| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The cestodes, or tapeworms, are also internal parasites, mainly of vertebrates. Tapeworms live in the intestinal tract of the primary host and remain fixed using a sucker on the anterior end, or scolex, of the tapeworm body. The remaining body of the tapeworm is made up of a long series of units called proglottids, each of which may contain an excretory system with flame cells, but will contain reproductive structures, both male and female. Tapeworms do not have a digestive system, they absorb nutrients from the food matter passing them in the host’s intestine. Proglottids are produced at the scolex and are pushed to the end of the tapeworm as new proglottids form, at which point, they are “mature” and all structures except fertilized eggs have degenerated. Most reproduction occurs by cross-fertilization. The proglottid detaches and is released in the feces of the host. The fertilized eggs are eaten by an intermediate host. The juvenile worms emerge and infect the intermediate host, taking up residence, usually in muscle tissue. When the muscle tissue is eaten by the primary host, the cycle is completed. There are several tapeworm parasites of humans that are acquired by eating uncooked or poorly cooked pork, beef, and fish.
The phylum Nematoda , or roundworms, includes more than 28,000 species with an estimated 16,000 parasitic species. The name Nematoda is derived from the Greek word “nemos,” which means “thread.” Nematodes are present in all habitats and are extremely common, although they are usually not visible ( [link] ).
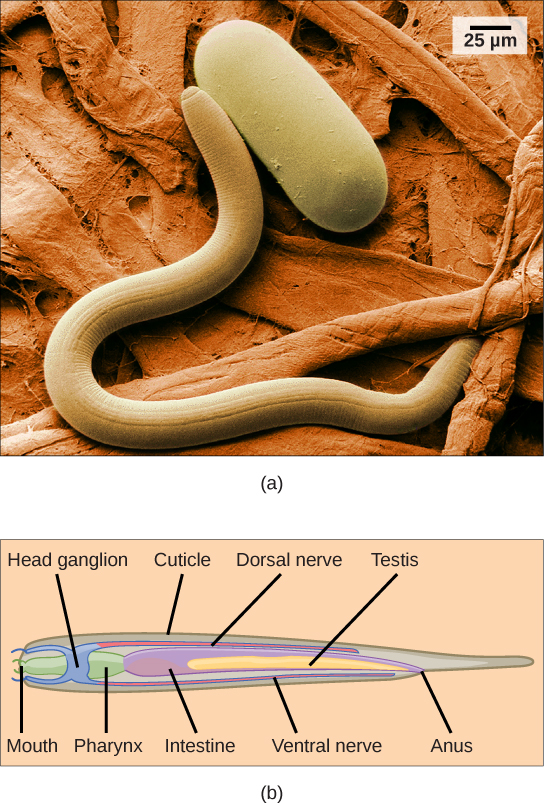
Most nematodes look similar to each other: slender tubes, tapered at each end ( [link] ). Nematodes are pseudocoelomates and have a complete digestive system with a distinct mouth and anus.
The nematode body is encased in a cuticle, a flexible but tough exoskeleton, or external skeleton, which offers protection and support. The cuticle contains a carbohydrate-protein polymer called chitin . The cuticle also lines the pharynx and rectum. Although the exoskeleton provides protection, it restricts growth, and therefore must be continually shed and replaced as the animal increases in size.
A nematode’s mouth opens at the anterior end with three or six lips and, in some species, teeth in the form of cuticular extensions. There may also be a sharp stylet that can protrude from the mouth to stab prey or pierce plant or animal cells. The mouth leads to a muscular pharynx and intestine, leading to the rectum and anal opening at the posterior end.
In nematodes, the excretory system is not specialized. Nitrogenous wastes are removed by diffusion. In marine nematodes, regulation of water and salt is achieved by specialized glands that remove unwanted ions while maintaining internal body fluid concentrations.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?