| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
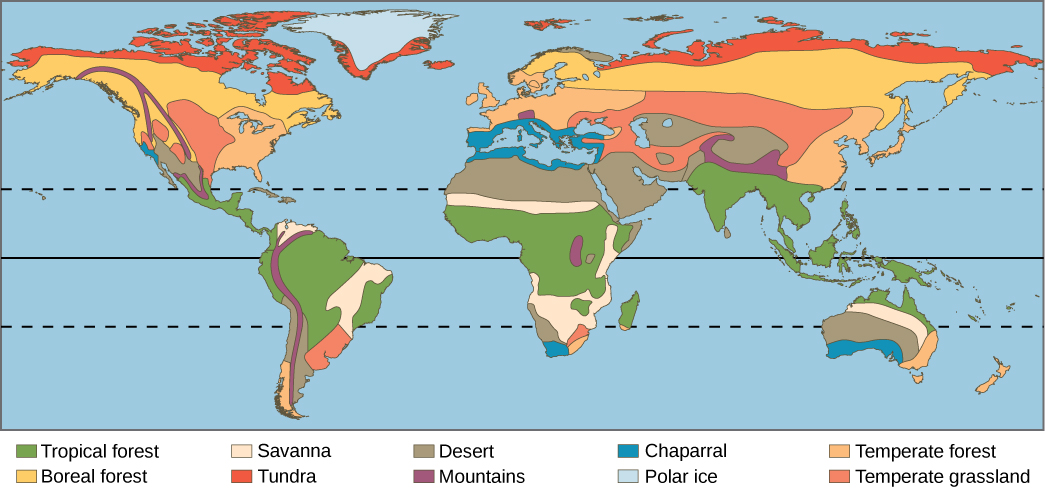
Earth’s biomes can be either terrestrial or aquatic. Terrestrial biomes are based on land, while aquatic biomes include both ocean and freshwater biomes. The eight major terrestrial biomes on Earth are each distinguished by characteristic temperatures and amount of precipitation. Annual totals and fluctuations of precipitation affect the kinds of vegetation and animal life that can exist in broad geographical regions. Temperature variation on a daily and seasonal basis is also important for predicting the geographic distribution of a biome. Since a biome is defined by climate, the same biome can occur in geographically distinct areas with similar climates ( [link] ). There are also large areas on Antarctica, Greenland, and in mountain ranges that are covered by permanent glaciers and support very little life. Strictly speaking, these are not considered biomes and in addition to extremes of cold, they are also often deserts with very low precipitation.
Tropical rainforests are also referred to as tropical wet forests. This biome is found in equatorial regions ( [link] ). Tropical rainforests are the most diverse terrestrial biome. This biodiversity is still largely unknown to science and is under extraordinary threat primarily through logging and deforestation for agriculture. Tropical rainforests have also been described as nature’s pharmacy because of the potential for new drugs that is largely hidden in the chemicals produced by the huge diversity of plants, animals, and other organisms. The vegetation is characterized by plants with spreading roots and broad leaves that fall off throughout the year, unlike the trees of deciduous forests that lose their leaves in one season. These forests are “evergreen,” year-round.
The temperature and sunlight profiles of tropical rainforests are stable in comparison to that of other terrestrial biomes, with average temperatures ranging from 20 o C to 34 o C (68 o F to 93 o F). Month-to-month temperatures are relatively constant in tropical rainforests, in contrast to forests further from the equator. This lack of temperature seasonality leads to year-round plant growth, rather than the seasonal growth seen in other biomes. In contrast to other ecosystems, a more constant daily amount of sunlight (11–12 hours per day) provides more solar radiation, thereby a longer period of time for plant growth.
The annual rainfall in tropical rainforests ranges from 250 cm to more than 450 cm (8.2–14.8 ft) with considerable seasonal variation. Tropical rainforests have wet months in which there can be more than 30 cm (11–12 in) of precipitation, as well as dry months in which there are fewer than 10 cm (3.5 in) of rainfall. However, the driest month of a tropical rainforest can still exceed the annual rainfall of some other biomes, such as deserts.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?