| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Most fungal hyphae are divided into separate cells by end walls called septa (singular, septum ). In most divisions (like plants, fungal phyla are called divisions by tradition) of fungi, tiny holes in the septa allow for the rapid flow of nutrients and small molecules from cell to cell along the hyphae. They are described as perforated septa. The hyphae in bread molds (which belong to the division Zygomycota) are not separated by septa. They are formed of large cells containing many nuclei, an arrangement described as coenocytic hyphae.
Fungi thrive in environments that are moist and slightly acidic, and can grow with or without light. They vary in their oxygen requirements. Most fungi are obligate aerobes, requiring oxygen to survive. Other species, such as the Chytridiomycota that reside in the rumen of cattle, are obligate anaerobes, meaning that they cannot grow and reproduce in an environment with oxygen. Yeasts are intermediate: They grow best in the presence of oxygen but can use fermentation in the absence of oxygen. The alcohol produced from yeast fermentation is used in wine and beer production, and the carbon dioxide they produce carbonates beer and sparkling wine, and makes bread rise.
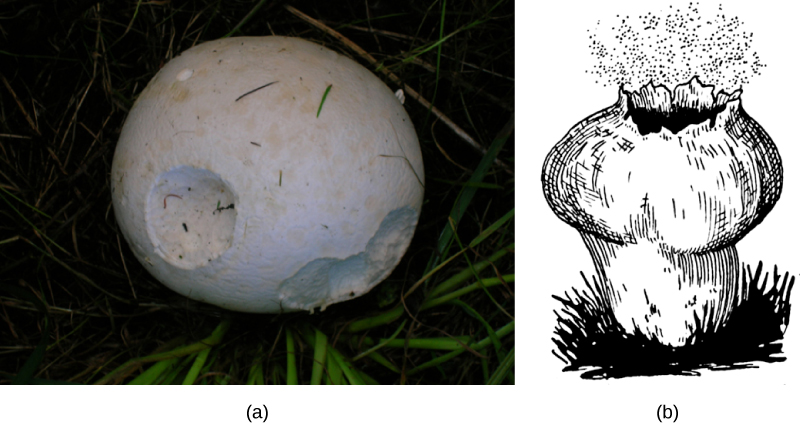
Fungi can reproduce sexually or asexually. In both sexual and asexual reproduction, fungi produce spores that disperse from the parent organism by either floating in the wind or hitching a ride on an animal. Fungal spores are smaller and lighter than plant seeds, but they are not usually released as high in the air. The giant puffball mushroom bursts open and releases trillions of spores: The huge number of spores released increases the likelihood of spores landing in an environment that will support growth ( [link] ).

Like animals, fungi are heterotrophs: They use complex organic compounds as a source of carbon rather than fixing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, as some bacteria and most plants do. In addition, fungi do not fix nitrogen from the atmosphere. Like animals, they must obtain it from their diet. However, unlike most animals that ingest food and then digest it internally in specialized organs, fungi perform these steps in the reverse order. Digestion precedes ingestion. First, exoenzymes, enzymes that catalyze reactions on compounds outside of the cell, are transported out of the hyphae where they break down nutrients in the environment. Then, the smaller molecules produced by the external digestion are absorbed through the large surface areas of the mycelium. As with animal cells, the fungal storage polysaccharide is glycogen rather than starch, as found in plants.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?