| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
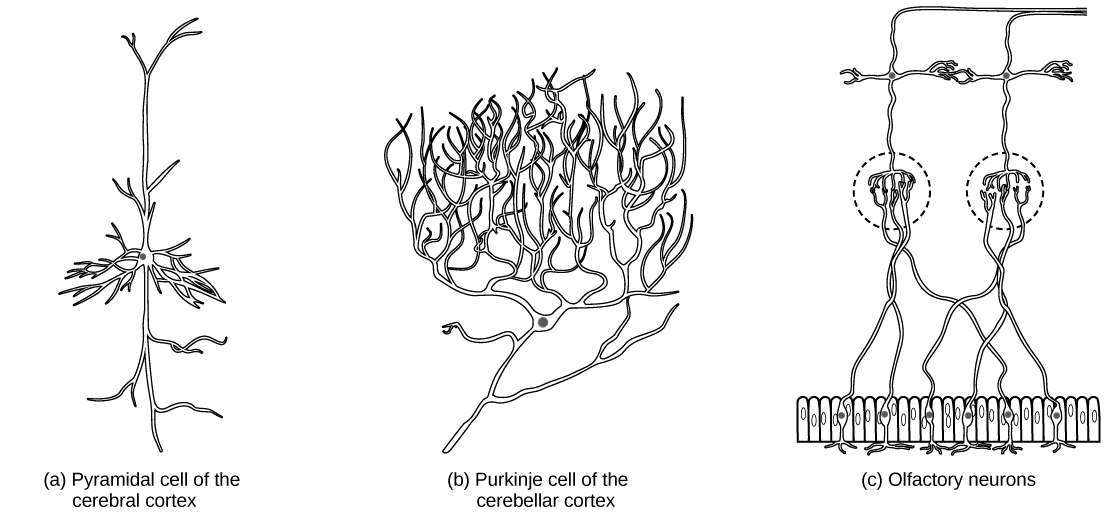
It is important to note that a single neuron does not act alone—neuronal communication depends on the connections that neurons make with one another (as well as with other cells, like muscle cells). Dendrites from a single neuron may receive synaptic contact from many other neurons. For example, dendrites from a Purkinje cell in the cerebellum are thought to receive contact from as many as 200,000 other neurons.
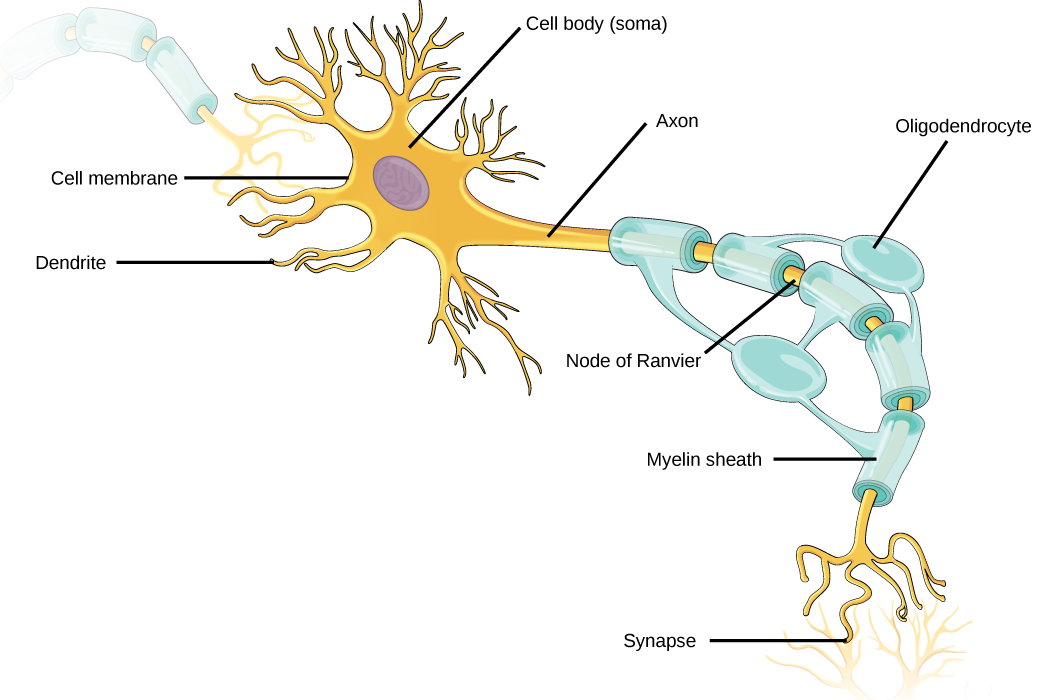
Which of the following statements is false?
There are different types of neurons, and the functional role of a given neuron is intimately dependent on its structure. There is an amazing diversity of neuron shapes and sizes found in different parts of the nervous system (and across species), as illustrated by the neurons shown in [link] .
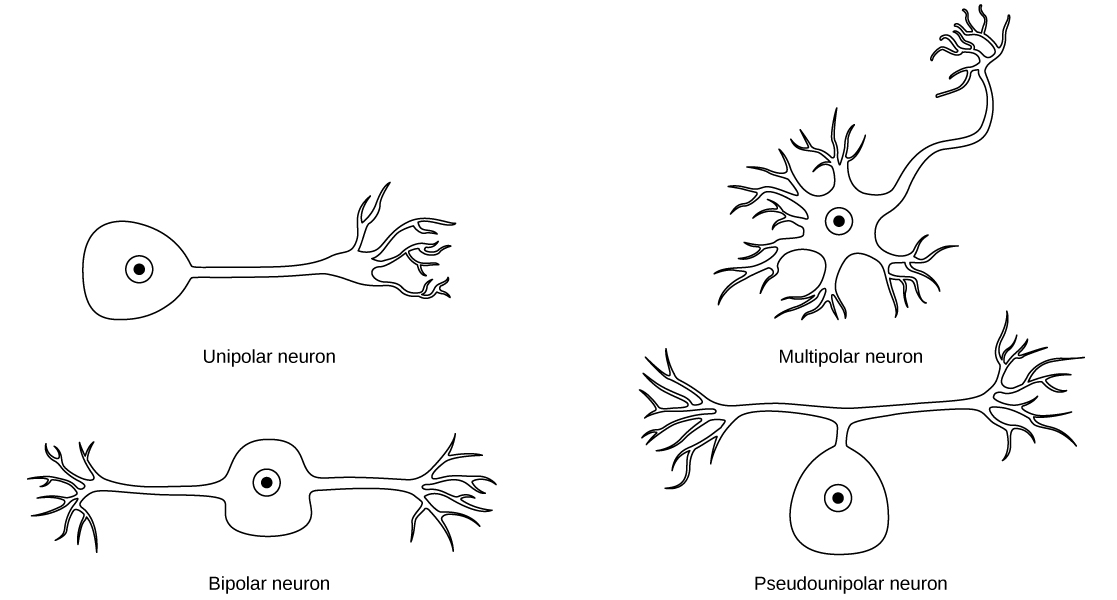
While there are many defined neuron cell subtypes, neurons are broadly divided into four basic types: unipolar, bipolar, multipolar, and pseudounipolar. [link] illustrates these four basic neuron types. Unipolar neurons have only one structure that extends away from the soma. These neurons are not found in vertebrates but are found in insects where they stimulate muscles or glands. A bipolar neuron has one axon and one dendrite extending from the soma. An example of a bipolar neuron is a retinal bipolar cell, which receives signals from photoreceptor cells that are sensitive to light and transmits these signals to ganglion cells that carry the signal to the brain. Multipolar neurons are the most common type of neuron. Each multipolar neuron contains one axon and multiple dendrites. Multipolar neurons can be found in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). An example of a multipolar neuron is a Purkinje cell in the cerebellum, which has many branching dendrites but only one axon. Pseudounipolar cells share characteristics with both unipolar and bipolar cells. A pseudounipolar cell has a single process that extends from the soma, like a unipolar cell, but this process later branches into two distinct structures, like a bipolar cell. Most sensory neurons are pseudounipolar and have an axon that branches into two extensions: one connected to dendrites that receive sensory information and another that transmits this information to the spinal cord.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?