| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Water’s lower density in its solid form is due to the way hydrogen bonds are oriented as it freezes: the water molecules are pushed farther apart compared to liquid water. With most other liquids, solidification when the temperature drops includes the lowering of kinetic energy between molecules, allowing them to pack even more tightly than in liquid form and giving the solid a greater density than the liquid.
The lower density of ice, illustrated and pictured in [link] , an anomaly, causes it to float at the surface of liquid water, such as in an iceberg or in the ice cubes in a glass of ice water. In lakes and ponds, ice will form on the surface of the water creating an insulating barrier that protects the animals and plant life in the pond from freezing. Without this layer of insulating ice, plants and animals living in the pond would freeze in the solid block of ice and could not survive. The detrimental effect of freezing on living organisms is caused by the expansion of ice relative to liquid water. The ice crystals that form upon freezing rupture the delicate membranes essential for the function of living cells, irreversibly damaging them. Cells can only survive freezing if the water in them is temporarily replaced by another liquid like glycerol.
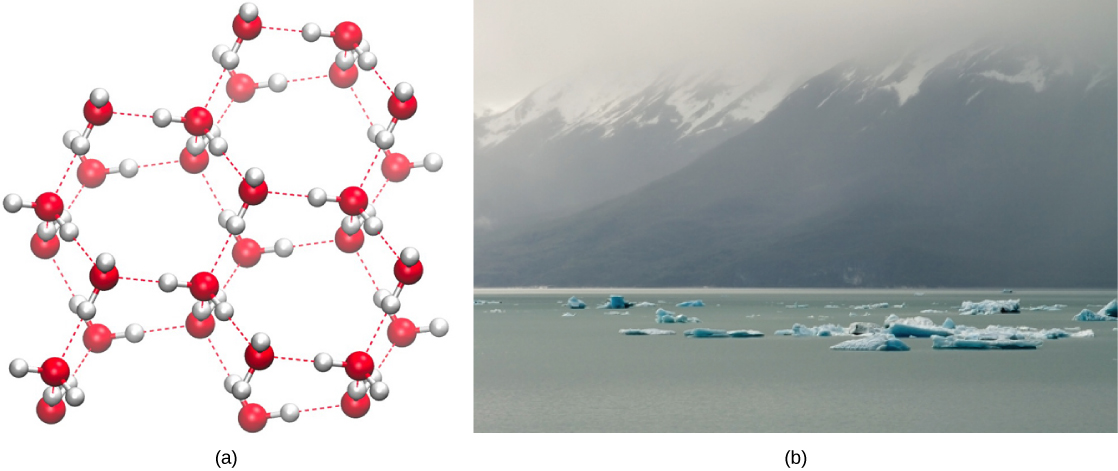
Click here to see a 3-D animation of the structure of an ice lattice. (Image credit: Jane Whitney. Image created using Visual Molecular Dynamics VMD software. W. Humphrey W., A. Dalke, and K. Schulten, “VMD—Visual Molecular Dynamics,” Journal of Molecular Graphics 14 (1996): 33-38. )
Water’s high heat capacity is a property caused by hydrogen bonding among water molecules. Water has the highest specific heat capacity of any liquids. Specific heat is defined as the amount of heat one gram of a substance must absorb or lose to change its temperature by one degree Celsius. For water, this amount is one calorie . It therefore takes water a long time to heat and long time to cool. In fact, the specific heat capacity of water is about five times more than that of sand. This explains why the land cools faster than the sea. Due to its high heat capacity, water is used by warm blooded animals to more evenly disperse heat in their bodies: it acts in a similar manner to a car’s cooling system, transporting heat from warm places to cool places, causing the body to maintain a more even temperature.
Water also has a high heat of vaporization , the amount of energy required to change one gram of a liquid substance to a gas. A considerable amount of heat energy (586 cal) is required to accomplish this change in water. This process occurs on the surface of water. As liquid water heats up, hydrogen bonding makes it difficult to separate the liquid water molecules from each other, which is required for it to enter its gaseous phase (steam). As a result, water acts as a heat sink or heat reservoir and requires much more heat to boil than does a liquid such as ethanol (grain alcohol), whose hydrogen bonding with other ethanol molecules is weaker than water’s hydrogen bonding. Eventually, as water reaches its boiling point of 100° Celsius (212° Fahrenheit), the heat is able to break the hydrogen bonds between the water molecules, and the kinetic energy (motion) between the water molecules allows them to escape from the liquid as a gas. Even when below its boiling point, water’s individual molecules acquire enough energy from other water molecules such that some surface water molecules can escape and vaporize: this process is known as evaporation .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?