| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
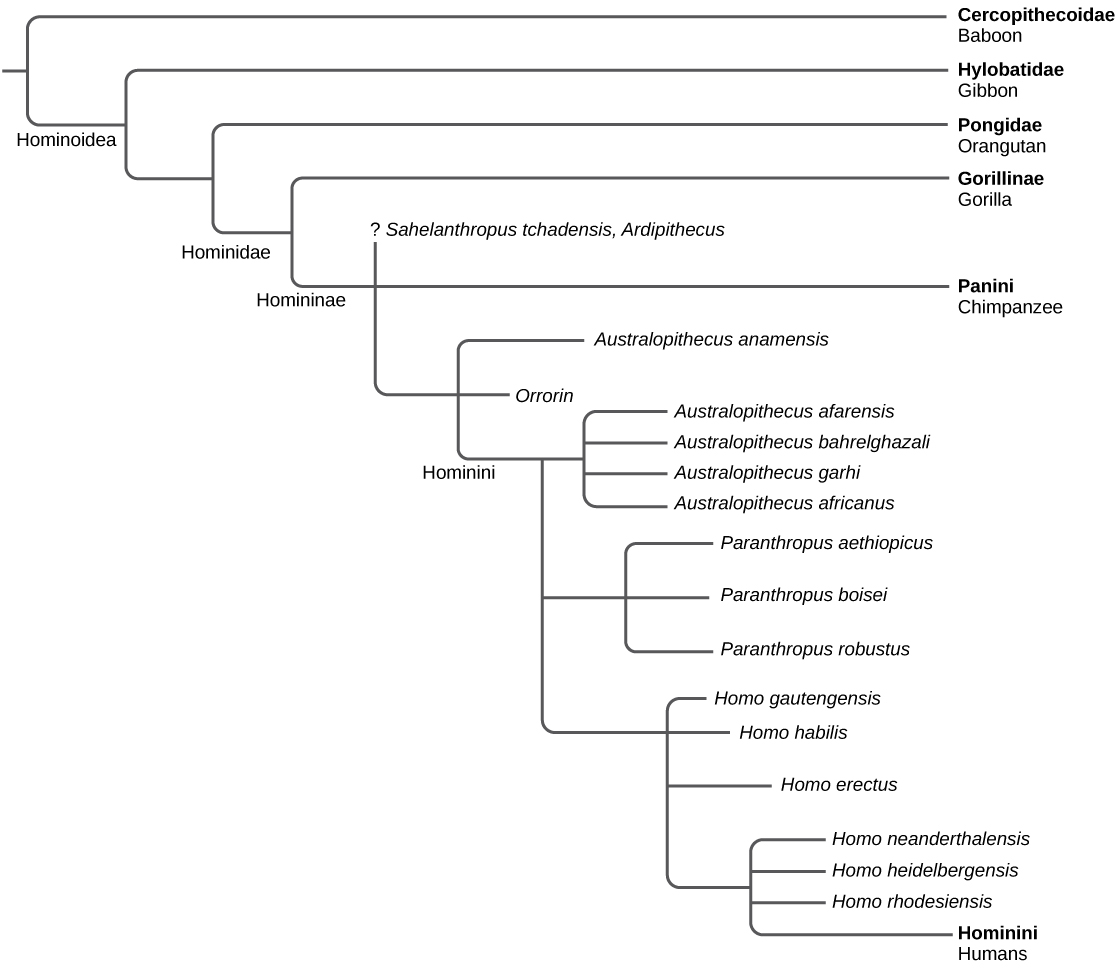
Three species of very early hominids have made news in the past few years. The oldest of these, Sahelanthropus tchadensis , has been dated to nearly 7 million years ago. There is a single specimen of this genus, a skull that was a surface find in Chad. The fossil, informally called “Toumai,” is a mosaic of primitive and evolved characteristics, and it is unclear how this fossil fits with the picture given by molecular data, namely that the line leading to modern humans and modern chimpanzees apparently bifurcated about 6 million years ago. It is not thought at this time that this species was an ancestor of modern humans.
A second, younger species, Orrorin tugenensis , is also a relatively recent discovery, found in 2000. There are several specimens of Orrorin . It is not known whether Orrorin was a human ancestor, but this possibility has not been ruled out. Some features of Orrorin are more similar to those of modern humans than are the australopiths, although Orrorin is much older.
A third genus, Ardipithecus , was discovered in the 1990s, and the scientists who discovered the first fossil found that some other scientists did not believe the organism to be a biped (thus, it would not be considered a hominid). In the intervening years, several more specimens of Ardipithecus , classified as two different species, demonstrated that the organism was bipedal. Again, the status of this genus as a human ancestor is uncertain.
Australopithecus (“southern ape”) is a genus of hominin that evolved in eastern Africa approximately 4 million years ago and went extinct about 2 million years ago. This genus is of particular interest to us as it is thought that our genus, genus Homo , evolved from Australopithecus about 2 million years ago (after likely passing through some transitional states). Australopithecus had a number of characteristics that were more similar to the great apes than to modern humans. For example, sexual dimorphism was more exaggerated than in modern humans. Males were up to 50 percent larger than females, a ratio that is similar to that seen in modern gorillas and orangutans. In contrast, modern human males are approximately 15 to 20 percent larger than females. The brain size of Australopithecus relative to its body mass was also smaller than modern humans and more similar to that seen in the great apes. A key feature that Australopithecus had in common with modern humans was bipedalism, although it is likely that Australopithecus also spent time in trees. Hominin footprints, similar to those of modern humans, were found in Laetoli, Tanzania and dated to 3.6 million years ago. They showed that hominins at the time of Australopithecus were walking upright.
There were a number of Australopithecus species, which are often referred to as australopiths . Australopithecus anamensis lived about 4.2 million years ago. More is known about another early species, Australopithecus afarensis , which lived between 3.9 and 2.9 million years ago. This species demonstrates a trend in human evolution: the reduction of the dentition and jaw in size. A . afarensis ( [link] ) had smaller canines and molars compared to apes, but these were larger than those of modern humans. Its brain size was 380–450 cubic centimeters, approximately the size of a modern chimpanzee brain. It also had prognathic jaws , which is a relatively longer jaw than that of modern humans. In the mid-1970s, the fossil of an adult female A . afarensis was found in the Afar region of Ethiopia and dated to 3.24 million years ago ( [link] ). The fossil, which is informally called “Lucy,” is significant because it was the most complete australopith fossil found, with 40 percent of the skeleton recovered.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?