| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Lipids include a diverse group of compounds that are united by a common feature. Lipids are hydrophobic (“water-fearing”), or insoluble in water, because they are nonpolar molecules. This is because they are hydrocarbons that include only nonpolar carbon-carbon or carbon-hydrogen bonds. Lipids perform many different functions in a cell. Cells store energy for long-term use in the form of lipids called fats. Lipids also provide insulation from the environment for plants and animals ( [link] ). For example, they help keep aquatic birds and mammals dry because of their water-repelling nature. Lipids are also the building blocks of many hormones and are an important constituent of the plasma membrane. Lipids include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids.

A fat molecule, such as a triglyceride, consists of two main components—glycerol and fatty acids. Glycerol is an organic compound with three carbon atoms, five hydrogen atoms, and three hydroxyl (–OH) groups. Fatty acids have a long chain of hydrocarbons to which an acidic carboxyl group is attached, hence the name “fatty acid.” The number of carbons in the fatty acid may range from 4 to 36; most common are those containing 12–18 carbons. In a fat molecule, a fatty acid is attached to each of the three oxygen atoms in the –OH groups of the glycerol molecule with a covalent bond ( [link] ).
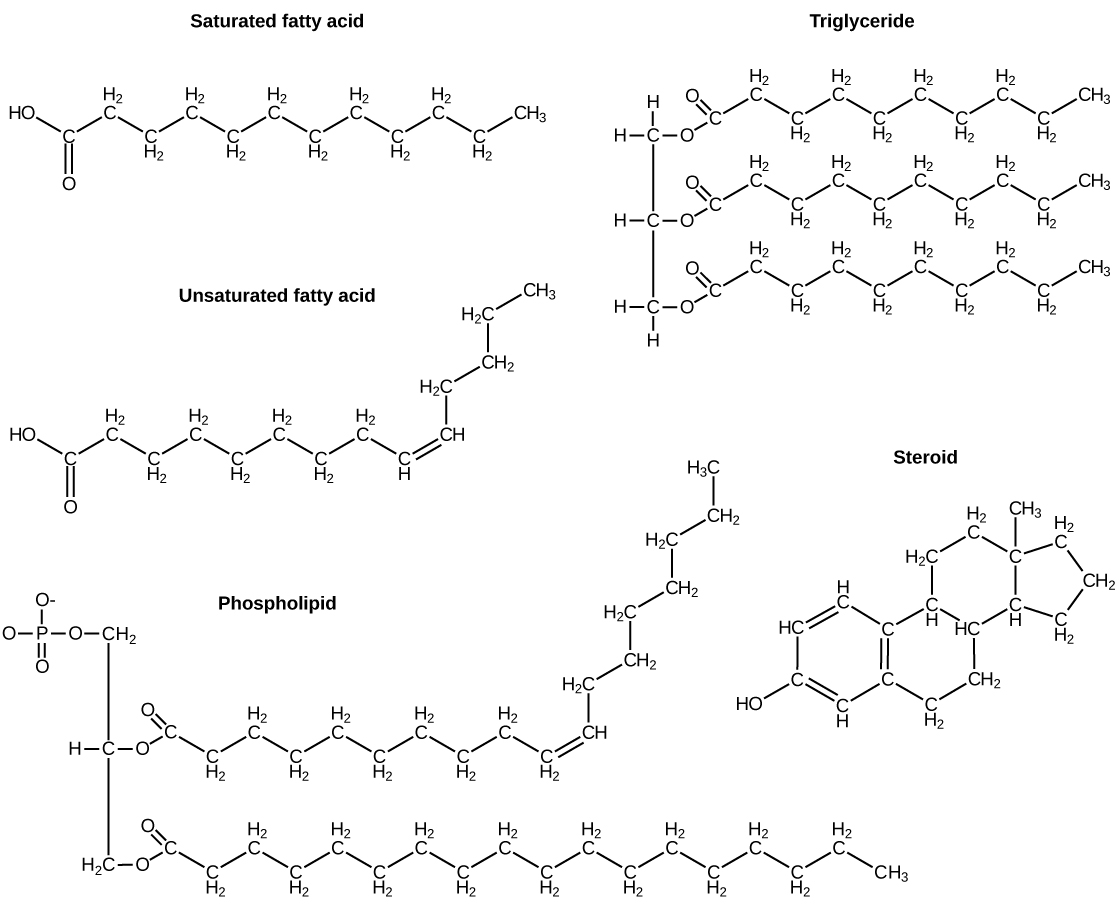
During this covalent bond formation, three water molecules are released. The three fatty acids in the fat may be similar or dissimilar. These fats are also called triglycerides because they have three fatty acids. Some fatty acids have common names that specify their origin. For example, palmitic acid, a saturated fatty acid, is derived from the palm tree. Arachidic acid is derived from Arachis hypogaea , the scientific name for peanuts.
Fatty acids may be saturated or unsaturated. In a fatty acid chain, if there are only single bonds between neighboring carbons in the hydrocarbon chain, the fatty acid is saturated. Saturated fatty acids are saturated with hydrogen; in other words, the number of hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon skeleton is maximized.
When the hydrocarbon chain contains a double bond, the fatty acid is an unsaturated fatty acid .
Most unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature and are called oils . If there is one double bond in the molecule, then it is known as a monounsaturated fat (e.g., olive oil), and if there is more than one double bond, then it is known as a polyunsaturated fat (e.g., canola oil).
Saturated fats tend to get packed tightly and are solid at room temperature. Animal fats with stearic acid and palmitic acid contained in meat, and the fat with butyric acid contained in butter, are examples of saturated fats. Mammals store fats in specialized cells called adipocytes, where globules of fat occupy most of the cell. In plants, fat or oil is stored in seeds and is used as a source of energy during embryonic development.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?