| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
It is easy to see how biotechnology can be used for medicinal purposes. Knowledge of the genetic makeup of our species, the genetic basis of heritable diseases, and the invention of technology to manipulate and fix mutant genes provides methods to treat diseases. Biotechnology in agriculture can enhance resistance to disease, pests, and environmental stress to improve both crop yield and quality.
The process of testing for suspected genetic defects before administering treatment is called genetic diagnosis by genetic testing. In some cases in which a genetic disease is present in an individual’s family, family members may be advised to undergo genetic testing. For example, mutations in the BRCA genes may increase the likelihood of developing breast and ovarian cancers in women and some other cancers in women and men. A woman with breast cancer can be screened for these mutations. If one of the high-risk mutations is found, her female relatives may also wish to be screened for that particular mutation, or simply be more vigilant for the occurrence of cancers. Genetic testing is also offered for fetuses (or embryos with in vitro fertilization) to determine the presence or absence of disease-causing genes in families with specific debilitating diseases.
See how human DNA is extracted for uses such as genetic testing.
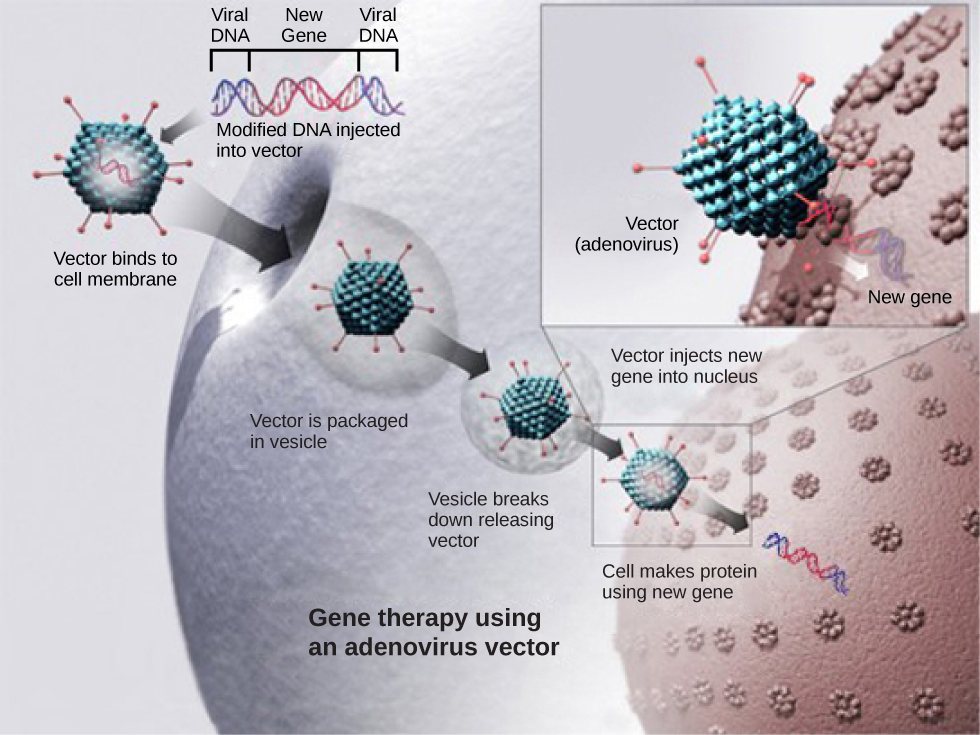
Gene therapy is a genetic engineering technique that may one day be used to cure certain genetic diseases. In its simplest form, it involves the introduction of a non-mutated gene at a random location in the genome to cure a disease by replacing a protein that may be absent in these individuals because of a genetic mutation. The non-mutated gene is usually introduced into diseased cells as part of a vector transmitted by a virus, such as an adenovirus, that can infect the host cell and deliver the foreign DNA into the genome of the targeted cell ( [link] ). To date, gene therapies have been primarily experimental procedures in humans. A few of these experimental treatments have been successful, but the methods may be important in the future as the factors limiting its success are resolved.
Traditional vaccination strategies use weakened or inactive forms of microorganisms or viruses to stimulate the immune system. Modern techniques use specific genes of microorganisms cloned into vectors and mass-produced in bacteria to make large quantities of specific substances to stimulate the immune system. The substance is then used as a vaccine. In some cases, such as the H1N1 flu vaccine, genes cloned from the virus have been used to combat the constantly changing strains of this virus.
Antibiotics kill bacteria and are naturally produced by microorganisms such as fungi; penicillin is perhaps the most well-known example. Antibiotics are produced on a large scale by cultivating and manipulating fungal cells. The fungal cells have typically been genetically modified to improve the yields of the antibiotic compound.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?