| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Meiosis is preceded by an interphase consisting of the G 1 , S, and G 2 phases, which are nearly identical to the phases preceding mitosis. The G 1 phase is the first phase of interphase and is focused on cell growth. In the S phase, the DNA of the chromosomes is replicated. Finally, in the G 2 phase, the cell undergoes the final preparations for meiosis.
During DNA duplication of the S phase, each chromosome becomes composed of two identical copies (called sister chromatids) that are held together at the centromere until they are pulled apart during meiosis II. In an animal cell, the centrosomes that organize the microtubules of the meiotic spindle also replicate. This prepares the cell for the first meiotic phase.
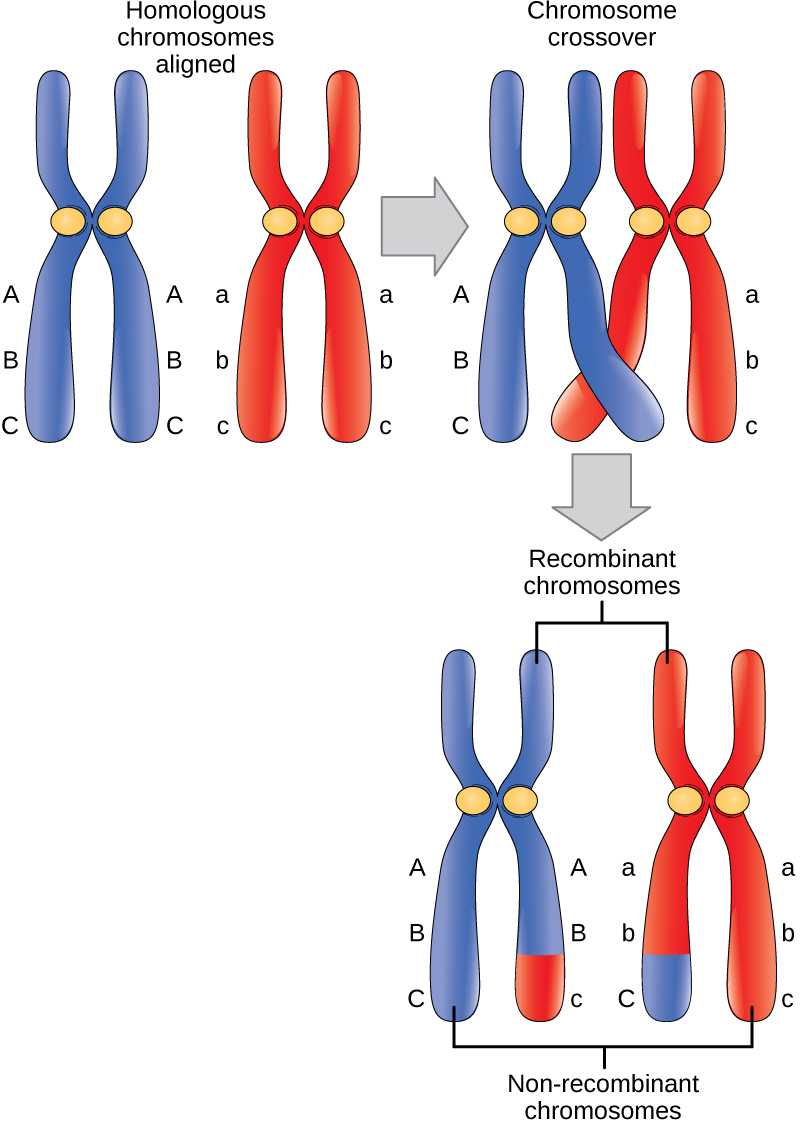
Early in prophase I, the chromosomes can be seen clearly microscopically. As the nuclear envelope begins to break down, the proteins associated with homologous chromosomes bring the pair close to each other. The tight pairing of the homologous chromosomes is called synapsis . In synapsis, the genes on the chromatids of the homologous chromosomes are precisely aligned with each other. An exchange of chromosome segments between non-sister homologous chromatids occurs and is called crossing over . This process is revealed visually after the exchange as chiasmata (singular = chiasma ) ( [link] ).
As prophase I progresses, the close association between homologous chromosomes begins to break down, and the chromosomes continue to condense, although the homologous chromosomes remain attached to each other at chiasmata. The number of chiasmata varies with the species and the length of the chromosome. At the end of prophase I, the pairs are held together only at chiasmata ( [link] ) and are called tetrads because the four sister chromatids of each pair of homologous chromosomes are now visible.
The crossover events are the first source of genetic variation produced by meiosis. A single crossover event between homologous non-sister chromatids leads to a reciprocal exchange of equivalent DNA between a maternal chromosome and a paternal chromosome. Now, when that sister chromatid is moved into a gamete, it will carry some DNA from one parent of the individual and some DNA from the other parent. The recombinant sister chromatid has a combination of maternal and paternal genes that did not exist before the crossover.
The key event in prometaphase I is the attachment of the spindle fiber microtubules to the kinetochore proteins at the centromeres. The microtubules assembled from centrosomes at opposite poles of the cell grow toward the middle of the cell. At the end of prometaphase I, each tetrad is attached to microtubules from both poles, with one homologous chromosome attached at one pole and the other homologous chromosome attached to the other pole. The homologous chromosomes are still held together at chiasmata. In addition, the nuclear membrane has broken down entirely.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?