| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
At this point, it should be clear that eukaryotic cells have a more complex structure than do prokaryotic cells. Organelles allow for various functions to occur in the cell at the same time. Before discussing the functions of organelles within a eukaryotic cell, let us first examine two important components of the cell: the plasma membrane and the cytoplasm.
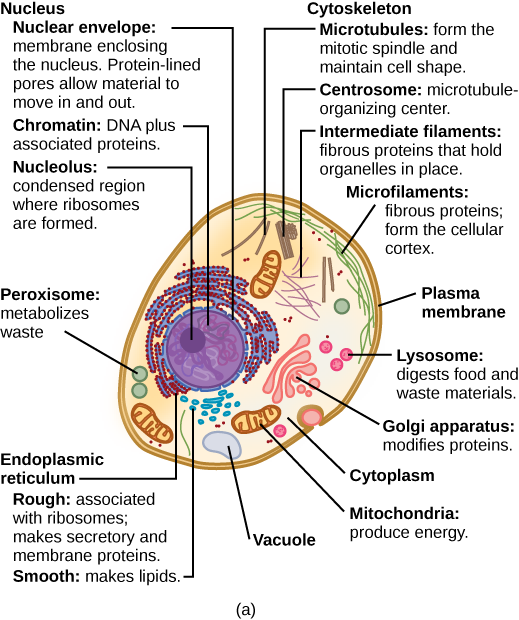
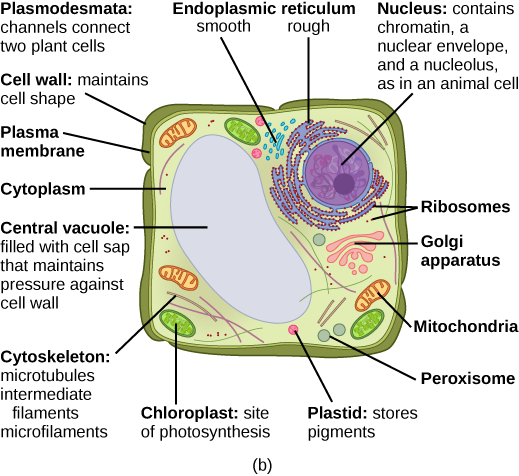
What structures does a plant cell have that an animal cell does not have? What structures does an animal cell have that a plant cell does not have?
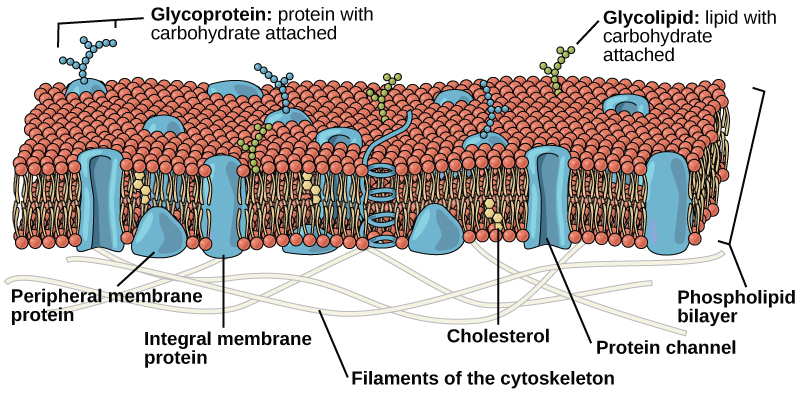
Like prokaryotes, eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane ( [link] ) made up of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that separates the internal contents of the cell from its surrounding environment. A phospholipid is a lipid molecule composed of two fatty acid chains, a glycerol backbone, and a phosphate group. The plasma membrane regulates the passage of some substances, such as organic molecules, ions, and water, preventing the passage of some to maintain internal conditions, while actively bringing in or removing others. Other compounds move passively across the membrane.
The plasma membranes of cells that specialize in absorption are folded into fingerlike projections called microvilli (singular = microvillus). This folding increases the surface area of the plasma membrane. Such cells are typically found lining the small intestine, the organ that absorbs nutrients from digested food. This is an excellent example of form matching the function of a structure.
People with celiac disease have an immune response to gluten, which is a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. The immune response damages microvilli, and thus, afflicted individuals cannot absorb nutrients. This leads to malnutrition, cramping, and diarrhea. Patients suffering from celiac disease must follow a gluten-free diet.
The cytoplasm comprises the contents of a cell between the plasma membrane and the nuclear envelope (a structure to be discussed shortly). It is made up of organelles suspended in the gel-like cytosol , the cytoskeleton, and various chemicals ( [link] ). Even though the cytoplasm consists of 70 to 80 percent water, it has a semi-solid consistency, which comes from the proteins within it. However, proteins are not the only organic molecules found in the cytoplasm. Glucose and other simple sugars, polysaccharides, amino acids, nucleic acids, fatty acids, and derivatives of glycerol are found there too. Ions of sodium, potassium, calcium, and many other elements are also dissolved in the cytoplasm. Many metabolic reactions, including protein synthesis, take place in the cytoplasm.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?