| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The lower limb consists of the thigh, the leg, and the foot. The bones of the lower limbs are thicker and stronger than the bones of the upper limbs to support the entire weight of the body and the forces from locomotion. The femur, or thighbone, is the longest, heaviest, and strongest bone in the body. The femur and pelvis form the hip joint. At its other end, the femur, along with the shinbone and kneecap, form the knee joint.
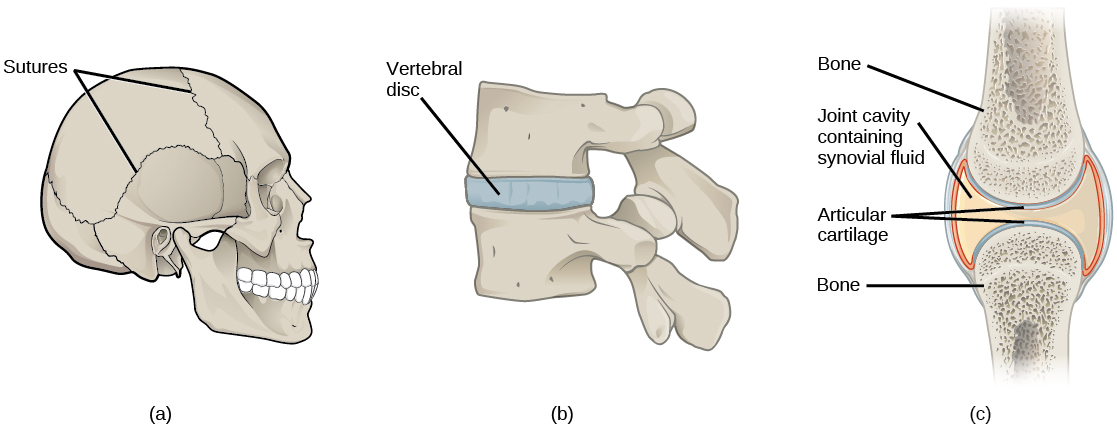
The point at which two or more bones meet is called a joint , or articulation. Joints are responsible for movement, such as the movement of limbs, and stability, such as the stability found in the bones of the skull.
There are two ways to classify joints: based on their structure or based on their function. The structural classification divides joints into fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial joints depending on the material composing the joint and the presence or absence of a cavity in the joint. The bones of fibrous joints are held together by fibrous connective tissue. There is no cavity, or space, present between the bones, so most fibrous joints do not move at all, or are only capable of minor movements. The joints between the bones in the skull and between the teeth and the bone of their sockets are examples of fibrous joints ( [link] a ).
Cartilaginous joints are joints in which the bones are connected by cartilage ( [link] b ). An example is found at the joints between vertebrae, the so-called “disks” of the backbone. Cartilaginous joints allow for very little movement.
Synovial joints are the only joints that have a space between the adjoining bones ( [link] c ). This space is referred to as the joint cavity and is filled with fluid. The fluid lubricates the joint, reducing friction between the bones and allowing for greater movement. The ends of the bones are covered with cartilage and the entire joint is surrounded by a capsule. Synovial joints are capable of the greatest movement of the joint types. Knees, elbows, and shoulders are examples of synovial joints.
The wide range of movement allowed by synovial joints produces different types of movements. Angular movements are produced when the angle between the bones of a joint changes. Flexion, or bending, occurs when the angle between the bones decreases. Moving the forearm upward at the elbow is an example of flexion. Extension is the opposite of flexion in that the angle between the bones of a joint increases. Rotational movement is the movement of a bone as it rotates around its own longitudinal axis. Movement of the head as in saying “no” is an example of rotation.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an inflammatory disorder that primarily affects synovial joints of the hands, feet, and cervical spine. Affected joints become swollen, stiff, and painful. Although it is known that RA is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue, the exact cause of RA remains unknown. Immune cells from the blood enter joints and the joint capsule causing cartilage breakdown and swelling of the joint lining. Breakdown of cartilage causes bones to rub against each other causing pain. RA is more common in women than men and the age of onset is usually between 40 to 50 years.
Rheumatologists can diagnose RA based on symptoms such as joint inflammation and pain, x-ray and MRI imaging, and blood tests. Arthrography is a type of medical imaging of joints that uses a contrast agent, such as a dye that is opaque to x-rays. This allows the soft tissue structures of joints—such as cartilage, tendons, and ligaments—to be visualized. An arthrogram differs from a regular x-ray by showing the surface of soft tissues lining the joint in addition to joint bones. An arthrogram allows early degenerative changes in joint cartilage to be detected before bones become affected.
There is currently no cure for RA; however, rheumatologists have a number of treatment options available. Treatments are divided into those that reduce the symptoms of the disease and those that reduce the damage to bone and cartilage caused by the disease. Early stages can be treated with rest of the affected joints through the use of a cane, or with joint splints that minimize inflammation. When inflammation has decreased, exercise can be used to strengthen muscles that surround the joint and to maintain joint flexibility. If joint damage is more extensive, medications can be used to relieve pain and decrease inflammation. Anti-inflammatory drugs that may be used include aspirin, topical pain relievers, and corticosteroid injections. Surgery may be required in cases where joint damage is severe. Physicians are now using drugs that reduce the damage to bones and cartilage caused by the disease to slow its development. These drugs are diverse in their mechanisms but they all act to reduce the impact of the autoimmune response, for example by inhibiting the inflammatory response or reducing the number of T lymphocytes, a cell of the immune system.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?