| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
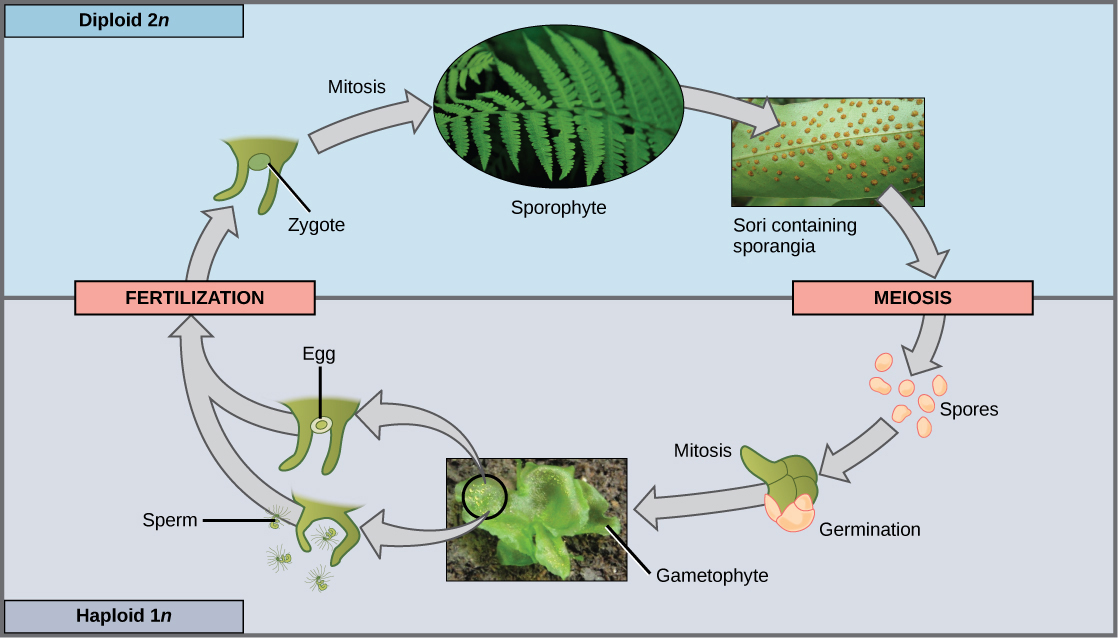
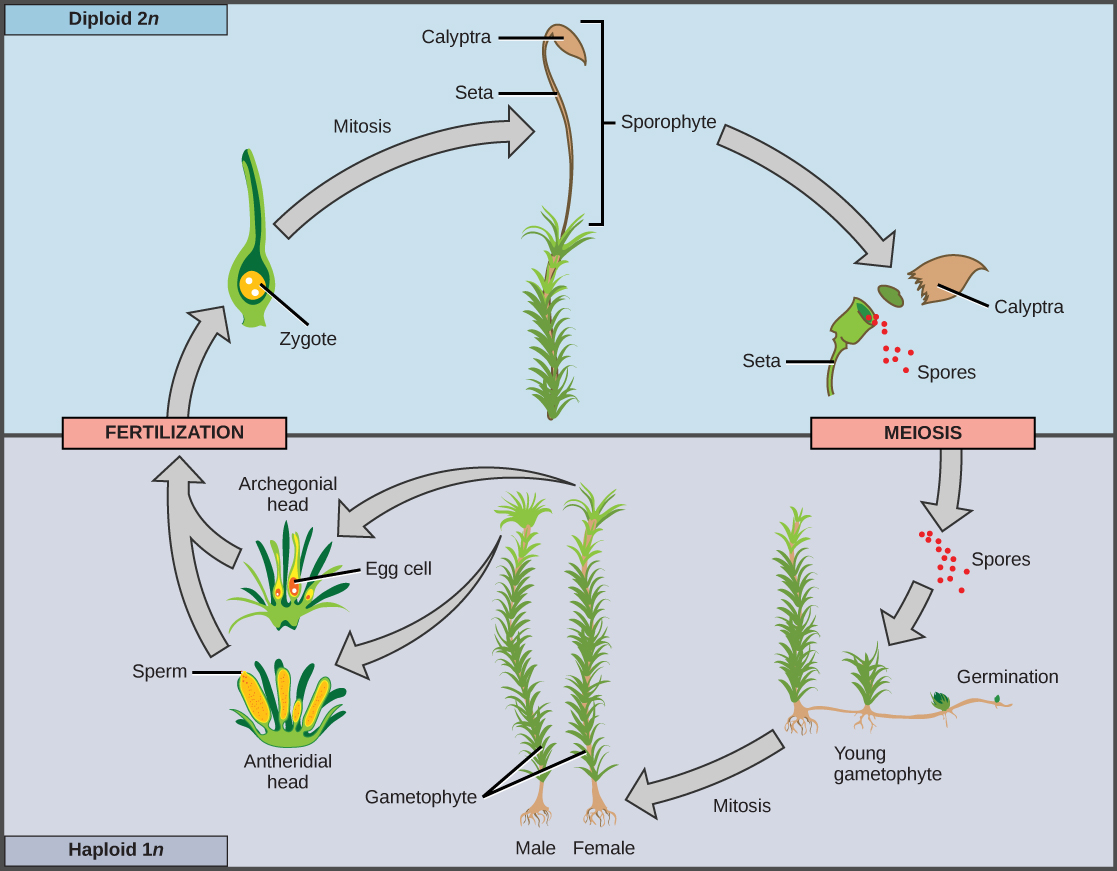
When the haploid spore germinates, it generates a multicellular gametophyte by mitosis. The gametophyte supports the zygote formed from the fusion of gametes and the resulting young sporophyte or vegetative form, and the cycle begins anew ( [link] and [link] ).
The spores of seedless plants and the pollen of seed plants are surrounded by thick cell walls containing a tough polymer known as sporopollenin. This substance is characterized by long chains of organic molecules related to fatty acids and carotenoids, and gives most pollen its yellow color. Sporopollenin is unusually resistant to chemical and biological degradation. Its toughness explains the existence of well-preserved fossils of pollen. Sporopollenin was once thought to be an innovation of land plants; however, the green algae Coleochaetes is now known to form spores that contain sporopollenin.
Protection of the embryo is a major requirement for land plants. The vulnerable embryo must be sheltered from desiccation and other environmental hazards. In both seedless and seed plants, the female gametophyte provides nutrition, and in seed plants, the embryo is also protected as it develops into the new generation of sporophyte.
Gametangia (singular, gametangium) are structures on the gametophytes of seedless plants in which gametes are produced by mitosis. The male gametangium, the antheridium, releases sperm. Many seedless plants produce sperm equipped with flagella that enable them to swim in a moist environment to the archegonia, the female gametangium. The embryo develops inside the archegonium as the sporophyte.
The shoots and roots of plants increase in length through rapid cell division within a tissue called the apical meristem ( [link] ). The apical meristem is a cap of cells at the shoot tip or root tip made of undifferentiated cells that continue to proliferate throughout the life of the plant. Meristematic cells give rise to all the specialized tissues of the plant. Elongation of the shoots and roots allows a plant to access additional space and resources: light in the case of the shoot, and water and minerals in the case of roots. A separate meristem, called the lateral meristem, produces cells that increase the diameter of stems and tree trunks. Apical meristems are an adaptation to allow vascular plants to grow in directions essential to their survival: upward to greater availability of sunlight, and downward into the soil to obtain water and essential minerals.

As plants adapted to dry land and became independent of the constant presence of water in damp habitats, new organs and structures made their appearance. Early land plants did not grow above a few inches off the ground, and on these low mats, they competed for light. By evolving a shoot and growing taller, individual plants captured more light. Because air offers substantially less support than water, land plants incorporated more rigid molecules in their stems (and later, tree trunks). The evolution of vascular tissue for the distribution of water and solutes was a necessary prerequisite for plants to evolve larger bodies. The vascular system contains xylem and phloem tissues. Xylem conducts water and minerals taken from the soil up to the shoot; phloem transports food derived from photosynthesis throughout the entire plant. The root system that evolved to take up water and minerals also anchored the increasingly taller shoot in the soil.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?