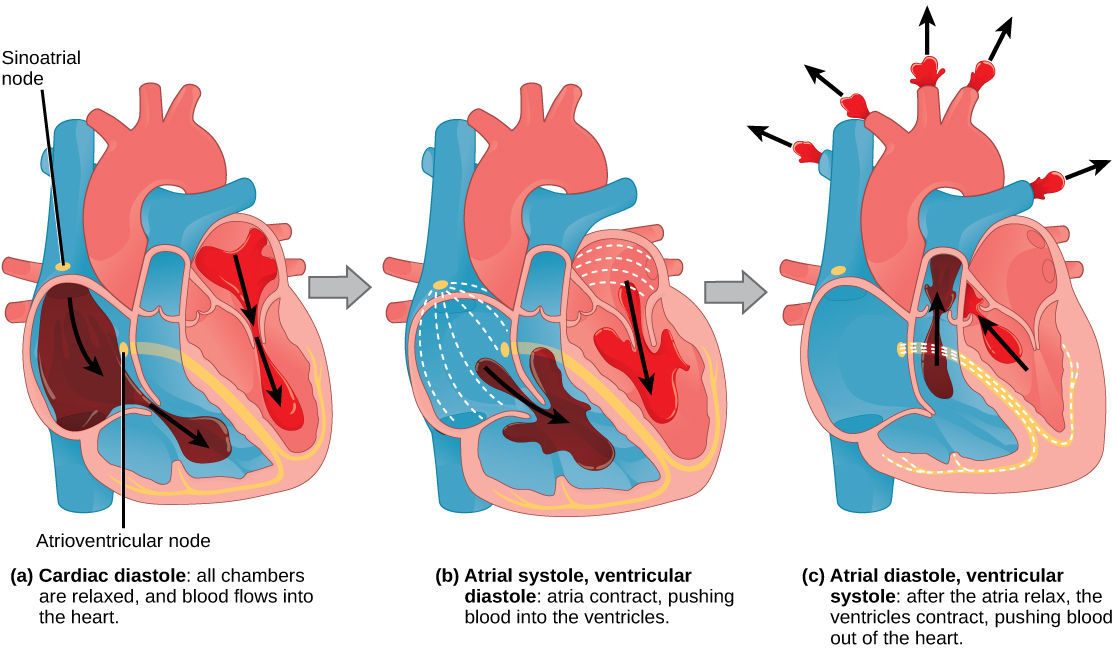
The pumping of the heart is a function of the cardiac muscle cells, or cardiomyocytes, that make up the heart muscle. Cardiomyocytes are distinctive muscle cells that are striated like skeletal muscle but pump rhythmically and involuntarily like smooth muscle; adjacent cells are connected by intercalated disks found only in cardiac muscle. These connections allow the electrical signal to travel directly to neighboring muscle cells.
The electrical impulses in the heart produce electrical currents that flow through the body and can be measured on the skin using electrodes. This information can be observed as an electrocardiogram (ECG) a recording of the electrical impulses of the cardiac muscle.
Visit the following website to see the heart’s pacemaker, or electrocardiogram system, in action.
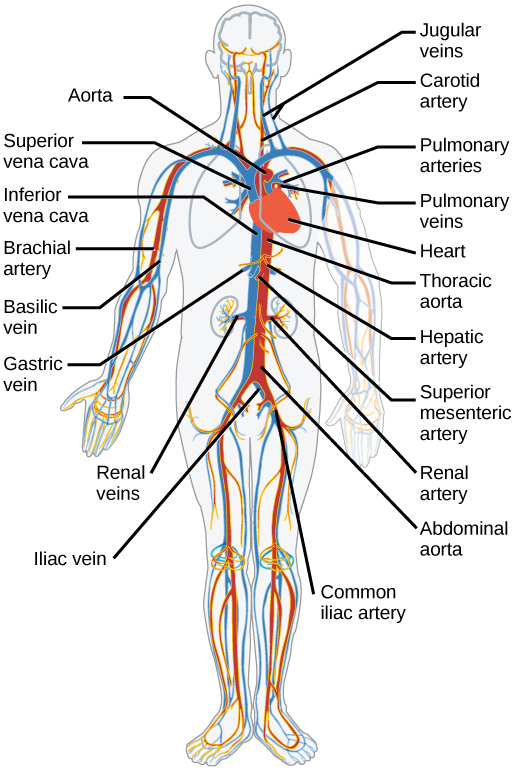
The blood from the heart is carried through the body by a complex network of blood vessels ( [link] ). Arteries take blood away from the heart. The main artery of the systemic circulation is the aorta; it branches into major arteries that take blood to different limbs and organs. The aorta and arteries near the heart have heavy but elastic walls that respond to and smooth out the pressure differences caused by the beating heart. Arteries farther away from the heart have more muscle tissue in their walls that can constrict to affect flow rates of blood. The major arteries diverge into minor arteries, and then smaller vessels called arterioles, to reach more deeply into the muscles and organs of the body.
Arterioles diverge into capillary beds. Capillary beds contain a large number, 10’s to 100’s of capillaries that branch among the cells of the body. Capillaries are narrow-diameter tubes that can fit single red blood cells and are the sites for the exchange of nutrients, waste, and oxygen with tissues at the cellular level. Fluid also leaks from the blood into the interstitial space from the capillaries. The capillaries converge again into venules that connect to minor veins that finally connect to major veins. Veins are blood vessels that bring blood high in carbon dioxide back to the heart. Veins are not as thick-walled as arteries, since pressure is lower, and they have valves along their length that prevent backflow of blood away from the heart. The major veins drain blood from the same organs and limbs that the major arteries supply.
Animal respiratory systems are designed to facilitate gas exchange. In mammals, air is warmed and humidified in the nasal cavity. Air then travels down the pharynx and larynx, through the trachea, and into the lungs. In the lungs, air passes through the branching bronchi, reaching the respiratory bronchioles. The respiratory bronchioles open up into the alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs, and alveoli. Because there are so many alveoli and alveolar sacs in the lung, the surface area for gas exchange is very large.
The mammalian circulatory system is a closed system with double circulation passing through the lungs and the body. It consists of a network of vessels containing blood that circulates because of pressure differences generated by the heart.
The heart contains two pumps that move blood through the pulmonary and systemic circulations. There is one atrium and one ventricle on the right side and one atrium and one ventricle on the left side. The pumping of the heart is a function of cardiomyocytes, distinctive muscle cells that are striated like skeletal muscle but pump rhythmically and involuntarily like smooth muscle. The signal for contraction begins in the wall of the right atrium. The electrochemical signal causes the two atria to contract in unison; then the signal causes the ventricles to contract. The blood from the heart is carried through the body by a complex network of blood vessels; arteries take blood away from the heart, and veins bring blood back to the heart.
[link] Which of the following statements about the human respiratory system is false?
[link] B
[link] Which of the following statements about the circulatory system is false?
[link] A

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?